mirror of
https://github.com/lancedb/lancedb.git
synced 2025-12-23 05:19:58 +00:00
Compare commits
1 Commits
python-v0.
...
add-async-
| Author | SHA1 | Date | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
5f187d4db6 |
@@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
||||
[tool.bumpversion]
|
||||
current_version = "0.15.0-beta.0"
|
||||
current_version = "0.13.1-beta.0"
|
||||
parse = """(?x)
|
||||
(?P<major>0|[1-9]\\d*)\\.
|
||||
(?P<minor>0|[1-9]\\d*)\\.
|
||||
|
||||
2
.github/workflows/build_mac_wheel/action.yml
vendored
2
.github/workflows/build_mac_wheel/action.yml
vendored
@@ -20,7 +20,7 @@ runs:
|
||||
uses: PyO3/maturin-action@v1
|
||||
with:
|
||||
command: build
|
||||
# TODO: pass through interpreter
|
||||
args: ${{ inputs.args }}
|
||||
docker-options: "-e PIP_EXTRA_INDEX_URL=https://pypi.fury.io/lancedb/"
|
||||
working-directory: python
|
||||
interpreter: 3.${{ inputs.python-minor-version }}
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -28,7 +28,7 @@ runs:
|
||||
args: ${{ inputs.args }}
|
||||
docker-options: "-e PIP_EXTRA_INDEX_URL=https://pypi.fury.io/lancedb/"
|
||||
working-directory: python
|
||||
- uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
|
||||
- uses: actions/upload-artifact@v3
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: windows-wheels
|
||||
path: python\target\wheels
|
||||
|
||||
4
.github/workflows/docs.yml
vendored
4
.github/workflows/docs.yml
vendored
@@ -72,9 +72,9 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- name: Setup Pages
|
||||
uses: actions/configure-pages@v2
|
||||
- name: Upload artifact
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-pages-artifact@v3
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-pages-artifact@v1
|
||||
with:
|
||||
path: "docs/site"
|
||||
- name: Deploy to GitHub Pages
|
||||
id: deployment
|
||||
uses: actions/deploy-pages@v4
|
||||
uses: actions/deploy-pages@v1
|
||||
|
||||
13
.github/workflows/make-release-commit.yml
vendored
13
.github/workflows/make-release-commit.yml
vendored
@@ -43,7 +43,7 @@ on:
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
make-release:
|
||||
# Creates tag and GH release. The GH release will trigger the build and release jobs.
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-24.04
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
permissions:
|
||||
contents: write
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
@@ -57,14 +57,15 @@ jobs:
|
||||
# trigger any workflows watching for new tags. See:
|
||||
# https://docs.github.com/en/actions/using-workflows/triggering-a-workflow#triggering-a-workflow-from-a-workflow
|
||||
token: ${{ secrets.LANCEDB_RELEASE_TOKEN }}
|
||||
- name: Validate Lance dependency is at stable version
|
||||
if: ${{ inputs.type == 'stable' }}
|
||||
run: python ci/validate_stable_lance.py
|
||||
- name: Set git configs for bumpversion
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
git config user.name 'Lance Release'
|
||||
git config user.email 'lance-dev@lancedb.com'
|
||||
- name: Set up Python 3.11
|
||||
uses: actions/setup-python@v5
|
||||
with:
|
||||
python-version: "3.11"
|
||||
- name: Bump Python version
|
||||
if: ${{ inputs.python }}
|
||||
working-directory: python
|
||||
@@ -96,7 +97,3 @@ jobs:
|
||||
if: ${{ !inputs.dry_run && inputs.other }}
|
||||
with:
|
||||
github_token: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
|
||||
- uses: ./.github/workflows/update_package_lock_nodejs
|
||||
if: ${{ !inputs.dry_run && inputs.other }}
|
||||
with:
|
||||
github_token: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
|
||||
|
||||
310
.github/workflows/npm-publish.yml
vendored
310
.github/workflows/npm-publish.yml
vendored
@@ -133,7 +133,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
free -h
|
||||
- name: Build Linux Artifacts
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
bash ci/build_linux_artifacts.sh ${{ matrix.config.arch }} ${{ matrix.config.arch }}-unknown-linux-gnu
|
||||
bash ci/build_linux_artifacts.sh ${{ matrix.config.arch }}
|
||||
- name: Upload Linux Artifacts
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
@@ -159,7 +159,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- name: Install common dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
apk add protobuf-dev curl clang mold grep npm bash
|
||||
curl --proto '=https' --tlsv1.3 -sSf https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rust-lang/rustup/refs/heads/master/rustup-init.sh | sh -s -- -y
|
||||
curl --proto '=https' --tlsv1.3 -sSf https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rust-lang/rustup/refs/heads/master/rustup-init.sh | sh -s -- -y --default-toolchain 1.80.0
|
||||
echo "source $HOME/.cargo/env" >> saved_env
|
||||
echo "export CC=clang" >> saved_env
|
||||
echo "export RUSTFLAGS='-Ctarget-cpu=haswell -Ctarget-feature=-crt-static,+avx2,+fma,+f16c -Clinker=clang -Clink-arg=-fuse-ld=mold'" >> saved_env
|
||||
@@ -167,7 +167,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
if: ${{ matrix.config.arch == 'aarch64' }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
source "$HOME/.cargo/env"
|
||||
rustup target add aarch64-unknown-linux-musl
|
||||
rustup target add aarch64-unknown-linux-musl --toolchain 1.80.0
|
||||
crt=$(realpath $(dirname $(rustup which rustc))/../lib/rustlib/aarch64-unknown-linux-musl/lib/self-contained)
|
||||
sysroot_lib=/usr/aarch64-unknown-linux-musl/usr/lib
|
||||
apk_url=https://dl-cdn.alpinelinux.org/alpine/latest-stable/main/aarch64/
|
||||
@@ -185,7 +185,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- name: Build Linux Artifacts
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
source ./saved_env
|
||||
bash ci/manylinux_node/build_vectordb.sh ${{ matrix.config.arch }} ${{ matrix.config.arch }}-unknown-linux-musl
|
||||
bash ci/manylinux_node/build_vectordb.sh ${{ matrix.config.arch }}
|
||||
- name: Upload Linux Artifacts
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
@@ -262,7 +262,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- name: Install common dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
apk add protobuf-dev curl clang mold grep npm bash openssl-dev openssl-libs-static
|
||||
curl --proto '=https' --tlsv1.3 -sSf https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rust-lang/rustup/refs/heads/master/rustup-init.sh | sh -s -- -y
|
||||
curl --proto '=https' --tlsv1.3 -sSf https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rust-lang/rustup/refs/heads/master/rustup-init.sh | sh -s -- -y --default-toolchain 1.80.0
|
||||
echo "source $HOME/.cargo/env" >> saved_env
|
||||
echo "export CC=clang" >> saved_env
|
||||
echo "export RUSTFLAGS='-Ctarget-cpu=haswell -Ctarget-feature=-crt-static,+avx2,+fma,+f16c -Clinker=clang -Clink-arg=-fuse-ld=mold'" >> saved_env
|
||||
@@ -272,7 +272,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
if: ${{ matrix.config.arch == 'aarch64' }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
source "$HOME/.cargo/env"
|
||||
rustup target add aarch64-unknown-linux-musl
|
||||
rustup target add aarch64-unknown-linux-musl --toolchain 1.80.0
|
||||
crt=$(realpath $(dirname $(rustup which rustc))/../lib/rustlib/aarch64-unknown-linux-musl/lib/self-contained)
|
||||
sysroot_lib=/usr/aarch64-unknown-linux-musl/usr/lib
|
||||
apk_url=https://dl-cdn.alpinelinux.org/alpine/latest-stable/main/aarch64/
|
||||
@@ -334,50 +334,109 @@ jobs:
|
||||
path: |
|
||||
node/dist/lancedb-vectordb-win32*.tgz
|
||||
|
||||
node-windows-arm64:
|
||||
name: vectordb ${{ matrix.config.arch }}-pc-windows-msvc
|
||||
# if: startsWith(github.ref, 'refs/tags/v')
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
container: alpine:edge
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
config:
|
||||
# - arch: x86_64
|
||||
- arch: aarch64
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Checkout
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
apk add protobuf-dev curl clang lld llvm19 grep npm bash msitools sed
|
||||
curl --proto '=https' --tlsv1.3 -sSf https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rust-lang/rustup/refs/heads/master/rustup-init.sh | sh -s -- -y
|
||||
echo "source $HOME/.cargo/env" >> saved_env
|
||||
echo "export CC=clang" >> saved_env
|
||||
echo "export AR=llvm-ar" >> saved_env
|
||||
source "$HOME/.cargo/env"
|
||||
rustup target add ${{ matrix.config.arch }}-pc-windows-msvc
|
||||
(mkdir -p sysroot && cd sysroot && sh ../ci/sysroot-${{ matrix.config.arch }}-pc-windows-msvc.sh)
|
||||
echo "export C_INCLUDE_PATH=/usr/${{ matrix.config.arch }}-pc-windows-msvc/usr/include" >> saved_env
|
||||
echo "export CARGO_BUILD_TARGET=${{ matrix.config.arch }}-pc-windows-msvc" >> saved_env
|
||||
- name: Configure x86_64 build
|
||||
if: ${{ matrix.config.arch == 'x86_64' }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "export RUSTFLAGS='-Ctarget-cpu=haswell -Ctarget-feature=+crt-static,+avx2,+fma,+f16c -Clinker=lld -Clink-arg=/LIBPATH:/usr/x86_64-pc-windows-msvc/usr/lib'" >> saved_env
|
||||
- name: Configure aarch64 build
|
||||
if: ${{ matrix.config.arch == 'aarch64' }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "export RUSTFLAGS='-Ctarget-feature=+crt-static,+neon,+fp16,+fhm,+dotprod -Clinker=lld -Clink-arg=/LIBPATH:/usr/aarch64-pc-windows-msvc/usr/lib -Clink-arg=arm64rt.lib'" >> saved_env
|
||||
- name: Build Windows Artifacts
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
source ./saved_env
|
||||
bash ci/manylinux_node/build_vectordb.sh ${{ matrix.config.arch }} ${{ matrix.config.arch }}-pc-windows-msvc
|
||||
- name: Upload Windows Artifacts
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: node-native-windows-${{ matrix.config.arch }}
|
||||
path: |
|
||||
node/dist/lancedb-vectordb-win32*.tgz
|
||||
# TODO: re-enable once working https://github.com/lancedb/lancedb/pull/1831
|
||||
# node-windows-arm64:
|
||||
# name: vectordb win32-arm64-msvc
|
||||
# runs-on: windows-4x-arm
|
||||
# if: startsWith(github.ref, 'refs/tags/v')
|
||||
# steps:
|
||||
# - uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
# - name: Install Git
|
||||
# run: |
|
||||
# Invoke-WebRequest -Uri "https://github.com/git-for-windows/git/releases/download/v2.44.0.windows.1/Git-2.44.0-64-bit.exe" -OutFile "git-installer.exe"
|
||||
# Start-Process -FilePath "git-installer.exe" -ArgumentList "/VERYSILENT", "/NORESTART" -Wait
|
||||
# shell: powershell
|
||||
# - name: Add Git to PATH
|
||||
# run: |
|
||||
# Add-Content $env:GITHUB_PATH "C:\Program Files\Git\bin"
|
||||
# $env:Path = [System.Environment]::GetEnvironmentVariable("Path","Machine") + ";" + [System.Environment]::GetEnvironmentVariable("Path","User")
|
||||
# shell: powershell
|
||||
# - name: Configure Git symlinks
|
||||
