mirror of
https://github.com/lancedb/lancedb.git
synced 2026-01-07 12:22:59 +00:00
docs: rag section in guide (#1619)
This PR adds the RAG section in the Guides. It includes all the RAGs with code snippet and some advanced techniques which improves RAG.
This commit is contained in:
@@ -106,6 +106,17 @@ nav:
|
||||
- Overview: hybrid_search/hybrid_search.md
|
||||
- Comparing Rerankers: hybrid_search/eval.md
|
||||
- Airbnb financial data example: notebooks/hybrid_search.ipynb
|
||||
- RAG:
|
||||
- Vanilla RAG: rag/vanilla_rag.md
|
||||
- Multi-head RAG: rag/multi_head_rag.md
|
||||
- Corrective RAG: rag/corrective_rag.md
|
||||
- Agentic RAG: rag/agentic_rag.md
|
||||
- Graph RAG: rag/graph_rag.md
|
||||
- Self RAG: rag/self_rag.md
|
||||
- Adaptive RAG: rag/adaptive_rag.md
|
||||
- Advanced Techniques:
|
||||
- HyDE: rag/advanced_techniques/hyde.md
|
||||
- FLARE: rag/advanced_techniques/flare.md
|
||||
- Reranking:
|
||||
- Quickstart: reranking/index.md
|
||||
- Cohere Reranker: reranking/cohere.md
|
||||
@@ -220,6 +231,17 @@ nav:
|
||||
- Overview: hybrid_search/hybrid_search.md
|
||||
- Comparing Rerankers: hybrid_search/eval.md
|
||||
- Airbnb financial data example: notebooks/hybrid_search.ipynb
|
||||
- RAG:
|
||||
- Vanilla RAG: rag/vanilla_rag.md
|
||||
- Multi-head RAG: rag/multi_head_rag.md
|
||||
- Corrective RAG: rag/corrective_rag.md
|
||||
- Agentic RAG: rag/agentic_rag.md
|
||||
- Graph RAG: rag/graph_rag.md
|
||||
- Self RAG: rag/self_rag.md
|
||||
- Adaptive RAG: rag/adaptive_rag.md
|
||||
- Advanced Techniques:
|
||||
- HyDE: rag/advanced_techniques/hyde.md
|
||||
- FLARE: rag/advanced_techniques/flare.md
|
||||
- Reranking:
|
||||
- Quickstart: reranking/index.md
|
||||
- Cohere Reranker: reranking/cohere.md
|
||||
|
||||
51
docs/src/rag/adaptive_rag.md
Normal file
51
docs/src/rag/adaptive_rag.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,51 @@
|
||||
**Adaptive RAG 🤹♂️**
|
||||
====================================================================
|
||||
Adaptive RAG introduces a RAG technique that combines query analysis with self-corrective RAG.
|
||||
|
||||
For Query Analysis, it uses a small classifier(LLM), to decide the query’s complexity. Query Analysis helps routing smoothly to adjust between different retrieval strategies No retrieval, Single-shot RAG or Iterative RAG.
|
||||
|
||||
**[Official Paper](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2403.14403)**
|
||||
|
||||
<figure markdown="span">
|
||||

|
||||
<figcaption>Adaptive-RAG: <a href="https://github.com/starsuzi/Adaptive-RAG">Source</a>
|
||||
</figcaption>
|
||||
</figure>
|
||||
|
||||
**[Offical Implementation](https://github.com/starsuzi/Adaptive-RAG)**
|
||||
|
||||
Here’s a code snippet for query analysis
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
|
||||
from langchain_core.pydantic_v1 import BaseModel, Field
|
||||
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
|
||||
|
||||
class RouteQuery(BaseModel):
|
||||
"""Route a user query to the most relevant datasource."""