# run: git config --global core.symlinks true
|
||||
# - uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
# - uses: actions/setup-python@v5
|
||||
# with:
|
||||
# python-version: "3.13"
|
||||
# - name: Install Visual Studio Build Tools
|
||||
# run: |
|
||||
# Invoke-WebRequest -Uri "https://aka.ms/vs/17/release/vs_buildtools.exe" -OutFile "vs_buildtools.exe"
|
||||
# Start-Process -FilePath "vs_buildtools.exe" -ArgumentList "--quiet", "--wait", "--norestart", "--nocache", `
|
||||
# "--installPath", "C:\BuildTools", `
|
||||
# "--add", "Microsoft.VisualStudio.Component.VC.Tools.ARM64", `
|
||||
# "--add", "Microsoft.VisualStudio.Component.VC.Tools.x86.x64", `
|
||||
# "--add", "Microsoft.VisualStudio.Component.Windows11SDK.22621", `
|
||||
# "--add", "Microsoft.VisualStudio.Component.VC.ATL", `
|
||||
# "--add", "Microsoft.VisualStudio.Component.VC.ATLMFC", `
|
||||
# "--add", "Microsoft.VisualStudio.Component.VC.Llvm.Clang" -Wait
|
||||
# shell: powershell
|
||||
# - name: Add Visual Studio Build Tools to PATH
|
||||
# run: |
|
||||
# $vsPath = "C:\BuildTools\VC\Tools\MSVC"
|
||||
# $latestVersion = (Get-ChildItem $vsPath | Sort-Object {[version]$_.Name} -Descending)[0].Name
|
||||
# Add-Content $env:GITHUB_PATH "C:\BuildTools\VC\Tools\MSVC\$latestVersion\bin\Hostx64\arm64"
|
||||
# Add-Content $env:GITHUB_PATH "C:\BuildTools\VC\Tools\MSVC\$latestVersion\bin\Hostx64\x64"
|
||||
# Add-Content $env:GITHUB_PATH "C:\Program Files (x86)\Windows Kits\10\bin\10.0.22621.0\arm64"
|
||||
# Add-Content $env:GITHUB_PATH "C:\Program Files (x86)\Windows Kits\10\bin\10.0.22621.0\x64"
|
||||
# Add-Content $env:GITHUB_PATH "C:\BuildTools\VC\Tools\Llvm\x64\bin"
|
||||
|
||||
# # Add MSVC runtime libraries to LIB
|
||||
# $env:LIB = "C:\BuildTools\VC\Tools\MSVC\$latestVersion\lib\arm64;" +
|
||||
# "C:\Program Files (x86)\Windows Kits\10\Lib\10.0.22621.0\um\arm64;" +
|
||||
# "C:\Program Files (x86)\Windows Kits\10\Lib\10.0.22621.0\ucrt\arm64"
|
||||
# Add-Content $env:GITHUB_ENV "LIB=$env:LIB"
|
||||
|
||||
# # Add INCLUDE paths
|
||||
# $env:INCLUDE = "C:\BuildTools\VC\Tools\MSVC\$latestVersion\include;" +
|
||||
# "C:\Program Files (x86)\Windows Kits\10\Include\10.0.22621.0\ucrt;" +
|
||||
# "C:\Program Files (x86)\Windows Kits\10\Include\10.0.22621.0\um;" +
|
||||
# "C:\Program Files (x86)\Windows Kits\10\Include\10.0.22621.0\shared"
|
||||
# Add-Content $env:GITHUB_ENV "INCLUDE=$env:INCLUDE"
|
||||
# shell: powershell
|
||||
# - name: Install Rust
|
||||
# run: |
|
||||
# Invoke-WebRequest https://win.rustup.rs/x86_64 -OutFile rustup-init.exe
|
||||
# .\rustup-init.exe -y --default-host aarch64-pc-windows-msvc
|
||||
# shell: powershell
|
||||
# - name: Add Rust to PATH
|
||||
# run: |
|
||||
# Add-Content $env:GITHUB_PATH "$env:USERPROFILE\.cargo\bin"
|
||||
# shell: powershell
|
||||
|
||||
# - uses: Swatinem/rust-cache@v2
|
||||
# with:
|
||||
# workspaces: rust
|
||||
# - name: Install 7-Zip ARM
|
||||
# run: |
|
||||
# New-Item -Path 'C:\7zip' -ItemType Directory
|
||||
# Invoke-WebRequest https://7-zip.org/a/7z2408-arm64.exe -OutFile C:\7zip\7z-installer.exe
|
||||
# Start-Process -FilePath C:\7zip\7z-installer.exe -ArgumentList '/S' -Wait
|
||||
# shell: powershell
|
||||
# - name: Add 7-Zip to PATH
|
||||
# run: Add-Content $env:GITHUB_PATH "C:\Program Files\7-Zip"
|
||||
# shell: powershell
|
||||
# - name: Install Protoc v21.12
|
||||
# working-directory: C:\
|
||||
# run: |
|
||||
# if (Test-Path 'C:\protoc') {
|
||||
# Write-Host "Protoc directory exists, skipping installation"
|
||||
# return
|
||||
# }
|
||||
# New-Item -Path 'C:\protoc' -ItemType Directory
|
||||
# Set-Location C:\protoc
|
||||
# Invoke-WebRequest https://github.com/protocolbuffers/protobuf/releases/download/v21.12/protoc-21.12-win64.zip -OutFile C:\protoc\protoc.zip
|
||||
# & 'C:\Program Files\7-Zip\7z.exe' x protoc.zip
|
||||
# shell: powershell
|
||||
# - name: Add Protoc to PATH
|
||||
# run: Add-Content $env:GITHUB_PATH "C:\protoc\bin"
|
||||
# shell: powershell
|
||||
# - name: Build Windows native node modules
|
||||
# run: .\ci\build_windows_artifacts.ps1 aarch64-pc-windows-msvc
|
||||
# - name: Upload Windows ARM64 Artifacts
|
||||
# uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
|
||||
# with:
|
||||
# name: node-native-windows-arm64
|
||||
# path: |
|
||||
# node/dist/*.node
|
||||
|
||||
nodejs-windows:
|
||||
name: lancedb ${{ matrix.target }}
|
||||
@@ -413,57 +472,103 @@ jobs:
|
||||
path: |
|
||||
nodejs/dist/*.node
|
||||
|
||||
nodejs-windows-arm64:
|
||||
name: lancedb ${{ matrix.config.arch }}-pc-windows-msvc
|
||||
# Only runs on tags that matches the make-release action
|
||||
# if: startsWith(github.ref, 'refs/tags/v')
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
container: alpine:edge
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
config:
|
||||
# - arch: x86_64
|
||||
- arch: aarch64
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Checkout
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
apk add protobuf-dev curl clang lld llvm19 grep npm bash msitools sed
|
||||
curl --proto '=https' --tlsv1.3 -sSf https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rust-lang/rustup/refs/heads/master/rustup-init.sh | sh -s -- -y
|
||||
echo "source $HOME/.cargo/env" >> saved_env
|
||||
echo "export CC=clang" >> saved_env
|
||||
echo "export AR=llvm-ar" >> saved_env
|
||||
source "$HOME/.cargo/env"
|
||||
rustup target add ${{ matrix.config.arch }}-pc-windows-msvc
|
||||
(mkdir -p sysroot && cd sysroot && sh ../ci/sysroot-${{ matrix.config.arch }}-pc-windows-msvc.sh)
|
||||
echo "export C_INCLUDE_PATH=/usr/${{ matrix.config.arch }}-pc-windows-msvc/usr/include" >> saved_env
|
||||
echo "export CARGO_BUILD_TARGET=${{ matrix.config.arch }}-pc-windows-msvc" >> saved_env
|
||||
printf '#!/bin/sh\ncargo "$@"' > $HOME/.cargo/bin/cargo-xwin
|
||||
chmod u+x $HOME/.cargo/bin/cargo-xwin
|
||||
- name: Configure x86_64 build
|
||||
if: ${{ matrix.config.arch == 'x86_64' }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "export RUSTFLAGS='-Ctarget-cpu=haswell -Ctarget-feature=+crt-static,+avx2,+fma,+f16c -Clinker=lld -Clink-arg=/LIBPATH:/usr/x86_64-pc-windows-msvc/usr/lib'" >> saved_env
|
||||
- name: Configure aarch64 build
|
||||
if: ${{ matrix.config.arch == 'aarch64' }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "export RUSTFLAGS='-Ctarget-feature=+crt-static,+neon,+fp16,+fhm,+dotprod -Clinker=lld -Clink-arg=/LIBPATH:/usr/aarch64-pc-windows-msvc/usr/lib -Clink-arg=arm64rt.lib'" >> saved_env
|
||||
- name: Build Windows Artifacts
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
source ./saved_env
|
||||
bash ci/manylinux_node/build_lancedb.sh ${{ matrix.config.arch }}
|
||||
- name: Upload Windows Artifacts
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: nodejs-native-windows-${{ matrix.config.arch }}
|
||||
path: |
|
||||
nodejs/dist/*.node
|
||||
# TODO: re-enable once working https://github.com/lancedb/lancedb/pull/1831
|
||||
# nodejs-windows-arm64:
|
||||
# name: lancedb win32-arm64-msvc
|
||||
# runs-on: windows-4x-arm
|
||||
# if: startsWith(github.ref, 'refs/tags/v')
|
||||
# steps:
|
||||
# - uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
# - name: Install Git
|
||||
# run: |
|
||||
# Invoke-WebRequest -Uri "https://github.com/git-for-windows/git/releases/download/v2.44.0.windows.1/Git-2.44.0-64-bit.exe" -OutFile "git-installer.exe"
|
||||
# Start-Process -FilePath "git-installer.exe" -ArgumentList "/VERYSILENT", "/NORESTART" -Wait
|
||||
# shell: powershell
|
||||
# - name: Add Git to PATH
|
||||
# run: |
|
||||
# Add-Content $env:GITHUB_PATH "C:\Program Files\Git\bin"
|
||||
# $env:Path = [System.Environment]::GetEnvironmentVariable("Path","Machine") + ";" + [System.Environment]::GetEnvironmentVariable("Path","User")
|
||||
# shell: powershell
|
||||
# - name: Configure Git symlinks
|
||||
# run: git config --global core.symlinks true
|
||||
# - uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
# - uses: actions/setup-python@v5
|
||||
# with:
|
||||
# python-version: "3.13"
|
||||
# - name: Install Visual Studio Build Tools
|
||||
# run: |
|
||||
# Invoke-WebRequest -Uri "https://aka.ms/vs/17/release/vs_buildtools.exe" -OutFile "vs_buildtools.exe"
|
||||
# Start-Process -FilePath "vs_buildtools.exe" -ArgumentList "--quiet", "--wait", "--norestart", "--nocache", `
|
||||
# "--installPath", "C:\BuildTools", `
|
||||
# "--add", "Microsoft.VisualStudio.Component.VC.Tools.ARM64", `
|
||||
# "--add", "Microsoft.VisualStudio.Component.VC.Tools.x86.x64", `
|
||||
# "--add", "Microsoft.VisualStudio.Component.Windows11SDK.22621", `
|
||||
# "--add", "Microsoft.VisualStudio.Component.VC.ATL", `
|
||||
# "--add", "Microsoft.VisualStudio.Component.VC.ATLMFC", `
|
||||
# "--add", "Microsoft.VisualStudio.Component.VC.Llvm.Clang" -Wait
|
||||
# shell: powershell
|
||||
# - name: Add Visual Studio Build Tools to PATH
|
||||
# run: |
|
||||
# $vsPath = "C:\BuildTools\VC\Tools\MSVC"
|
||||
# $latestVersion = (Get-ChildItem $vsPath | Sort-Object {[version]$_.Name} -Descending)[0].Name
|
||||
# Add-Content $env:GITHUB_PATH "C:\BuildTools\VC\Tools\MSVC\$latestVersion\bin\Hostx64\arm64"
|
||||
# Add-Content $env:GITHUB_PATH "C:\BuildTools\VC\Tools\MSVC\$latestVersion\bin\Hostx64\x64"
|
||||
# Add-Content $env:GITHUB_PATH "C:\Program Files (x86)\Windows Kits\10\bin\10.0.22621.0\arm64"
|
||||
# Add-Content $env:GITHUB_PATH "C:\Program Files (x86)\Windows Kits\10\bin\10.0.22621.0\x64"
|
||||
# Add-Content $env:GITHUB_PATH "C:\BuildTools\VC\Tools\Llvm\x64\bin"
|
||||
|
||||
# $env:LIB = ""
|
||||
# Add-Content $env:GITHUB_ENV "LIB=C:\Program Files (x86)\Windows Kits\10\Lib\10.0.22621.0\um\arm64;C:\Program Files (x86)\Windows Kits\10\Lib\10.0.22621.0\ucrt\arm64"
|
||||
# shell: powershell
|
||||
# - name: Install Rust
|
||||
# run: |
|
||||
# Invoke-WebRequest https://win.rustup.rs/x86_64 -OutFile rustup-init.exe
|
||||
# .\rustup-init.exe -y --default-host aarch64-pc-windows-msvc
|
||||
# shell: powershell
|
||||
# - name: Add Rust to PATH
|
||||
# run: |
|
||||
# Add-Content $env:GITHUB_PATH "$env:USERPROFILE\.cargo\bin"
|
||||
# shell: powershell
|
||||
|
||||
# - uses: Swatinem/rust-cache@v2
|
||||
# with:
|
||||
# workspaces: rust
|
||||
# - name: Install 7-Zip ARM
|
||||
# run: |
|
||||
# New-Item -Path 'C:\7zip' -ItemType Directory
|
||||
# Invoke-WebRequest https://7-zip.org/a/7z2408-arm64.exe -OutFile C:\7zip\7z-installer.exe
|
||||
# Start-Process -FilePath C:\7zip\7z-installer.exe -ArgumentList '/S' -Wait
|
||||
# shell: powershell
|
||||
# - name: Add 7-Zip to PATH
|
||||
# run: Add-Content $env:GITHUB_PATH "C:\Program Files\7-Zip"
|
||||
# shell: powershell
|
||||
# - name: Install Protoc v21.12
|
||||
# working-directory: C:\
|
||||
# run: |
|
||||
# if (Test-Path 'C:\protoc') {
|
||||
# Write-Host "Protoc directory exists, skipping installation"
|
||||
# return
|
||||
# }
|
||||
# New-Item -Path 'C:\protoc' -ItemType Directory
|
||||
# Set-Location C:\protoc
|
||||
# Invoke-WebRequest https://github.com/protocolbuffers/protobuf/releases/download/v21.12/protoc-21.12-win64.zip -OutFile C:\protoc\protoc.zip
|
||||
# & 'C:\Program Files\7-Zip\7z.exe' x protoc.zip
|
||||
# shell: powershell
|
||||
# - name: Add Protoc to PATH
|
||||
# run: Add-Content $env:GITHUB_PATH "C:\protoc\bin"
|
||||
# shell: powershell
|
||||
# - name: Build Windows native node modules
|
||||
# run: .\ci\build_windows_artifacts_nodejs.ps1 aarch64-pc-windows-msvc
|
||||
# - name: Upload Windows ARM64 Artifacts
|
||||
# uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
|
||||
# with:
|
||||
# name: nodejs-native-windows-arm64
|
||||
# path: |
|
||||
# nodejs/dist/*.node
|
||||
|
||||
release:
|
||||
name: vectordb NPM Publish
|
||||
needs: [node, node-macos, node-linux-gnu, node-linux-musl, node-windows, node-windows-arm64]
|
||||
needs: [node, node-macos, node-linux-gnu, node-linux-musl, node-windows]
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
# Only runs on tags that matches the make-release action
|
||||
if: startsWith(github.ref, 'refs/tags/v')
|
||||
@@ -503,7 +608,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
|
||||
release-nodejs:
|
||||
name: lancedb NPM Publish
|
||||
needs: [nodejs-macos, nodejs-linux-gnu, nodejs-linux-musl, nodejs-windows, nodejs-windows-arm64]
|
||||
needs: [nodejs-macos, nodejs-linux-gnu, nodejs-linux-musl, nodejs-windows]
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
# Only runs on tags that matches the make-release action
|
||||
if: startsWith(github.ref, 'refs/tags/v')
|
||||
@@ -561,7 +666,6 @@ jobs:
|
||||
SLACK_WEBHOOK_URL: ${{ secrets.ACTION_MONITORING_SLACK }}
|
||||
|
||||
update-package-lock:
|
||||
if: startsWith(github.ref, 'refs/tags/v')
|
||||
needs: [release]
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
permissions:
|
||||
@@ -571,7 +675,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
ref: main
|
||||
token: ${{ secrets.LANCEDB_RELEASE_TOKEN }}
|
||||
persist-credentials: false
|
||||
fetch-depth: 0
|
||||
lfs: true
|
||||
- uses: ./.github/workflows/update_package_lock
|
||||
@@ -579,7 +683,6 @@ jobs:
|
||||
github_token: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
|
||||
|
||||
update-package-lock-nodejs:
|
||||
if: startsWith(github.ref, 'refs/tags/v')
|
||||
needs: [release-nodejs]
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
permissions:
|
||||
@@ -589,7 +692,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
ref: main
|
||||
token: ${{ secrets.LANCEDB_RELEASE_TOKEN }}
|
||||
persist-credentials: false
|
||||
fetch-depth: 0
|
||||
lfs: true
|
||||
- uses: ./.github/workflows/update_package_lock_nodejs
|
||||
@@ -597,7 +700,6 @@ jobs:
|
||||
github_token: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
|
||||
|
||||
gh-release:
|
||||
if: startsWith(github.ref, 'refs/tags/v')
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
permissions:
|
||||
contents: write
|
||||
|
||||
2
.github/workflows/pypi-publish.yml
vendored
2
.github/workflows/pypi-publish.yml
vendored
@@ -83,7 +83,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- name: Set up Python
|
||||
uses: actions/setup-python@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
python-version: 3.12
|
||||
python-version: 3.8
|
||||
- uses: ./.github/workflows/build_windows_wheel
|
||||
with:
|
||||
python-minor-version: 8
|
||||
|
||||
4
.github/workflows/python.yml
vendored
4
.github/workflows/python.yml
vendored
@@ -30,10 +30,10 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- name: Set up Python
|
||||
uses: actions/setup-python@v5
|
||||
with:
|
||||
python-version: "3.12"
|
||||
python-version: "3.11"
|
||||
- name: Install ruff
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
pip install ruff==0.8.4
|
||||
pip install ruff==0.5.4
|
||||
- name: Format check
|
||||
run: ruff format --check .
|
||||
- name: Lint
|
||||
|
||||
40
.github/workflows/rust.yml
vendored
40
.github/workflows/rust.yml
vendored
@@ -185,7 +185,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
Add-Content $env:GITHUB_PATH "C:\BuildTools\VC\Tools\Llvm\x64\bin"
|
||||
|
||||
# Add MSVC runtime libraries to LIB
|
||||
$env:LIB = "C:\BuildTools\VC\Tools\MSVC\$latestVersion\lib\arm64;" +
|
||||
$env:LIB = "C:\BuildTools\VC\Tools\MSVC\$latestVersion\lib\arm64;" +
|
||||
"C:\Program Files (x86)\Windows Kits\10\Lib\10.0.22621.0\um\arm64;" +
|
||||
"C:\Program Files (x86)\Windows Kits\10\Lib\10.0.22621.0\ucrt\arm64"
|
||||
Add-Content $env:GITHUB_ENV "LIB=$env:LIB"
|
||||
@@ -238,41 +238,3 @@ jobs:
|
||||
$env:VCPKG_ROOT = $env:VCPKG_INSTALLATION_ROOT
|
||||
cargo build --target aarch64-pc-windows-msvc
|
||||
cargo test --target aarch64-pc-windows-msvc
|
||||
|
||||
msrv:
|
||||
# Check the minimum supported Rust version
|
||||
name: MSRV Check - Rust v${{ matrix.msrv }}
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-24.04
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
msrv: ["1.78.0"] # This should match up with rust-version in Cargo.toml
|
||||
env:
|
||||
# Need up-to-date compilers for kernels
|
||||
CC: clang-18
|
||||
CXX: clang++-18
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
submodules: true
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
sudo apt update
|
||||
sudo apt install -y protobuf-compiler libssl-dev
|
||||
- name: Install ${{ matrix.msrv }}
|
||||
uses: dtolnay/rust-toolchain@master
|
||||
with:
|
||||
toolchain: ${{ matrix.msrv }}
|
||||
- name: Downgrade dependencies
|
||||
# These packages have newer requirements for MSRV
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
cargo update -p aws-sdk-bedrockruntime --precise 1.64.0
|
||||
cargo update -p aws-sdk-dynamodb --precise 1.55.0
|
||||
cargo update -p aws-config --precise 1.5.10
|
||||
cargo update -p aws-sdk-kms --precise 1.51.0
|
||||
cargo update -p aws-sdk-s3 --precise 1.65.0
|
||||
cargo update -p aws-sdk-sso --precise 1.50.0
|
||||
cargo update -p aws-sdk-ssooidc --precise 1.51.0
|
||||
cargo update -p aws-sdk-sts --precise 1.51.0
|
||||
cargo update -p home --precise 0.5.9
|
||||
- name: cargo +${{ matrix.msrv }} check
|
||||
run: cargo check --workspace --tests --benches --all-features
|
||||
|
||||
5
.github/workflows/upload_wheel/action.yml
vendored
5
.github/workflows/upload_wheel/action.yml
vendored
@@ -17,12 +17,11 @@ runs:
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
pip install twine
|
||||
python3 -m pip install --upgrade pkginfo
|
||||
- name: Choose repo
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
id: choose_repo
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
if [[ ${{ github.ref }} == *beta* ]]; then
|
||||
if [ ${{ github.ref }} == "*beta*" ]; then
|
||||
echo "repo=fury" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
|
||||
else
|
||||
echo "repo=pypi" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
|
||||
@@ -33,7 +32,7 @@ runs:
|
||||
FURY_TOKEN: ${{ inputs.fury_token }}
|
||||
PYPI_TOKEN: ${{ inputs.pypi_token }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
if [[ ${{ steps.choose_repo.outputs.repo }} == fury ]]; then
|
||||
if [ ${{ steps.choose_repo.outputs.repo }} == "fury" ]; then
|
||||
WHEEL=$(ls target/wheels/lancedb-*.whl 2> /dev/null | head -n 1)
|
||||
echo "Uploading $WHEEL to Fury"
|
||||
curl -f -F package=@$WHEEL https://$FURY_TOKEN@push.fury.io/lancedb/
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,78 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Contributing to LanceDB
|
||||
|
||||
LanceDB is an open-source project and we welcome contributions from the community.
|
||||
This document outlines the process for contributing to LanceDB.
|
||||
|
||||
## Reporting Issues
|
||||
|
||||
If you encounter a bug or have a feature request, please open an issue on the
|
||||
[GitHub issue tracker](https://github.com/lancedb/lancedb).
|
||||
|
||||
## Picking an issue
|
||||
|
||||
We track issues on the GitHub issue tracker. If you are looking for something to
|
||||
work on, check the [good first issue](https://github.com/lancedb/lancedb/contribute) label. These issues are typically the best described and have the smallest scope.
|
||||
|
||||
If there's an issue you are interested in working on, please leave a comment on the issue. This will help us avoid duplicate work. Additionally, if you have questions about the issue, please ask them in the issue comments. We are happy to provide guidance on how to approach the issue.
|
||||
|
||||
## Configuring Git
|
||||
|
||||
First, fork the repository on GitHub, then clone your fork:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/<username>/lancedb.git
|
||||
cd lancedb
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then add the main repository as a remote:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git remote add upstream https://github.com/lancedb/lancedb.git
|
||||
git fetch upstream
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Setting up your development environment
|
||||
|
||||
We have development environments for Python, Typescript, and Java. Each environment has its own setup instructions.
|
||||
|
||||
* [Python](python/CONTRIBUTING.md)
|
||||
* [Typescript](nodejs/CONTRIBUTING.md)
|
||||
<!-- TODO: add Java contributing guide -->
|
||||
* [Documentation](docs/README.md)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Best practices for pull requests
|
||||
|
||||
For the best chance of having your pull request accepted, please follow these guidelines:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Unit test all bug fixes and new features. Your code will not be merged if it
|
||||
doesn't have tests.
|
||||
1. If you change the public API, update the documentation in the `docs` directory.
|
||||
1. Aim to minimize the number of changes in each pull request. Keep to solving
|
||||
one problem at a time, when possible.
|
||||
1. Before marking a pull request ready-for-review, do a self review of your code.
|
||||
Is it clear why you are making the changes? Are the changes easy to understand?
|
||||
1. Use [conventional commit messages](https://www.conventionalcommits.org/en/) as pull request titles. Examples:
|
||||
* New feature: `feat: adding foo API`
|
||||
* Bug fix: `fix: issue with foo API`
|
||||
* Documentation change: `docs: adding foo API documentation`
|
||||
1. If your pull request is a work in progress, leave the pull request as a draft.
|
||||
We will assume the pull request is ready for review when it is opened.
|
||||
1. When writing tests, test the error cases. Make sure they have understandable
|
||||
error messages.