|
||||
|
||||
datasource: Literal["vectorstore", "web_search"] = Field(
|
||||
...,
|
||||
description="Given a user question choose to route it to web search or a vectorstore.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# LLM with function call
|
||||
llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-3.5-turbo-0125", temperature=0)
|
||||
structured_llm_router = llm.with_structured_output(RouteQuery)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For defining and querying retriever
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# add documents in LanceDB
|
||||
vectorstore = LanceDB.from_documents(
|
||||
documents=doc_splits,
|
||||
embedding=OpenAIEmbeddings(),
|
||||
)
|
||||
retriever = vectorstore.as_retriever()
|
||||
|
||||
# query using defined retriever
|
||||
question = "How adaptive RAG works"
|
||||
docs = retriever.get_relevant_documents(question)
|
||||
```
|
||||
38
docs/src/rag/advanced_techniques/flare.md
Normal file
38
docs/src/rag/advanced_techniques/flare.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
|
||||
**FLARE 💥**
|
||||
====================================================================
|
||||
FLARE, stands for Forward-Looking Active REtrieval augmented generation is a generic retrieval-augmented generation method that actively decides when and what to retrieve using a prediction of the upcoming sentence to anticipate future content and utilize it as the query to retrieve relevant documents if it contains low-confidence tokens.
|
||||
|
||||
**[Official Paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2305.06983)**
|
||||
|
||||
<figure markdown="span">
|
||||

|
||||
<figcaption>FLARE: <a href="https://github.com/jzbjyb/FLARE">Source</a></figcaption>
|
||||
</figure>
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/examples/better-rag-FLAIR/main.ipynb)
|
||||
|
||||
Here’s a code snippet for using FLARE with Langchain
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from langchain.vectorstores import LanceDB
|
||||
from langchain.document_loaders import ArxivLoader
|
||||
from langchain.chains import FlareChain
|
||||
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
|
||||
from langchain.chains import LLMChain
|
||||
from langchain.llms import OpenAI
|
||||
|
||||
llm = OpenAI()
|
||||
|
||||
# load dataset
|
||||
|
||||
# LanceDB retriever
|
||||
vector_store = LanceDB.from_documents(doc_chunks, embeddings, connection=table)
|
||||
retriever = vector_store.as_retriever()
|
||||
|
||||
# define flare chain
|
||||
flare = FlareChain.from_llm(llm=llm,retriever=vector_store_retriever,max_generation_len=300,min_prob=0.45)
|
||||
|
||||
result = flare.run(input_text)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/examples/better-rag-FLAIR/main.ipynb)
|
||||
55
docs/src/rag/advanced_techniques/hyde.md
Normal file
55
docs/src/rag/advanced_techniques/hyde.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,55 @@
|
||||
**HyDE: Hypothetical Document Embeddings 🤹♂️**
|
||||
====================================================================
|
||||
HyDE, stands for Hypothetical Document Embeddings is an approach used for precise zero-shot dense retrieval without relevance labels. It focuses on augmenting and improving similarity searches, often intertwined with vector stores in information retrieval. The method generates a hypothetical document for an incoming query, which is then embedded and used to look up real documents that are similar to the hypothetical document.
|
||||
|
||||
**[Official Paper](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2212.10496)**
|
||||
|
||||
<figure markdown="span">
|
||||

|
||||
<figcaption>HyDE: <a href="https://arxiv.org/pdf/2212.10496">Source</a></figcaption>
|
||||
</figure>
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/examples/Advance-RAG-with-HyDE/main.ipynb)
|
||||
|
||||
Here’s a code snippet for using HyDE with Langchain
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from langchain.llms import OpenAI
|
||||
from langchain.embeddings import OpenAIEmbeddings
|
||||
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
|
||||
from langchain.chains import LLMChain, HypotheticalDocumentEmbedder
|
||||
from langchain.vectorstores import LanceDB
|
||||
|
||||
# set OPENAI_API_KEY as env variable before this step
|
||||
# initialize LLM and embedding function
|
||||
llm = OpenAI()
|
||||
emebeddings = OpenAIEmbeddings()
|
||||
|
||||
# HyDE embedding
|
||||
embeddings = HypotheticalDocumentEmbedder(llm_chain=llm_chain,base_embeddings=embeddings)
|
||||
|
||||
# load dataset
|
||||
|
||||
# LanceDB retriever
|
||||
retriever = LanceDB.from_documents(documents, embeddings, connection=table)
|
||||
|
||||
# prompt template
|
||||
prompt_template = """
|
||||
As a knowledgeable and helpful research assistant, your task is to provide informative answers based on the given context. Use your extensive knowledge base to offer clear, concise, and accurate responses to the user's inquiries.