|
||||
|
||||
## Project structure
|
||||
|
||||
The core library is written in Rust. The Python, Typescript, and Java libraries
|
||||
are wrappers around the Rust library.
|
||||
|
||||
* `src/lancedb`: Rust library source code
|
||||
* `python`: Python package source code
|
||||
* `nodejs`: Typescript package source code
|
||||
* `node`: **Deprecated** Typescript package source code
|
||||
* `java`: Java package source code
|
||||
* `docs`: Documentation source code
|
||||
|
||||
## Release process
|
||||
|
||||
For information on the release process, see: [release_process.md](release_process.md)
|
||||
39
Cargo.toml
39
Cargo.toml
@@ -18,30 +18,31 @@ repository = "https://github.com/lancedb/lancedb"
|
||||
description = "Serverless, low-latency vector database for AI applications"
|
||||
keywords = ["lancedb", "lance", "database", "vector", "search"]
|
||||
categories = ["database-implementations"]
|
||||
rust-version = "1.78.0"
|
||||
rust-version = "1.80.0" # TODO: lower this once we upgrade Lance again.
|
||||
|
||||
[workspace.dependencies]
|
||||
lance = { "version" = "=0.22.0", "features" = ["dynamodb"] }
|
||||
lance-io = "=0.22.0"
|
||||
lance-index = "=0.22.0"
|
||||
lance-linalg = "=0.22.0"
|
||||
lance-table = "=0.22.0"
|
||||
lance-testing = "=0.22.0"
|
||||
lance-datafusion = "=0.22.0"
|
||||
lance-encoding = "=0.22.0"
|
||||
lance = { "version" = "=0.20.0", "features" = [
|
||||
"dynamodb",
|
||||
], git = "https://github.com/lancedb/lance.git", tag = "v0.20.0-beta.2" }
|
||||
lance-index = { version = "=0.20.0", git = "https://github.com/lancedb/lance.git", tag = "v0.20.0-beta.2" }
|
||||
lance-linalg = { version = "=0.20.0", git = "https://github.com/lancedb/lance.git", tag = "v0.20.0-beta.2" }
|
||||
lance-table = { version = "=0.20.0", git = "https://github.com/lancedb/lance.git", tag = "v0.20.0-beta.2" }
|
||||
lance-testing = { version = "=0.20.0", git = "https://github.com/lancedb/lance.git", tag = "v0.20.0-beta.2" }
|
||||
lance-datafusion = { version = "=0.20.0", git = "https://github.com/lancedb/lance.git", tag = "v0.20.0-beta.2" }
|
||||
lance-encoding = { version = "=0.20.0", git = "https://github.com/lancedb/lance.git", tag = "v0.20.0-beta.2" }
|
||||
# Note that this one does not include pyarrow
|
||||
arrow = { version = "53.2", optional = false }
|
||||
arrow-array = "53.2"
|
||||
arrow-data = "53.2"
|
||||
arrow-ipc = "53.2"
|
||||
arrow-ord = "53.2"
|
||||
arrow-schema = "53.2"
|
||||
arrow-arith = "53.2"
|
||||
arrow-cast = "53.2"
|
||||
arrow = { version = "52.2", optional = false }
|
||||
arrow-array = "52.2"
|
||||
arrow-data = "52.2"
|
||||
arrow-ipc = "52.2"
|
||||
arrow-ord = "52.2"
|
||||
arrow-schema = "52.2"
|
||||
arrow-arith = "52.2"
|
||||
arrow-cast = "52.2"
|
||||
async-trait = "0"
|
||||
chrono = "0.4.35"
|
||||
datafusion-common = "44.0"
|
||||
datafusion-physical-plan = "44.0"
|
||||
datafusion-common = "41.0"
|
||||
datafusion-physical-plan = "41.0"
|
||||
env_logger = "0.10"
|
||||
half = { "version" = "=2.4.1", default-features = false, features = [
|
||||
"num-traits",
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,9 +1,8 @@
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
set -e
|
||||
ARCH=${1:-x86_64}
|
||||
TARGET_TRIPLE=${2:-x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu}
|
||||
|
||||
# We pass down the current user so that when we later mount the local files
|
||||
# We pass down the current user so that when we later mount the local files
|
||||
# into the container, the files are accessible by the current user.
|
||||
pushd ci/manylinux_node
|
||||
docker build \
|
||||
@@ -19,4 +18,4 @@ docker run \
|
||||
-v $(pwd):/io -w /io \
|
||||
--memory-swap=-1 \
|
||||
lancedb-node-manylinux \
|
||||
bash ci/manylinux_node/build_vectordb.sh $ARCH $TARGET_TRIPLE
|
||||
bash ci/manylinux_node/build_vectordb.sh $ARCH
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -2,7 +2,6 @@
|
||||
# Builds the node module for manylinux. Invoked by ci/build_linux_artifacts.sh.
|
||||
set -e
|
||||
ARCH=${1:-x86_64}
|
||||
TARGET_TRIPLE=${2:-x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu}
|
||||
|
||||
if [ "$ARCH" = "x86_64" ]; then
|
||||
export OPENSSL_LIB_DIR=/usr/local/lib64/
|
||||
@@ -18,4 +17,4 @@ FILE=$HOME/.bashrc && test -f $FILE && source $FILE
|
||||
cd node
|
||||
npm ci
|
||||
npm run build-release
|
||||
npm run pack-build -- -t $TARGET_TRIPLE
|
||||
npm run pack-build
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,105 +0,0 @@
|
||||
#!/bin/sh
|
||||
|
||||
# https://github.com/mstorsjo/msvc-wine/blob/master/vsdownload.py
|
||||
# https://github.com/mozilla/gecko-dev/blob/6027d1d91f2d3204a3992633b3ef730ff005fc64/build/vs/vs2022-car.yaml
|
||||
|
||||
# function dl() {
|
||||
# curl -O https://download.visualstudio.microsoft.com/download/pr/$1
|
||||
# }
|
||||
|
||||
# [[.h]]
|
||||
|
||||
# "id": "Win11SDK_10.0.26100"
|
||||
# "version": "10.0.26100.7"
|
||||
|
||||
# libucrt.lib
|
||||
|
||||
# example: <assert.h>
|
||||
# dir: ucrt/
|
||||
curl -O https://download.visualstudio.microsoft.com/download/pr/32863b8d-a46d-4231-8e84-0888519d20a9/2ee3a5fc6e9fc832af7295b138e93839/universal%20crt%20headers%20libraries%20and%20sources-x86_en-us.msi
|
||||
curl -O https://download.visualstudio.microsoft.com/download/pr/32863b8d-a46d-4231-8e84-0888519d20a9/b1aa09b90fe314aceb090f6ec7626624/16ab2ea2187acffa6435e334796c8c89.cab
|
||||
curl -O https://download.visualstudio.microsoft.com/download/pr/32863b8d-a46d-4231-8e84-0888519d20a9/400609bb0ff5804e36dbe6dcd42a7f01/6ee7bbee8435130a869cf971694fd9e2.cab
|
||||
curl -O https://download.visualstudio.microsoft.com/download/pr/32863b8d-a46d-4231-8e84-0888519d20a9/2ac327317abb865a0e3f56b2faefa918/78fa3c824c2c48bd4a49ab5969adaaf7.cab
|
||||
curl -O https://download.visualstudio.microsoft.com/download/pr/32863b8d-a46d-4231-8e84-0888519d20a9/f034bc0b2680f67dccd4bfeea3d0f932/7afc7b670accd8e3cc94cfffd516f5cb.cab
|
||||
curl -O https://download.visualstudio.microsoft.com/download/pr/32863b8d-a46d-4231-8e84-0888519d20a9/7ed5e12f9d50f80825a8b27838cf4c7f/96076045170fe5db6d5dcf14b6f6688e.cab
|
||||
curl -O https://download.visualstudio.microsoft.com/download/pr/32863b8d-a46d-4231-8e84-0888519d20a9/764edc185a696bda9e07df8891dddbbb/a1e2a83aa8a71c48c742eeaff6e71928.cab
|
||||
curl -O https://download.visualstudio.microsoft.com/download/pr/32863b8d-a46d-4231-8e84-0888519d20a9/66854bedc6dbd5ccb5dd82c8e2412231/b2f03f34ff83ec013b9e45c7cd8e8a73.cab
|
||||
|
||||
# example: <windows.h>
|
||||
# dir: um/
|
||||
curl -O https://download.visualstudio.microsoft.com/download/pr/32863b8d-a46d-4231-8e84-0888519d20a9/b286efac4d83a54fc49190bddef1edc9/windows%20sdk%20for%20windows%20store%20apps%20headers-x86_en-us.msi
|
||||
curl -O https://download.visualstudio.microsoft.com/download/pr/32863b8d-a46d-4231-8e84-0888519d20a9/e0dc3811d92ab96fcb72bf63d6c08d71/766c0ffd568bbb31bf7fb6793383e24a.cab
|
||||
curl -O https://download.visualstudio.microsoft.com/download/pr/32863b8d-a46d-4231-8e84-0888519d20a9/613503da4b5628768497822826aed39f/8125ee239710f33ea485965f76fae646.cab
|
||||
|
||||
# example: <winapifamily.h>
|
||||
# dir: /shared
|
||||
curl -O https://download.visualstudio.microsoft.com/download/pr/32863b8d-a46d-4231-8e84-0888519d20a9/122979f0348d3a2a36b6aa1a111d5d0c/windows%20sdk%20for%20windows%20store%20apps%20headers%20onecoreuap-x86_en-us.msi
|
||||
curl -O https://download.visualstudio.microsoft.com/download/pr/32863b8d-a46d-4231-8e84-0888519d20a9/766e04beecdfccff39e91dd9eb32834a/e89e3dcbb016928c7e426238337d69eb.cab
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# "id": "Microsoft.VisualC.14.16.CRT.Headers"
|
||||
# "version": "14.16.27045"
|
||||
|
||||
# example: <vcruntime.h>
|
||||
# dir: MSVC/
|
||||
curl -O https://download.visualstudio.microsoft.com/download/pr/bac0afd7-cc9e-4182-8a83-9898fa20e092/87bbe41e09a2f83711e72696f49681429327eb7a4b90618c35667a6ba2e2880e/Microsoft.VisualC.14.16.CRT.Headers.vsix
|
||||
|
||||
# [[.lib]]
|
||||
|
||||
# advapi32.lib bcrypt.lib kernel32.lib ntdll.lib user32.lib uuid.lib ws2_32.lib userenv.lib cfgmgr32.lib runtimeobject.lib
|
||||
curl -O https://download.visualstudio.microsoft.com/download/pr/32863b8d-a46d-4231-8e84-0888519d20a9/944c4153b849a1f7d0c0404a4f1c05ea/windows%20sdk%20for%20windows%20store%20apps%20libs-x86_en-us.msi
|
||||
curl -O https://download.visualstudio.microsoft.com/download/pr/32863b8d-a46d-4231-8e84-0888519d20a9/5306aed3e1a38d1e8bef5934edeb2a9b/05047a45609f311645eebcac2739fc4c.cab
|
||||
curl -O https://download.visualstudio.microsoft.com/download/pr/32863b8d-a46d-4231-8e84-0888519d20a9/13c8a73a0f5a6474040b26d016a26fab/13d68b8a7b6678a368e2d13ff4027521.cab
|
||||
curl -O https://download.visualstudio.microsoft.com/download/pr/32863b8d-a46d-4231-8e84-0888519d20a9/149578fb3b621cdb61ee1813b9b3e791/463ad1b0783ebda908fd6c16a4abfe93.cab
|
||||
curl -O https://download.visualstudio.microsoft.com/download/pr/32863b8d-a46d-4231-8e84-0888519d20a9/5c986c4f393c6b09d5aec3b539e9fb4a/5a22e5cde814b041749fb271547f4dd5.cab
|
||||
|
||||
# dbghelp.lib fwpuclnt.lib arm64rt.lib
|
||||
curl -O https://download.visualstudio.microsoft.com/download/pr/32863b8d-a46d-4231-8e84-0888519d20a9/7a332420d812f7c1d41da865ae5a7c52/windows%20sdk%20desktop%20libs%20arm64-x86_en-us.msi
|
||||
curl -O https://download.visualstudio.microsoft.com/download/pr/32863b8d-a46d-4231-8e84-0888519d20a9/19de98ed4a79938d0045d19c047936b3/3e2f7be479e3679d700ce0782e4cc318.cab