|
||||
if quetion is not related to documents simply say you dont know
|
||||
Question: {question}
|
||||
|
||||
Answer:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = PromptTemplate(input_variables=["question"], template=prompt_template)
|
||||
|
||||
# LLM Chain
|
||||
llm_chain = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=prompt)
|
||||
|
||||
# vector search
|
||||
retriever.similarity_search(query)
|
||||
llm_chain.run(query)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/examples/Advance-RAG-with-HyDE/main.ipynb)
|
||||
101
docs/src/rag/agentic_rag.md
Normal file
101
docs/src/rag/agentic_rag.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,101 @@
|
||||
**Agentic RAG 🤖**
|
||||
====================================================================
|
||||
Agentic RAG is Agent-based RAG introduces an advanced framework for answering questions by using intelligent agents instead of just relying on large language models. These agents act like expert researchers, handling complex tasks such as detailed planning, multi-step reasoning, and using external tools. They navigate multiple documents, compare information, and generate accurate answers. This system is easily scalable, with each new document set managed by a sub-agent, making it a powerful tool for tackling a wide range of information needs.
|
||||
|
||||
<figure markdown="span">
|
||||
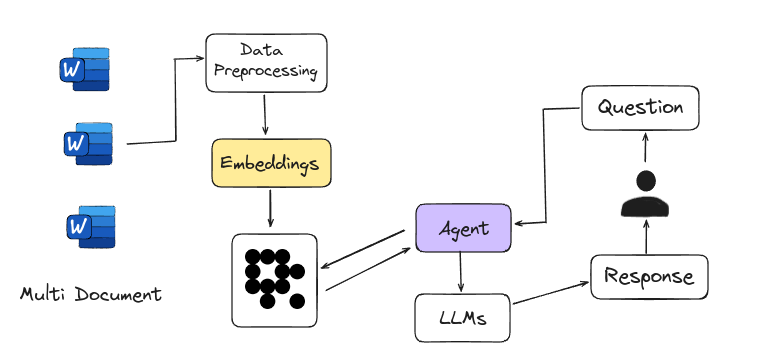
|
||||
<figcaption>Agent-based RAG</figcaption>
|
||||
</figure>
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/tutorials/Agentic_RAG/main.ipynb)
|
||||
|
||||
Here’s a code snippet for defining retriever using Langchain
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from langchain.text_splitter import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
|
||||
from langchain_community.document_loaders import WebBaseLoader
|
||||
from langchain_community.vectorstores import LanceDB
|
||||
from langchain_openai import OpenAIEmbeddings
|
||||
|
||||
urls = [
|
||||
"https://content.dgft.gov.in/Website/CIEP.pdf",
|
||||
"https://content.dgft.gov.in/Website/GAE.pdf",
|
||||
"https://content.dgft.gov.in/Website/HTE.pdf",
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
docs = [WebBaseLoader(url).load() for url in urls]
|
||||
docs_list = [item for sublist in docs for item in sublist]
|
||||
|
||||
text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter.from_tiktoken_encoder(
|
||||
chunk_size=100, chunk_overlap=50
|
||||
)
|
||||
doc_splits = text_splitter.split_documents(docs_list)
|
||||
|
||||
# add documents in LanceDB
|
||||
vectorstore = LanceDB.from_documents(
|
||||
documents=doc_splits,
|
||||
embedding=OpenAIEmbeddings(),
|
||||
)
|
||||
retriever = vectorstore.as_retriever()
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Agent that formulates an improved query for better retrieval results and then grades the retrieved documents
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
def grade_documents(state) -> Literal["generate", "rewrite"]:
|
||||
class grade(BaseModel):
|
||||
binary_score: str = Field(description="Relevance score 'yes' or 'no'")
|
||||
|
||||
model = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0, model="gpt-4-0125-preview", streaming=True)
|
||||
llm_with_tool = model.with_structured_output(grade)
|
||||
prompt = PromptTemplate(
|
||||
template="""You are a grader assessing relevance of a retrieved document to a user question. \n