|
||||
|
||||
# libcmt.lib libvcruntime.lib
|
||||
curl -O https://download.visualstudio.microsoft.com/download/pr/bac0afd7-cc9e-4182-8a83-9898fa20e092/227f40682a88dc5fa0ccb9cadc9ad30af99ad1f1a75db63407587d079f60d035/Microsoft.VisualC.14.16.CRT.ARM64.Desktop.vsix
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
msiextract universal%20crt%20headers%20libraries%20and%20sources-x86_en-us.msi
|
||||
msiextract windows%20sdk%20for%20windows%20store%20apps%20headers-x86_en-us.msi
|
||||
msiextract windows%20sdk%20for%20windows%20store%20apps%20headers%20onecoreuap-x86_en-us.msi
|
||||
msiextract windows%20sdk%20for%20windows%20store%20apps%20libs-x86_en-us.msi
|
||||
msiextract windows%20sdk%20desktop%20libs%20arm64-x86_en-us.msi
|
||||
unzip -o Microsoft.VisualC.14.16.CRT.Headers.vsix
|
||||
unzip -o Microsoft.VisualC.14.16.CRT.ARM64.Desktop.vsix
|
||||
|
||||
mkdir -p /usr/aarch64-pc-windows-msvc/usr/include
|
||||
mkdir -p /usr/aarch64-pc-windows-msvc/usr/lib
|
||||
|
||||
# lowercase folder/file names
|
||||
echo "$(find . -regex ".*/[^/]*[A-Z][^/]*")" | xargs -I{} sh -c 'mv "$(echo "{}" | sed -E '"'"'s/(.*\/)/\L\1/'"'"')" "$(echo "{}" | tr [A-Z] [a-z])"'
|
||||
|
||||
# .h
|
||||
(cd 'program files/windows kits/10/include/10.0.26100.0' && cp -r ucrt/* um/* shared/* -t /usr/aarch64-pc-windows-msvc/usr/include)
|
||||
|
||||
cp -r contents/vc/tools/msvc/14.16.27023/include/* /usr/aarch64-pc-windows-msvc/usr/include
|
||||
|
||||
# lowercase #include "" and #include <>
|
||||
find /usr/aarch64-pc-windows-msvc/usr/include -type f -exec sed -i -E 's/(#include <[^<>]*?[A-Z][^<>]*?>)|(#include "[^"]*?[A-Z][^"]*?")/\L\1\2/' "{}" ';'
|
||||
|
||||
# ARM intrinsics
|
||||
# original dir: MSVC/
|
||||
|
||||
# '__n128x4' redefined in arm_neon.h
|
||||
# "arm64_neon.h" included from intrin.h
|
||||
|
||||
(cd /usr/lib/llvm19/lib/clang/19/include && cp arm_neon.h intrin.h -t /usr/aarch64-pc-windows-msvc/usr/include)
|
||||
|
||||
# .lib
|
||||
|
||||
# _Interlocked intrinsics
|
||||
# must always link with arm64rt.lib
|
||||
# reason: https://developercommunity.visualstudio.com/t/libucrtlibstreamobj-error-lnk2001-unresolved-exter/1544787#T-ND1599818
|
||||
# I don't understand the 'correct' fix for this, arm64rt.lib is supposed to be the workaround
|
||||
|
||||
(cd 'program files/windows kits/10/lib/10.0.26100.0/um/arm64' && cp advapi32.lib bcrypt.lib kernel32.lib ntdll.lib user32.lib uuid.lib ws2_32.lib userenv.lib cfgmgr32.lib runtimeobject.lib dbghelp.lib fwpuclnt.lib arm64rt.lib -t /usr/aarch64-pc-windows-msvc/usr/lib)
|
||||
|
||||
(cd 'contents/vc/tools/msvc/14.16.27023/lib/arm64' && cp libcmt.lib libvcruntime.lib -t /usr/aarch64-pc-windows-msvc/usr/lib)
|
||||
|
||||
cp 'program files/windows kits/10/lib/10.0.26100.0/ucrt/arm64/libucrt.lib' /usr/aarch64-pc-windows-msvc/usr/lib
|
||||
@@ -1,105 +0,0 @@
|
||||
#!/bin/sh
|
||||
|
||||
# https://github.com/mstorsjo/msvc-wine/blob/master/vsdownload.py
|
||||
# https://github.com/mozilla/gecko-dev/blob/6027d1d91f2d3204a3992633b3ef730ff005fc64/build/vs/vs2022-car.yaml
|
||||
|
||||
# function dl() {
|
||||
# curl -O https://download.visualstudio.microsoft.com/download/pr/$1
|
||||
# }
|
||||
|
||||
# [[.h]]
|
||||
|
||||
# "id": "Win11SDK_10.0.26100"
|
||||
# "version": "10.0.26100.7"
|
||||
|
||||
# libucrt.lib
|
||||
|
||||
# example: <assert.h>
|
||||
# dir: ucrt/
|
||||
curl -O https://download.visualstudio.microsoft.com/download/pr/32863b8d-a46d-4231-8e84-0888519d20a9/2ee3a5fc6e9fc832af7295b138e93839/universal%20crt%20headers%20libraries%20and%20sources-x86_en-us.msi
|
||||
curl -O https://download.visualstudio.microsoft.com/download/pr/32863b8d-a46d-4231-8e84-0888519d20a9/b1aa09b90fe314aceb090f6ec7626624/16ab2ea2187acffa6435e334796c8c89.cab
|
||||
curl -O https://download.visualstudio.microsoft.com/download/pr/32863b8d-a46d-4231-8e84-0888519d20a9/400609bb0ff5804e36dbe6dcd42a7f01/6ee7bbee8435130a869cf971694fd9e2.cab
|
||||
curl -O https://download.visualstudio.microsoft.com/download/pr/32863b8d-a46d-4231-8e84-0888519d20a9/2ac327317abb865a0e3f56b2faefa918/78fa3c824c2c48bd4a49ab5969adaaf7.cab
|
||||
curl -O https://download.visualstudio.microsoft.com/download/pr/32863b8d-a46d-4231-8e84-0888519d20a9/f034bc0b2680f67dccd4bfeea3d0f932/7afc7b670accd8e3cc94cfffd516f5cb.cab
|
||||
curl -O https://download.visualstudio.microsoft.com/download/pr/32863b8d-a46d-4231-8e84-0888519d20a9/7ed5e12f9d50f80825a8b27838cf4c7f/96076045170fe5db6d5dcf14b6f6688e.cab
|
||||
curl -O https://download.visualstudio.microsoft.com/download/pr/32863b8d-a46d-4231-8e84-0888519d20a9/764edc185a696bda9e07df8891dddbbb/a1e2a83aa8a71c48c742eeaff6e71928.cab
|
||||
curl -O https://download.visualstudio.microsoft.com/download/pr/32863b8d-a46d-4231-8e84-0888519d20a9/66854bedc6dbd5ccb5dd82c8e2412231/b2f03f34ff83ec013b9e45c7cd8e8a73.cab
|
||||
|
||||
# example: <windows.h>
|
||||
# dir: um/
|
||||
curl -O https://download.visualstudio.microsoft.com/download/pr/32863b8d-a46d-4231-8e84-0888519d20a9/b286efac4d83a54fc49190bddef1edc9/windows%20sdk%20for%20windows%20store%20apps%20headers-x86_en-us.msi
|
||||
curl -O https://download.visualstudio.microsoft.com/download/pr/32863b8d-a46d-4231-8e84-0888519d20a9/e0dc3811d92ab96fcb72bf63d6c08d71/766c0ffd568bbb31bf7fb6793383e24a.cab
|
||||
curl -O https://download.visualstudio.microsoft.com/download/pr/32863b8d-a46d-4231-8e84-0888519d20a9/613503da4b5628768497822826aed39f/8125ee239710f33ea485965f76fae646.cab
|
||||
|
||||
# example: <winapifamily.h>
|
||||
# dir: /shared
|
||||
curl -O https://download.visualstudio.microsoft.com/download/pr/32863b8d-a46d-4231-8e84-0888519d20a9/122979f0348d3a2a36b6aa1a111d5d0c/windows%20sdk%20for%20windows%20store%20apps%20headers%20onecoreuap-x86_en-us.msi
|
||||
curl -O https://download.visualstudio.microsoft.com/download/pr/32863b8d-a46d-4231-8e84-0888519d20a9/766e04beecdfccff39e91dd9eb32834a/e89e3dcbb016928c7e426238337d69eb.cab
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# "id": "Microsoft.VisualC.14.16.CRT.Headers"
|
||||
# "version": "14.16.27045"
|
||||
|
||||
# example: <vcruntime.h>
|
||||
# dir: MSVC/
|
||||
curl -O https://download.visualstudio.microsoft.com/download/pr/bac0afd7-cc9e-4182-8a83-9898fa20e092/87bbe41e09a2f83711e72696f49681429327eb7a4b90618c35667a6ba2e2880e/Microsoft.VisualC.14.16.CRT.Headers.vsix
|
||||
|
||||
# [[.lib]]
|
||||
|
||||
# advapi32.lib bcrypt.lib kernel32.lib ntdll.lib user32.lib uuid.lib ws2_32.lib userenv.lib cfgmgr32.lib
|
||||
curl -O https://download.visualstudio.microsoft.com/download/pr/32863b8d-a46d-4231-8e84-0888519d20a9/944c4153b849a1f7d0c0404a4f1c05ea/windows%20sdk%20for%20windows%20store%20apps%20libs-x86_en-us.msi
|
||||
curl -O https://download.visualstudio.microsoft.com/download/pr/32863b8d-a46d-4231-8e84-0888519d20a9/5306aed3e1a38d1e8bef5934edeb2a9b/05047a45609f311645eebcac2739fc4c.cab
|
||||
curl -O https://download.visualstudio.microsoft.com/download/pr/32863b8d-a46d-4231-8e84-0888519d20a9/13c8a73a0f5a6474040b26d016a26fab/13d68b8a7b6678a368e2d13ff4027521.cab
|
||||
curl -O https://download.visualstudio.microsoft.com/download/pr/32863b8d-a46d-4231-8e84-0888519d20a9/149578fb3b621cdb61ee1813b9b3e791/463ad1b0783ebda908fd6c16a4abfe93.cab
|
||||
curl -O https://download.visualstudio.microsoft.com/download/pr/32863b8d-a46d-4231-8e84-0888519d20a9/5c986c4f393c6b09d5aec3b539e9fb4a/5a22e5cde814b041749fb271547f4dd5.cab
|
||||
curl -O https://download.visualstudio.microsoft.com/download/pr/32863b8d-a46d-4231-8e84-0888519d20a9/bfc3904a0195453419ae4dfea7abd6fb/e10768bb6e9d0ea730280336b697da66.cab
|
||||
curl -O https://download.visualstudio.microsoft.com/download/pr/32863b8d-a46d-4231-8e84-0888519d20a9/637f9f3be880c71f9e3ca07b4d67345c/f9b24c8280986c0683fbceca5326d806.cab
|
||||
|
||||
# dbghelp.lib fwpuclnt.lib
|
||||
curl -O https://download.visualstudio.microsoft.com/download/pr/32863b8d-a46d-4231-8e84-0888519d20a9/9f51690d5aa804b1340ce12d1ec80f89/windows%20sdk%20desktop%20libs%20x64-x86_en-us.msi
|
||||
curl -O https://download.visualstudio.microsoft.com/download/pr/32863b8d-a46d-4231-8e84-0888519d20a9/d3a7df4ca3303a698640a29e558a5e5b/58314d0646d7e1a25e97c902166c3155.cab
|
||||
|
||||
# libcmt.lib libvcruntime.lib
|
||||
curl -O https://download.visualstudio.microsoft.com/download/pr/bac0afd7-cc9e-4182-8a83-9898fa20e092/8728f21ae09940f1f4b4ee47b4a596be2509e2a47d2f0c83bbec0ea37d69644b/Microsoft.VisualC.14.16.CRT.x64.Desktop.vsix
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
msiextract universal%20crt%20headers%20libraries%20and%20sources-x86_en-us.msi
|
||||
msiextract windows%20sdk%20for%20windows%20store%20apps%20headers-x86_en-us.msi
|
||||
msiextract windows%20sdk%20for%20windows%20store%20apps%20headers%20onecoreuap-x86_en-us.msi
|
||||
msiextract windows%20sdk%20for%20windows%20store%20apps%20libs-x86_en-us.msi
|
||||
msiextract windows%20sdk%20desktop%20libs%20x64-x86_en-us.msi
|
||||
unzip -o Microsoft.VisualC.14.16.CRT.Headers.vsix
|
||||
unzip -o Microsoft.VisualC.14.16.CRT.x64.Desktop.vsix
|
||||
|
||||
mkdir -p /usr/x86_64-pc-windows-msvc/usr/include
|
||||
mkdir -p /usr/x86_64-pc-windows-msvc/usr/lib
|
||||
|
||||
# lowercase folder/file names
|
||||
echo "$(find . -regex ".*/[^/]*[A-Z][^/]*")" | xargs -I{} sh -c 'mv "$(echo "{}" | sed -E '"'"'s/(.*\/)/\L\1/'"'"')" "$(echo "{}" | tr [A-Z] [a-z])"'
|
||||
|
||||
# .h
|
||||
(cd 'program files/windows kits/10/include/10.0.26100.0' && cp -r ucrt/* um/* shared/* -t /usr/x86_64-pc-windows-msvc/usr/include)
|
||||
|
||||
cp -r contents/vc/tools/msvc/14.16.27023/include/* /usr/x86_64-pc-windows-msvc/usr/include
|
||||
|
||||
# lowercase #include "" and #include <>
|
||||
find /usr/x86_64-pc-windows-msvc/usr/include -type f -exec sed -i -E 's/(#include <[^<>]*?[A-Z][^<>]*?>)|(#include "[^"]*?[A-Z][^"]*?")/\L\1\2/' "{}" ';'
|
||||
|
||||
# x86 intrinsics
|
||||
# original dir: MSVC/
|
||||
|
||||
# '_mm_movemask_epi8' defined in emmintrin.h
|
||||
# '__v4sf' defined in xmmintrin.h
|
||||
# '__v2si' defined in mmintrin.h
|
||||
# '__m128d' redefined in immintrin.h
|
||||
# '__m128i' redefined in intrin.h
|
||||
# '_mm_comlt_epu8' defined in ammintrin.h
|
||||
|
||||
(cd /usr/lib/llvm19/lib/clang/19/include && cp emmintrin.h xmmintrin.h mmintrin.h immintrin.h intrin.h ammintrin.h -t /usr/x86_64-pc-windows-msvc/usr/include)
|
||||
|
||||
# .lib
|
||||
(cd 'program files/windows kits/10/lib/10.0.26100.0/um/x64' && cp advapi32.lib bcrypt.lib kernel32.lib ntdll.lib user32.lib uuid.lib ws2_32.lib userenv.lib cfgmgr32.lib dbghelp.lib fwpuclnt.lib -t /usr/x86_64-pc-windows-msvc/usr/lib)
|
||||
|
||||
(cd 'contents/vc/tools/msvc/14.16.27023/lib/x64' && cp libcmt.lib libvcruntime.lib -t /usr/x86_64-pc-windows-msvc/usr/lib)
|
||||
|
||||
cp 'program files/windows kits/10/lib/10.0.26100.0/ucrt/x64/libucrt.lib' /usr/x86_64-pc-windows-msvc/usr/lib
|
||||
@@ -1,34 +0,0 @@
|
||||
import tomllib
|
||||
|
||||
found_preview_lance = False
|
||||
|
||||
with open("Cargo.toml", "rb") as f:
|
||||
cargo_data = tomllib.load(f)
|
||||
|
||||
for name, dep in cargo_data["workspace"]["dependencies"].items():
|
||||
if name == "lance" or name.startswith("lance-"):
|
||||
if isinstance(dep, str):
|
||||
version = dep
|
||||
elif isinstance(dep, dict):
|
||||
# Version doesn't have the beta tag in it, so we instead look
|
||||
# at the git tag.
|
||||
version = dep.get('tag', dep.get('version'))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
raise ValueError("Unexpected type for dependency: " + str(dep))
|
||||
|
||||
if "beta" in version:
|
||||
found_preview_lance = True
|
||||
print(f"Dependency '{name}' is a preview version: {version}")
|
||||
|
||||
with open("python/pyproject.toml", "rb") as f:
|
||||
py_proj_data = tomllib.load(f)
|
||||
|
||||
for dep in py_proj_data["project"]["dependencies"]:
|
||||
if dep.startswith("pylance"):
|
||||
if "b" in dep:
|
||||
found_preview_lance = True
|
||||
print(f"Dependency '{dep}' is a preview version")
|
||||
break # Only one pylance dependency
|
||||
|
||||
if found_preview_lance:
|
||||
raise ValueError("Found preview version of Lance in dependencies")
|
||||
@@ -9,81 +9,36 @@ unreleased features.
|
||||
## Building the docs
|
||||
|
||||
### Setup
|
||||
1. Install LanceDB Python. See setup in [Python contributing guide](../python/CONTRIBUTING.md).
|
||||
Run `make develop` to install the Python package.
|
||||
2. Install documentation dependencies. From LanceDB repo root: `pip install -r docs/requirements.txt`
|
||||
1. Install LanceDB. From LanceDB repo root: `pip install -e python`
|
||||
2. Install dependencies. From LanceDB repo root: `pip install -r docs/requirements.txt`
|
||||
3. Make sure you have node and npm setup
|
||||
4. Make sure protobuf and libssl are installed
|
||||
|
||||
### Preview the docs
|
||||
### Building node module and create markdown files
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
See [Javascript docs README](./src/javascript/README.md)
|
||||
|
||||
### Build docs
|
||||
From LanceDB repo root:
|
||||
|
||||
Run: `PYTHONPATH=. mkdocs build -f docs/mkdocs.yml`
|
||||
|
||||
If successful, you should see a `docs/site` directory that you can verify locally.
|
||||
|
||||
### Run local server
|
||||
|
||||
You can run a local server to test the docs prior to deployment by navigating to the `docs` directory and running the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cd docs
|
||||
mkdocs serve
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to just generate the HTML files:
|
||||
### Run doctest for typescript example
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
PYTHONPATH=. mkdocs build -f docs/mkdocs.yml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If successful, you should see a `docs/site` directory that you can verify locally.
|
||||
|
||||
## Adding examples
|
||||
|
||||
To make sure examples are correct, we put examples in test files so they can be
|
||||
run as part of our test suites.
|
||||
|
||||
You can see the tests are at:
|
||||
|
||||
* Python: `python/python/tests/docs`
|
||||
* Typescript: `nodejs/examples/`
|
||||
|
||||
### Checking python examples
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
cd python
|
||||
pytest -vv python/tests/docs
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Checking typescript examples
|
||||
|
||||
The `@lancedb/lancedb` package must be built before running the tests:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
pushd nodejs
|
||||
npm ci
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cd lancedb/docs
|
||||
npm i
|
||||
npm run build
|
||||
popd
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then you can run the examples by going to the `nodejs/examples` directory and
|
||||
running the tests like a normal npm package:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
pushd nodejs/examples
|
||||
npm ci
|
||||
npm test
|
||||
popd
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## API documentation
|
||||
|
||||
### Python
|
||||
|
||||
The Python API documentation is organized based on the file `docs/src/python/python.md`.
|
||||
We manually add entries there so we can control the organization of the reference page.
|
||||
**However, this means any new types must be manually added to the file.** No additional
|
||||
steps are needed to generate the API documentation.
|
||||
|
||||
### Typescript
|
||||
|
||||
The typescript API documentation is generated from the typescript source code using [typedoc](https://typedoc.org/).
|
||||
|
||||
When new APIs are added, you must manually re-run the typedoc command to update the API documentation.
|
||||
The new files should be checked into the repository.
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
pushd nodejs
|
||||
npm run docs
|
||||
popd
|
||||
npm run all
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -55,14 +55,10 @@ plugins:
|
||||
show_signature_annotations: true
|
||||
show_root_heading: true
|
||||
members_order: source
|
||||
docstring_section_style: list
|
||||
signature_crossrefs: true
|
||||
separate_signature: true
|
||||
import:
|
||||
# for cross references
|
||||
- https://arrow.apache.org/docs/objects.inv
|
||||
- https://pandas.pydata.org/docs/objects.inv
|
||||
- https://lancedb.github.io/lance/objects.inv
|
||||
- mkdocs-jupyter
|
||||
- render_swagger:
|
||||
allow_arbitrary_locations: true
|
||||
@@ -146,9 +142,7 @@ nav:
|
||||
- Building Custom Rerankers: reranking/custom_reranker.md
|
||||
- Example: notebooks/lancedb_reranking.ipynb
|
||||
- Filtering: sql.md
|
||||
- Versioning & Reproducibility:
|
||||
- sync API: notebooks/reproducibility.ipynb
|
||||
- async API: notebooks/reproducibility_async.ipynb
|
||||
- Versioning & Reproducibility: notebooks/reproducibility.ipynb
|
||||
- Configuring Storage: guides/storage.md
|
||||
- Migration Guide: migration.md
|
||||
- Tuning retrieval performance:
|
||||
@@ -234,7 +228,6 @@ nav:
|
||||
- 🐍 Python: python/saas-python.md
|
||||
- 👾 JavaScript: javascript/modules.md
|
||||
- REST API: cloud/rest.md
|
||||
- FAQs: cloud/cloud_faq.md
|
||||
|
||||
- Quick start: basic.md
|
||||
- Concepts:
|
||||
@@ -280,9 +273,7 @@ nav:
|
||||
- Building Custom Rerankers: reranking/custom_reranker.md
|
||||
- Example: notebooks/lancedb_reranking.ipynb
|
||||
- Filtering: sql.md
|
||||
- Versioning & Reproducibility:
|
||||
- sync API: notebooks/reproducibility.ipynb
|
||||
- async API: notebooks/reproducibility_async.ipynb
|
||||
- Versioning & Reproducibility: notebooks/reproducibility.ipynb
|
||||
- Configuring Storage: guides/storage.md
|
||||
- Migration Guide: migration.md
|
||||
- Tuning retrieval performance:
|
||||
@@ -363,7 +354,6 @@ nav:
|
||||
- 🐍 Python: python/saas-python.md
|
||||
- 👾 JavaScript: javascript/modules.md
|
||||
- REST API: cloud/rest.md
|
||||
- FAQs: cloud/cloud_faq.md
|
||||
|
||||
extra_css:
|
||||
- styles/global.css
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -18,24 +18,25 @@ See the [indexing](concepts/index_ivfpq.md) concepts guide for more information
|
||||
Lance supports `IVF_PQ` index type by default.
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Python"
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
|
||||
Creating indexes is done via the [create_index](https://lancedb.github.io/lancedb/python/#lancedb.table.LanceTable.create_index) method.
|
||||
Creating indexes is done via the [create_index](https://lancedb.github.io/lancedb/python/#lancedb.table.LanceTable.create_index) method.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_index.py:import-lancedb"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_index.py:import-numpy"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_index.py:create_ann_index"
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
Creating indexes is done via the [create_index](https://lancedb.github.io/lancedb/python/#lancedb.table.LanceTable.create_index) method.