|
||||
Here is the retrieved document: \n\n {context} \n\n
|
||||
Here is the user question: {question} \n
|
||||
If the document contains keyword(s) or semantic meaning related to the user question, grade it as relevant. \n
|
||||
Give a binary score 'yes' or 'no' score to indicate whether the document is relevant to the question.""",
|
||||
input_variables=["context", "question"],
|
||||
)
|
||||
chain = prompt | llm_with_tool
|
||||
|
||||
messages = state["messages"]
|
||||
last_message = messages[-1]
|
||||
question = messages[0].content
|
||||
docs = last_message.content
|
||||
|
||||
scored_result = chain.invoke({"question": question, "context": docs})
|
||||
score = scored_result.binary_score
|
||||
|
||||
return "generate" if score == "yes" else "rewrite"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def agent(state):
|
||||
messages = state["messages"]
|
||||
model = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0, streaming=True, model="gpt-4-turbo")
|
||||
model = model.bind_tools(tools)
|
||||
response = model.invoke(messages)
|
||||
return {"messages": [response]}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def rewrite(state):
|
||||
messages = state["messages"]
|
||||
question = messages[0].content
|
||||
msg = [
|
||||
HumanMessage(
|
||||
content=f""" \n
|
||||
Look at the input and try to reason about the underlying semantic intent / meaning. \n
|
||||
Here is the initial question:
|
||||
\n ------- \n
|
||||
{question}
|
||||
\n ------- \n
|
||||
Formulate an improved question: """,
|
||||
)
|
||||
]
|
||||
model = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0, model="gpt-4-0125-preview", streaming=True)
|
||||
response = model.invoke(msg)
|
||||
return {"messages": [response]}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/tutorials/Agentic_RAG/main.ipynb)
|
||||
120
docs/src/rag/corrective_rag.md
Normal file
120
docs/src/rag/corrective_rag.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,120 @@
|
||||
**Corrective RAG ✅**
|
||||
====================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
Corrective-RAG (CRAG) is a strategy for Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) that includes self-reflection and self-grading of retrieved documents. Here’s a simplified breakdown of the steps involved:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Relevance Check**: If at least one document meets the relevance threshold, the process moves forward to the generation phase.
|
||||
2. **Knowledge Refinement**: Before generating an answer, the process refines the knowledge by dividing the document into smaller segments called "knowledge strips."
|
||||
3. **Grading and Filtering**: Each "knowledge strip" is graded, and irrelevant ones are filtered out.
|
||||
4. **Additional Data Source**: If all documents are below the relevance threshold, or if the system is unsure about their relevance, it will seek additional information by performing a web search to supplement the retrieved data.
|
||||
|
||||
Above steps are mentioned in
|
||||
**[Official Paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2401.15884)**
|
||||
|
||||
<figure markdown="span">
|
||||

|
||||
<figcaption>Corrective RAG: <a href="https://github.com/HuskyInSalt/CRAG">Source</a>
|
||||
</figcaption>
|
||||
</figure>
|
||||
|
||||
Corrective Retrieval-Augmented Generation (CRAG) is a method that works like a **built-in fact-checker**.
|
||||
|
||||
**[Offical Implementation](https://github.com/HuskyInSalt/CRAG)**
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/tutorials/Corrective-RAG-with_Langgraph/CRAG_with_Langgraph.ipynb)
|
||||
|
||||
Here’s a code snippet for defining a table with the [Embedding API](https://lancedb.github.io/lancedb/embeddings/embedding_functions/), and retrieves the relevant documents.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import pandas as pd
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
from lancedb.pydantic import LanceModel, Vector
|
||||
from lancedb.embeddings import get_registry
|
||||
|
||||
db = lancedb.connect("/tmp/db")
|
||||
model = get_registry().get("sentence-transformers").create(name="BAAI/bge-small-en-v1.5", device="cpu")
|
||||
|
||||
class Docs(LanceModel):
|
||||
text: str = model.SourceField()
|
||||
vector: Vector(model.ndims()) = model.VectorField()
|
||||
|
||||
table = db.create_table("docs", schema=Docs)
|
||||
|
||||
# considering chunks are in list format
|
||||
df = pd.DataFrame({'text':chunks})
|
||||
table.add(data=df)
|
||||
|
||||
# as per document feeded
|
||||
query = "How Transformers work?"
|
||||
actual = table.search(query).limit(1).to_list()[0]
|
||||
print(actual.text)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Code snippet for grading retrieved documents, filtering out irrelevant ones, and performing a web search if necessary:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
def grade_documents(state):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Determines whether the retrieved documents are relevant to the question
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
state (dict): The current graph state
|
||||
|
||||
Returns:
|
||||
state (dict): Updates documents key with relevant documents
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
state_dict = state["keys"]
|
||||
question = state_dict["question"]
|
||||
documents = state_dict["documents"]
|
||||
|
||||
class grade(BaseModel):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Binary score for relevance check
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
binary_score: str = Field(description="Relevance score 'yes' or 'no'")
|
||||
|
||||
model = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0, model="gpt-4-0125-preview", streaming=True)
|
||||
# grading using openai
|
||||
grade_tool_oai = convert_to_openai_tool(grade)
|
||||
llm_with_tool = model.bind(
|
||||
tools=[convert_to_openai_tool(grade_tool_oai)],
|
||||
tool_choice={"type": "function", "function": {"name": "grade"}},
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
parser_tool = PydanticToolsParser(tools=[grade])
|
||||
prompt = PromptTemplate(
|
||||
template="""You are a grader assessing relevance of a retrieved document to a user question. \n
|
||||
Here is the retrieved document: \n\n {context} \n\n
|
||||
Here is the user question: {question} \n
|
||||
If the document contains keyword(s) or semantic meaning related to the user question, grade it as relevant. \n
|
||||
Give a binary score 'yes' or 'no' score to indicate whether the document is relevant to the question.""",
|
||||
input_variables=["context", "question"],
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
chain = prompt | llm_with_tool | parser_tool
|
||||
|
||||
filtered_docs = []
|
||||
search = "No"
|
||||
for d in documents:
|
||||
score = chain.invoke({"question": question, "context": d.page_content})
|
||||
grade = score[0].binary_score
|
||||
if grade == "yes":
|
||||
filtered_docs.append(d)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
search = "Yes"
|
||||
continue
|
||||
|
||||
return {
|
||||
"keys": {
|
||||
"documents": filtered_docs,
|
||||
"question": question,
|
||||
"run_web_search": search,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Check Colab for the Implementation of CRAG with Langgraph
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/tutorials/Corrective-RAG-with_Langgraph/CRAG_with_Langgraph.ipynb)
|
||||
54
docs/src/rag/graph_rag.md
Normal file
54
docs/src/rag/graph_rag.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,54 @@
|
||||
**Graph RAG 📊**
|
||||
====================================================================
|
||||
Graph RAG uses knowledge graphs together with large language models (LLMs) to improve how information is retrieved and generated. It overcomes the limits of traditional search methods by using knowledge graphs, which organize data as connected entities and relationships.