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
uri = "data/sample-lancedb"
|
||||
db = lancedb.connect(uri)
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_index.py:import-lancedb"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_index.py:import-numpy"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_index.py:import-lancedb-ivfpq"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_index.py:create_ann_index_async"
|
||||
```
|
||||
# Create 10,000 sample vectors
|
||||
data = [{"vector": row, "item": f"item {i}"}
|
||||
for i, row in enumerate(np.random.random((10_000, 1536)).astype('float32'))]
|
||||
|
||||
# Add the vectors to a table
|
||||
tbl = db.create_table("my_vectors", data=data)
|
||||
|
||||
# Create and train the index - you need to have enough data in the table for an effective training step
|
||||
tbl.create_index(num_partitions=256, num_sub_vectors=96)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
=== "TypeScript"
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -82,7 +83,6 @@ The following IVF_PQ paramters can be specified:
|
||||
- **num_sub_vectors**: The number of sub-vectors (M) that will be created during Product Quantization (PQ).
|
||||
For D dimensional vector, it will be divided into `M` subvectors with dimension `D/M`, each of which is replaced by
|
||||
a single PQ code. The default is the dimension of the vector divided by 16.
|
||||
- **num_bits**: The number of bits used to encode each sub-vector. Only 4 and 8 are supported. The higher the number of bits, the higher the accuracy of the index, also the slower search. The default is 8.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -126,9 +126,7 @@ You can specify the GPU device to train IVF partitions via
|
||||
accelerator="mps"
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
!!! note
|
||||
GPU based indexing is not yet supported with our asynchronous client.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Troubleshooting:
|
||||
|
||||
If you see `AssertionError: Torch not compiled with CUDA enabled`, you need to [install
|
||||
@@ -144,25 +142,23 @@ There are a couple of parameters that can be used to fine-tune the search:
|
||||
- **nprobes** (default: 20): The number of probes used. A higher number makes search more accurate but also slower.<br/>
|
||||
Most of the time, setting nprobes to cover 5-15% of the dataset should achieve high recall with low latency.<br/>
|
||||
- _For example_, For a dataset of 1 million vectors divided into 256 partitions, `nprobes` should be set to ~20-40. This value can be adjusted to achieve the optimal balance between search latency and search quality. <br/>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- **refine_factor** (default: None): Refine the results by reading extra elements and re-ranking them in memory.<br/>
|
||||
A higher number makes search more accurate but also slower. If you find the recall is less than ideal, try refine_factor=10 to start.<br/>
|
||||
- _For example_, For a dataset of 1 million vectors divided into 256 partitions, setting the `refine_factor` to 200 will initially retrieve the top 4,000 candidates (top k * refine_factor) from all searched partitions. These candidates are then reranked to determine the final top 20 results.<br/>
|
||||
!!! note
|
||||
!!! note
|
||||
Both `nprobes` and `refine_factor` are only applicable if an ANN index is present. If specified on a table without an ANN index, those parameters are ignored.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Python"
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_index.py:vector_search"
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_index.py:vector_search_async"
|
||||
```
|
||||
```python
|
||||
tbl.search(np.random.random((1536))) \
|
||||
.limit(2) \
|
||||
.nprobes(20) \
|
||||
.refine_factor(10) \
|
||||
.to_pandas()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
vector item _distance
|
||||
@@ -199,16 +195,10 @@ The search will return the data requested in addition to the distance of each it
|
||||
You can further filter the elements returned by a search using a where clause.
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Python"
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_index.py:vector_search_with_filter"
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_index.py:vector_search_async_with_filter"
|
||||
```
|
||||
```python
|
||||
tbl.search(np.random.random((1536))).where("item != 'item 1141'").to_pandas()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
=== "TypeScript"
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -230,16 +220,10 @@ You can select the columns returned by the query using a select clause.
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Python"
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
```python
|
||||
tbl.search(np.random.random((1536))).select(["vector"]).to_pandas()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_index.py:vector_search_with_select"
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_index.py:vector_search_async_with_select"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
vector _distance
|
||||
@@ -304,4 +288,4 @@ less space distortion, and thus yields better accuracy. However, a higher `num_s
|
||||
|
||||
`m` determines the number of connections a new node establishes with its closest neighbors upon entering the graph. Typically, `m` falls within the range of 5 to 48. Lower `m` values are suitable for low-dimensional data or scenarios where recall is less critical. Conversely, higher `m` values are beneficial for high-dimensional data or when high recall is required. In essence, a larger `m` results in a denser graph with increased connectivity, but at the expense of higher memory consumption.
|
||||
|
||||
`ef_construction` balances build speed and accuracy. Higher values increase accuracy but slow down the build process. A typical range is 150 to 300. For good search results, a minimum value of 100 is recommended. In most cases, setting this value above 500 offers no additional benefit. Ensure that `ef_construction` is always set to a value equal to or greater than `ef` in the search phase
|
||||
`ef_construction` balances build speed and accuracy. Higher values increase accuracy but slow down the build process. A typical range is 150 to 300. For good search results, a minimum value of 100 is recommended. In most cases, setting this value above 500 offers no additional benefit. Ensure that `ef_construction` is always set to a value equal to or greater than `ef` in the search phase
|
||||
Binary file not shown.
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 10 KiB |
@@ -141,6 +141,14 @@ recommend switching to stable releases.
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_basic.py:connect_async"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note "Asynchronous Python API"
|
||||
|
||||
The asynchronous Python API is new and has some slight differences compared
|
||||
to the synchronous API. Feel free to start using the asynchronous version.
|
||||
Once all features have migrated we will start to move the synchronous API to
|
||||
use the same syntax as the asynchronous API. To help with this migration we
|
||||
have created a [migration guide](migration.md) detailing the differences.
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Typescript[^1]"
|
||||
|
||||
=== "@lancedb/lancedb"
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,34 +0,0 @@
|
||||
This section provides answers to the most common questions asked about LanceDB Cloud. By following these guidelines, you can ensure a smooth, performant experience with LanceDB Cloud.
|
||||
|
||||
### Should I reuse the database connection?
|
||||
Yes! It is recommended to establish a single database connection and maintain it throughout your interaction with the tables within.
|
||||
|
||||
LanceDB uses HTTP connections to communicate with the servers. By re-using the Connection object, you avoid the overhead of repeatedly establishing HTTP connections, significantly improving efficiency.
|
||||
|
||||
### Should I re-use the `Table` object?
|
||||
`table = db.open_table()` should be called once and used for all subsequent table operations. If there are changes to the opened table, `table` always reflect the **latest version** of the data.
|
||||
|
||||
### What should I do if I need to search for rows by `id`?
|
||||
LanceDB Cloud currently does not support an ID or primary key column. You are recommended to add a
|
||||
user-defined ID column. To significantly improve the query performance with SQL causes, a scalar BITMAP/BTREE index should be created on this column.
|
||||
|
||||
### What are the vector indexing types supported by LanceDB Cloud?
|
||||
We support `IVF_PQ` and `IVF_HNSW_SQ` as the `index_type` which is passed to `create_index`. LanceDB Cloud tunes the indexing parameters automatically to achieve the best tradeoff between query latency and query quality.
|
||||
|
||||
### When I add new rows to a table, do I need to manually update the index?
|
||||
No! LanceDB Cloud triggers an asynchronous background job to index the new vectors.
|
||||
|
||||
Even though indexing is asynchronous, your vectors will still be immediately searchable. LanceDB uses brute-force search to search over unindexed rows. This makes you new data is immediately available, but does increase latency temporarily. To disable the brute-force part of search, set the `fast_search` flag in your query to `true`.
|
||||
|
||||
### Do I need to reindex the whole dataset if only a small portion of the data is deleted or updated?
|
||||
No! Similar to adding data to the table, LanceDB Cloud triggers an asynchronous background job to update the existing indices. Therefore, no action is needed from users and there is absolutely no
|
||||
downtime expected.
|
||||
|
||||
### How do I know whether an index has been created?
|
||||
While index creation in LanceDB Cloud is generally fast, querying immediately after a `create_index` call may result in errors. It's recommended to use `list_indices` to verify index creation before querying.
|
||||
|
||||
### Why is my query latency higher than expected?
|
||||
Multiple factors can impact query latency. To reduce query latency, consider the following:
|
||||
- Send pre-warm queries: send a few queries to warm up the cache before an actual user query.
|
||||
- Check network latency: LanceDB Cloud is hosted in AWS `us-east-1` region. It is recommended to run queries from an EC2 instance that is in the same region.
|
||||
- Create scalar indices: If you are filtering on metadata, it is recommended to create scalar indices on those columns. This will speedup searches with metadata filtering. See [here](../guides/scalar_index.md) for more details on creating a scalar index.
|
||||
@@ -7,7 +7,7 @@ Approximate Nearest Neighbor (ANN) search is a method for finding data points ne
|
||||
There are three main types of ANN search algorithms:
|
||||
|
||||
* **Tree-based search algorithms**: Use a tree structure to organize and store data points.
|
||||
* **Hash-based search algorithms**: Use a specialized geometric hash table to store and manage data points. These algorithms typically focus on theoretical guarantees, and don't usually perform as well as the other approaches in practice.
|
||||
* * **Hash-based search algorithms**: Use a specialized geometric hash table to store and manage data points. These algorithms typically focus on theoretical guarantees, and don't usually perform as well as the other approaches in practice.
|
||||
* **Graph-based search algorithms**: Use a graph structure to store data points, which can be a bit complex.
|
||||
|
||||
HNSW is a graph-based algorithm. All graph-based search algorithms rely on the idea of a k-nearest neighbor (or k-approximate nearest neighbor) graph, which we outline below.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -6,7 +6,6 @@ LanceDB registers the OpenAI embeddings function in the registry by default, as
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|
|
||||
| `name` | `str` | `"text-embedding-ada-002"` | The name of the model. |
|
||||
| `dim` | `int` | Model default | For OpenAI's newer text-embedding-3 model, we can specify a dimensionality that is smaller than the 1536 size. This feature supports it |
|
||||
| `use_azure` | bool | `False` | Set true to use Azure OpenAPI SDK |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
|
||||
117
docs/src/fts.md
117
docs/src/fts.md
@@ -10,20 +10,28 @@ LanceDB provides support for full-text search via Lance, allowing you to incorpo
|
||||
Consider that we have a LanceDB table named `my_table`, whose string column `text` we want to index and query via keyword search, the FTS index must be created before you can search via keywords.
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Python"
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_search.py:import-lancedb"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_search.py:import-lancedb-fts"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_search.py:basic_fts"
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_search.py:import-lancedb"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_search.py:import-lancedb-fts"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_search.py:basic_fts_async"
|
||||
```
|
||||
uri = "data/sample-lancedb"
|
||||
db = lancedb.connect(uri)
|
||||
|
||||
table = db.create_table(
|
||||
"my_table",
|
||||
data=[
|
||||
{"vector": [3.1, 4.1], "text": "Frodo was a happy puppy"},
|
||||
{"vector": [5.9, 26.5], "text": "There are several kittens playing"},
|
||||
],
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# passing `use_tantivy=False` to use lance FTS index
|
||||
# `use_tantivy=True` by default
|
||||
table.create_fts_index("text", use_tantivy=False)
|
||||
table.search("puppy").limit(10).select(["text"]).to_list()
|
||||
# [{'text': 'Frodo was a happy puppy', '_score': 0.6931471824645996}]
|
||||
# ...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
=== "TypeScript"
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -42,7 +50,7 @@ Consider that we have a LanceDB table named `my_table`, whose string column `tex
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
await tbl
|
||||
.search("puppy", "fts")
|
||||
.search("puppy", queryType="fts")
|
||||
.select(["text"])
|
||||
.limit(10)
|
||||
.toArray();
|
||||
@@ -85,32 +93,22 @@ By default the text is tokenized by splitting on punctuation and whitespaces, an
|
||||
Stemming is useful for improving search results by reducing words to their root form, e.g. "running" to "run". LanceDB supports stemming for multiple languages, you can specify the tokenizer name to enable stemming by the pattern `tokenizer_name="{language_code}_stem"`, e.g. `en_stem` for English.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, to enable stemming for English:
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_search.py:fts_config_stem"
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_search.py:fts_config_stem_async"
|
||||
```
|
||||
```python
|
||||
table.create_fts_index("text", use_tantivy=True, tokenizer_name="en_stem")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
the following [languages](https://docs.rs/tantivy/latest/tantivy/tokenizer/enum.Language.html) are currently supported.
|
||||
|
||||
The tokenizer is customizable, you can specify how the tokenizer splits the text, and how it filters out words, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, for language with accents, you can specify the tokenizer to use `ascii_folding` to remove accents, e.g. 'é' to 'e':
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_search.py:fts_config_folding"
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_search.py:fts_config_folding_async"
|
||||
```
|
||||
```python
|
||||
table.create_fts_index("text",
|
||||
use_tantivy=False,
|
||||
language="French",
|
||||
stem=True,
|
||||
ascii_folding=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Filtering
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -121,16 +119,9 @@ This can be invoked via the familiar `where` syntax.
|
||||
With pre-filtering:
|
||||
=== "Python"
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_search.py:fts_prefiltering"
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_search.py:fts_prefiltering_async"
|
||||
```
|
||||
```python
|
||||
table.search("puppy").limit(10).where("meta='foo'", prefilte=True).to_list()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
=== "TypeScript"
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -160,16 +151,9 @@ With pre-filtering:
|
||||
With post-filtering:
|
||||
=== "Python"
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_search.py:fts_postfiltering"
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_search.py:fts_postfiltering_async"
|
||||
```
|
||||
```python
|
||||
table.search("puppy").limit(10).where("meta='foo'", prefilte=False).to_list()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
=== "TypeScript"
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -207,16 +191,9 @@ or a **terms** search query like `old man sea`. For more details on the terms
|
||||
query syntax, see Tantivy's [query parser rules](https://docs.rs/tantivy/latest/tantivy/query/struct.QueryParser.html).