|
||||
|
||||
One of the main benefits of Graph RAG is its ability to capture and represent complex relationships between entities, something that traditional text-based retrieval systems struggle with. By using this structured knowledge, LLMs can better grasp the context and details of a query, resulting in more accurate and insightful answers.
|
||||
|
||||
**[Official Paper](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2404.16130)**
|
||||
|
||||
**[Offical Implementation](https://github.com/microsoft/graphrag)**
|
||||
|
||||
[Microsoft Research Blog](https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/blog/graphrag-unlocking-llm-discovery-on-narrative-private-data/)
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note "Default VectorDB"
|
||||
|
||||
Graph RAG uses LanceDB as the default vector database for performing vector search to retrieve relevant entities.
|
||||
|
||||
Working with Graph RAG is quite straightforward
|
||||
|
||||
- **Installation and API KEY as env variable**
|
||||
|
||||
Set `OPENAI_API_KEY` as `GRAPHRAG_API_KEY`
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install graphrag
|
||||
export GRAPHRAG_API_KEY="sk-..."
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- **Initial structure for indexing dataset**
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python3 -m graphrag.index --init --root dataset-dir
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- **Index Dataset**
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python3 -m graphrag.index --root dataset-dir
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- **Execute Query**
|
||||
|
||||
Global Query Execution gives a broad overview of dataset
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python3 -m graphrag.query --root dataset-dir --method global "query-question"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Local Query Execution gives a detailed and specific answers based on the context of the entities
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python3 -m graphrag.query --root dataset-dir --method local "query-question"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/examples/Graphrag/main.ipynb)
|
||||
49
docs/src/rag/multi_head_rag.md
Normal file
49
docs/src/rag/multi_head_rag.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,49 @@
|
||||
**Multi-Head RAG 📃**
|
||||
====================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
Multi-head RAG (MRAG) is designed to handle queries that need multiple documents with diverse content. These queries are tough because the documents’ embeddings can be far apart, making retrieval difficult. MRAG simplifies this by using the activations from a Transformer's multi-head attention layer, rather than the decoder layer, to fetch these varied documents. Different attention heads capture different aspects of the data, so using these activations helps create embeddings that better represent various data facets and improves retrieval accuracy for complex queries.
|
||||
|
||||
**[Official Paper](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2406.05085)**
|
||||
|
||||
<figure markdown="span">
|
||||

|
||||
<figcaption>Multi-Head RAG: <a href="https://github.com/spcl/MRAG">Source</a>
|
||||
</figcaption>
|
||||
</figure>
|
||||
|
||||
MRAG is cost-effective and energy-efficient because it avoids extra LLM queries, multiple model instances, increased storage, and additional inference passes.
|
||||
|
||||
**[Official Implementation](https://github.com/spcl/MRAG)**
|
||||
|
||||
Here’s a code snippet for defining different embedding spaces with the [Embedding API](https://lancedb.github.io/lancedb/embeddings/embedding_functions/)
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
from lancedb.pydantic import LanceModel, Vector
|
||||
from lancedb.embeddings import get_registry
|
||||
|
||||
# model definition using LanceDB Embedding API
|
||||
model1 = get_registry().get("openai").create()
|
||||
model2 = get_registry().get("ollama").create(name="llama3")
|
||||
model3 = get_registry().get("ollama").create(name="mistral")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# define schema for creating embedding spaces with Embedding API
|
||||
class Space1(LanceModel):
|
||||
text: str = model1.SourceField()
|
||||
vector: Vector(model1.ndims()) = model1.VectorField()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Space2(LanceModel):
|
||||
text: str = model2.SourceField()
|
||||
vector: Vector(model2.ndims()) = model2.VectorField()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Space3(LanceModel):
|
||||
text: str = model3.SourceField()
|
||||
vector: Vector(model3.ndims()) = model3.VectorField()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Create different tables using defined embedding spaces, then make queries to each embedding space. Use the resulted closest documents from each embedding space to generate answers.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
96
docs/src/rag/self_rag.md
Normal file
96
docs/src/rag/self_rag.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,96 @@
|
||||
**Self RAG 🤳**
|
||||
====================================================================
|
||||
Self-RAG is a strategy for Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) to get better retrieved information, generated text, and checking their own work, all without losing their flexibility. Unlike the traditional Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) method, Self-RAG retrieves information as needed, can skip retrieval if not needed, and evaluates its own output while generating text. It also uses a process to pick the best output based on different preferences.
|
||||
|
||||
**[Official Paper](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2310.11511)**
|
||||
|
||||
<figure markdown="span">
|
||||

|
||||
<figcaption>Self RAG: <a href="https://github.com/AkariAsai/self-rag">Source</a>
|
||||
</figcaption>
|
||||
</figure>
|
||||
|
||||
**[Offical Implementation](https://github.com/AkariAsai/self-rag)**
|
||||
|
||||
Self-RAG starts by generating a response without retrieving extra info if it's not needed. For questions that need more details, it retrieves to get the necessary information.
|
||||
|
||||
Here’s a code snippet for defining retriever using Langchain
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from langchain.text_splitter import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
|
||||
from langchain_community.document_loaders import WebBaseLoader
|
||||
from langchain_community.vectorstores import LanceDB
|
||||
from langchain_openai import OpenAIEmbeddings
|
||||
|
||||
urls = [
|
||||
"https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent/",
|
||||
"https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-03-15-prompt-engineering/",
|
||||
"https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-10-25-adv-attack-llm/",
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
docs = [WebBaseLoader(url).load() for url in urls]
|
||||
docs_list = [item for sublist in docs for item in sublist]
|
||||
|
||||
text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter.from_tiktoken_encoder(
|
||||
chunk_size=100, chunk_overlap=50
|
||||
)
|
||||
doc_splits = text_splitter.split_documents(docs_list)
|
||||
|
||||
# add documents in LanceDB
|
||||
vectorstore = LanceDB.from_documents(
|
||||
documents=doc_splits,
|
||||
embedding=OpenAIEmbeddings(),
|
||||
)
|
||||
retriever = vectorstore.as_retriever()
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Functions that grades the retrieved documents and if required formulates an improved query for better retrieval results
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
def grade_documents(state) -> Literal["generate", "rewrite"]:
|
||||
class grade(BaseModel):
|
||||
binary_score: str = Field(description="Relevance score 'yes' or 'no'")
|
||||
|
||||
model = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0, model="gpt-4-0125-preview", streaming=True)
|
||||
llm_with_tool = model.with_structured_output(grade)
|
||||
prompt = PromptTemplate(
|
||||
template="""You are a grader assessing relevance of a retrieved document to a user question. \n
|
||||
Here is the retrieved document: \n\n {context} \n\n
|
||||
Here is the user question: {question} \n
|
||||
If the document contains keyword(s) or semantic meaning related to the user question, grade it as relevant. \n
|
||||
Give a binary score 'yes' or 'no' score to indicate whether the document is relevant to the question.""",
|
||||
input_variables=["context", "question"],
|
||||
)
|
||||
chain = prompt | llm_with_tool
|
||||
|
||||
messages = state["messages"]
|
||||
last_message = messages[-1]
|
||||
question = messages[0].content
|
||||
docs = last_message.content
|
||||
|
||||
scored_result = chain.invoke({"question": question, "context": docs})
|
||||
score = scored_result.binary_score
|
||||
|
||||
return "generate" if score == "yes" else "rewrite"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def rewrite(state):
|
||||
messages = state["messages"]
|
||||
question = messages[0].content
|
||||
msg = [
|
||||
HumanMessage(
|
||||
content=f""" \n
|
||||
Look at the input and try to reason about the underlying semantic intent / meaning. \n
|
||||
Here is the initial question:
|
||||
\n ------- \n
|
||||
{question}
|
||||
\n ------- \n
|
||||
Formulate an improved question: """,
|
||||
)
|
||||
]
|
||||
model = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0, model="gpt-4-0125-preview", streaming=True)
|
||||
response = model.invoke(msg)
|
||||
return {"messages": [response]}
|
||||
```
|
||||
54
docs/src/rag/vanilla_rag.md
Normal file
54
docs/src/rag/vanilla_rag.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,54 @@
|
||||
**Vanilla RAG 🌱**
|
||||
====================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
RAG(Retrieval-Augmented Generation) works by finding documents related to the user's question, combining them with a prompt for a large language model (LLM), and then using the LLM to create more accurate and relevant answers.
|
||||
|
||||
Here’s a simple guide to building a RAG pipeline from scratch:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Data Loading**: Gather and load the documents you want to use for answering questions.
|
||||
|
||||
2. **Chunking and Embedding**: Split the documents into smaller chunks and convert them into numerical vectors (embeddings) that capture their meaning.
|
||||
|
||||
3. **Vector Store**: Create a LanceDB table to store and manage these vectors for quick access during retrieval.
|
||||
|
||||
4. **Retrieval & Prompt Preparation**: When a question is asked, find the most relevant document chunks from the table and prepare a prompt combining these chunks with the question.
|
||||
|
||||
5. **Answer Generation**: Send the prepared prompt to a LLM to generate a detailed and accurate answer.
|
||||
|
||||
<figure markdown="span">
|
||||

|
||||
<figcaption>Vanilla RAG
|
||||
</figcaption>
|
||||
</figure>
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/tutorials/RAG-from-Scratch/RAG_from_Scratch.ipynb)
|
||||
|
||||
Here’s a code snippet for defining a table with the [Embedding API](https://lancedb.github.io/lancedb/embeddings/embedding_functions/), which simplifies the process by handling embedding extraction and querying in one step.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import pandas as pd
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
from lancedb.pydantic import LanceModel, Vector
|
||||
from lancedb.embeddings import get_registry
|
||||
|
||||
db = lancedb.connect("/tmp/db")
|
||||
model = get_registry().get("sentence-transformers").create(name="BAAI/bge-small-en-v1.5", device="cpu")
|
||||
|
||||
class Docs(LanceModel):
|
||||
text: str = model.SourceField()
|
||||
vector: Vector(model.ndims()) = model.VectorField()
|
||||
|
||||
table = db.create_table("docs", schema=Docs)
|
||||
|
||||
# considering chunks are in list format
|
||||
df = pd.DataFrame({'text':chunks})
|
||||
table.add(data=df)
|
||||
|
||||
query = "What is issue date of lease?"
|
||||
actual = table.search(query).limit(1).to_list()[0]
|
||||
print(actual.text)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Check Colab for the complete code
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/tutorials/RAG-from-Scratch/RAG_from_Scratch.ipynb)
|
||||
@@ -20,7 +20,11 @@ excluded_globs = [
|
||||
"../src/reranking/*.md",
|
||||
"../src/guides/tuning_retrievers/*.md",
|
||||
"../src/embeddings/available_embedding_models/text_embedding_functions/*.md",
|
||||
"../src/embeddings/available_embedding_models/multimodal_embedding_functions/*.md"
|
||||
"../src/embeddings/available_embedding_models/multimodal_embedding_functions/*.md",
|
||||
"../src/rag/*.md",
|
||||
"../src/rag/advanced_techniques/*.md"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
python_prefix = "py"
|
||||
|
||||
Reference in New Issue
Block a user