|
||||
|
||||
To search for a phrase, the index must be created with `with_position=True`:
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_search.py:fts_with_position"
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_search.py:fts_with_position_async"
|
||||
```
|
||||
```python
|
||||
table.create_fts_index("text", use_tantivy=False, with_position=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
This will allow you to search for phrases, but it will also significantly increase the index size and indexing time.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -228,16 +205,10 @@ This can make the query more efficient, especially when the table is large and t
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Python"
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_search.py:fts_incremental_index"
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_search.py:fts_incremental_index_async"
|
||||
```
|
||||
```python
|
||||
table.add([{"vector": [3.1, 4.1], "text": "Frodo was a happy puppy"}])
|
||||
table.optimize()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
=== "TypeScript"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -2,7 +2,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
LanceDB also provides support for full-text search via [Tantivy](https://github.com/quickwit-oss/tantivy), allowing you to incorporate keyword-based search (based on BM25) in your retrieval solutions.
|
||||
|
||||
The tantivy-based FTS is only available in Python synchronous APIs and does not support building indexes on object storage or incremental indexing. If you need these features, try native FTS [native FTS](fts.md).
|
||||
The tantivy-based FTS is only available in Python and does not support building indexes on object storage or incremental indexing. If you need these features, try native FTS [native FTS](fts.md).
|
||||
|
||||
## Installation
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,51 +1,38 @@
|
||||
# Building a Scalar Index
|
||||
# Building Scalar Index
|
||||
|
||||
Scalar indices organize data by scalar attributes (e.g. numbers, categorical values), enabling fast filtering of vector data. In vector databases, scalar indices accelerate the retrieval of scalar data associated with vectors, thus enhancing the query performance when searching for vectors that meet certain scalar criteria.
|
||||
|
||||
Similar to many SQL databases, LanceDB supports several types of scalar indices to accelerate search
|
||||
Similar to many SQL databases, LanceDB supports several types of Scalar indices to accelerate search
|
||||
over scalar columns.
|
||||
|
||||
- `BTREE`: The most common type is BTREE. The index stores a copy of the
|
||||
column in sorted order. This sorted copy allows a binary search to be used to
|
||||
satisfy queries.
|
||||
- `BITMAP`: this index stores a bitmap for each unique value in the column. It
|
||||
uses a series of bits to indicate whether a value is present in a row of a table
|
||||
- `LABEL_LIST`: a special index that can be used on `List<T>` columns to
|
||||
support queries with `array_contains_all` and `array_contains_any`
|
||||
using an underlying bitmap index.
|
||||
- `BTREE`: The most common type is BTREE. This index is inspired by the btree data structure
|
||||
although only the first few layers of the btree are cached in memory.
|
||||
It will perform well on columns with a large number of unique values and few rows per value.
|
||||
- `BITMAP`: this index stores a bitmap for each unique value in the column.
|
||||
This index is useful for columns with a finite number of unique values and many rows per value.
|
||||
For example, columns that represent "categories", "labels", or "tags"
|
||||
- `LABEL_LIST`: a special index that is used to index list columns whose values have a finite set of possibilities.
|
||||
For example, a column that contains lists of tags (e.g. `["tag1", "tag2", "tag3"]`) can be indexed with a `LABEL_LIST` index.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tips "How to choose the right scalar index type"
|
||||
|
||||
`BTREE`: This index is good for scalar columns with mostly distinct values and does best when the query is highly selective.
|
||||
|
||||
`BITMAP`: This index works best for low-cardinality numeric or string columns, where the number of unique values is small (i.e., less than a few thousands).
|
||||
|
||||
`LABEL_LIST`: This index should be used for columns containing list-type data.
|
||||
|
||||
| Data Type | Filter | Index Type |
|
||||
| --------------------------------------------------------------- | ----------------------------------------- | ------------ |
|
||||
| Numeric, String, Temporal | `<`, `=`, `>`, `in`, `between`, `is null` | `BTREE` |
|
||||
| Boolean, numbers or strings with fewer than 1,000 unique values | `<`, `=`, `>`, `in`, `between`, `is null` | `BITMAP` |
|
||||
| List of low cardinality of numbers or strings | `array_has_any`, `array_has_all` | `LABEL_LIST` |
|
||||
|
||||
### Create a scalar index
|
||||
=== "Python"
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
books = [
|
||||
{"book_id": 1, "publisher": "plenty of books", "tags": ["fantasy", "adventure"]},
|
||||
{"book_id": 2, "publisher": "book town", "tags": ["non-fiction"]},
|
||||
{"book_id": 3, "publisher": "oreilly", "tags": ["textbook"]}
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_index.py:import-lancedb"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_index.py:import-lancedb-btree-bitmap"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_index.py:basic_scalar_index"
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_index.py:import-lancedb"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_index.py:import-lancedb-btree-bitmap"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_index.py:basic_scalar_index_async"
|
||||
```
|
||||
db = lancedb.connect("./db")
|
||||
table = db.create_table("books", books)
|
||||
table.create_scalar_index("book_id") # BTree by default
|
||||
table.create_scalar_index("publisher", index_type="BITMAP")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Typescript"
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -59,22 +46,16 @@ over scalar columns.
|
||||
await tlb.create_index("publisher", { config: lancedb.Index.bitmap() })
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The following scan will be faster if the column `book_id` has a scalar index:
|
||||
For example, the following scan will be faster if the column `my_col` has a scalar index:
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Python"
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_index.py:import-lancedb"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_index.py:search_with_scalar_index"
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_index.py:import-lancedb"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_index.py:search_with_scalar_index_async"
|
||||
```
|
||||
table = db.open_table("books")
|
||||
my_df = table.search().where("book_id = 2").to_pandas()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Typescript"
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -95,18 +76,22 @@ Scalar indices can also speed up scans containing a vector search or full text s
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Python"
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_index.py:import-lancedb"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_index.py:vector_search_with_scalar_index"
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
data = [
|
||||
{"book_id": 1, "vector": [1, 2]},
|
||||
{"book_id": 2, "vector": [3, 4]},
|
||||
{"book_id": 3, "vector": [5, 6]}
|
||||
]
|
||||
table = db.create_table("book_with_embeddings", data)
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_index.py:import-lancedb"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_index.py:vector_search_with_scalar_index_async"
|
||||
```
|
||||
(
|
||||
table.search([1, 2])
|
||||
.where("book_id != 3", prefilter=True)
|
||||
.to_pandas()
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Typescript"
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -121,36 +106,3 @@ Scalar indices can also speed up scans containing a vector search or full text s
|
||||
.limit(10)
|
||||
.toArray();
|
||||
```
|
||||
### Update a scalar index
|
||||
Updating the table data (adding, deleting, or modifying records) requires that you also update the scalar index. This can be done by calling `optimize`, which will trigger an update to the existing scalar index.
|
||||
=== "Python"
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_index.py:update_scalar_index"
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_index.py:update_scalar_index_async"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
=== "TypeScript"
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
await tbl.add([{ vector: [7, 8], book_id: 4 }]);
|
||||
await tbl.optimize();
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Rust"
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
let more_data: Box<dyn RecordBatchReader + Send> = create_some_records()?;
|
||||
tbl.add(more_data).execute().await?;
|
||||
tbl.optimize(OptimizeAction::All).execute().await?;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note
|
||||
|
||||
New data added after creating the scalar index will still appear in search results if optimize is not used, but with increased latency due to a flat search on the unindexed portion. LanceDB Cloud automates the optimize process, minimizing the impact on search speed.
|
||||
@@ -12,52 +12,25 @@ LanceDB OSS supports object stores such as AWS S3 (and compatible stores), Azure
|
||||
=== "Python"
|
||||
|
||||
AWS S3:
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
db = lancedb.connect("s3://bucket/path")
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
async_db = await lancedb.connect_async("s3://bucket/path")
|
||||
```
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
db = lancedb.connect("s3://bucket/path")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Google Cloud Storage:
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
db = lancedb.connect("gs://bucket/path")
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
async_db = await lancedb.connect_async("gs://bucket/path")
|
||||
```
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
db = lancedb.connect("gs://bucket/path")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Azure Blob Storage:
|
||||
|
||||
<!-- skip-test -->
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
db = lancedb.connect("az://bucket/path")
|
||||
```
|
||||
<!-- skip-test -->
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
async_db = await lancedb.connect_async("az://bucket/path")
|
||||
```
|
||||
Note that for Azure, storage credentials must be configured. See [below](#azure-blob-storage) for more details.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
db = lancedb.connect("az://bucket/path")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
=== "TypeScript"
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -114,28 +87,22 @@ In most cases, when running in the respective cloud and permissions are set up c
|
||||
export TIMEOUT=60s
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note "`storage_options` availability"
|
||||
|
||||
The `storage_options` parameter is only available in Python *async* API and JavaScript API.
|
||||
It is not yet supported in the Python synchronous API.
|
||||
|
||||
If you only want this to apply to one particular connection, you can pass the `storage_options` argument when opening the connection:
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Python"
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
db = lancedb.connect(
|
||||
"s3://bucket/path",
|
||||
storage_options={"timeout": "60s"}
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
async_db = await lancedb.connect_async(
|
||||
"s3://bucket/path",
|
||||
storage_options={"timeout": "60s"}
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
db = await lancedb.connect_async(
|
||||
"s3://bucket/path",
|
||||
storage_options={"timeout": "60s"}
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
=== "TypeScript"
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -163,29 +130,15 @@ Getting even more specific, you can set the `timeout` for only a particular tabl
|
||||
=== "Python"
|
||||
|
||||
<!-- skip-test -->
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
db = lancedb.connect("s3://bucket/path")
|
||||
table = db.create_table(
|
||||
"table",
|
||||
[{"a": 1, "b": 2}],
|
||||
storage_options={"timeout": "60s"}
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
<!-- skip-test -->
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
async_db = await lancedb.connect_async("s3://bucket/path")
|
||||
async_table = await async_db.create_table(
|
||||
"table",
|
||||
[{"a": 1, "b": 2}],
|
||||
storage_options={"timeout": "60s"}
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
db = await lancedb.connect_async("s3://bucket/path")
|
||||
table = await db.create_table(
|
||||
"table",
|
||||
[{"a": 1, "b": 2}],
|
||||
storage_options={"timeout": "60s"}
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
=== "TypeScript"
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -243,32 +196,17 @@ These can be set as environment variables or passed in the `storage_options` par
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Python"
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
db = lancedb.connect(
|
||||
"s3://bucket/path",
|
||||
storage_options={
|
||||
"aws_access_key_id": "my-access-key",
|
||||
"aws_secret_access_key": "my-secret-key",
|
||||
"aws_session_token": "my-session-token",
|
||||
}
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
async_db = await lancedb.connect_async(
|
||||
"s3://bucket/path",
|
||||
storage_options={
|
||||
"aws_access_key_id": "my-access-key",
|
||||
"aws_secret_access_key": "my-secret-key",
|
||||
"aws_session_token": "my-session-token",
|
||||
}
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
db = await lancedb.connect_async(
|
||||
"s3://bucket/path",
|
||||
storage_options={
|
||||
"aws_access_key_id": "my-access-key",
|
||||
"aws_secret_access_key": "my-secret-key",
|
||||
"aws_session_token": "my-session-token",
|
||||
}
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
=== "TypeScript"
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -412,22 +350,12 @@ name of the table to use.
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Python"
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
db = lancedb.connect(
|
||||
"s3+ddb://bucket/path?ddbTableName=my-dynamodb-table",
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
async_db = await lancedb.connect_async(
|
||||
"s3+ddb://bucket/path?ddbTableName=my-dynamodb-table",
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
db = await lancedb.connect_async(
|
||||
"s3+ddb://bucket/path?ddbTableName=my-dynamodb-table",
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
=== "JavaScript"
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -515,30 +443,16 @@ LanceDB can also connect to S3-compatible stores, such as MinIO. To do so, you m
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Python"
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
db = lancedb.connect(
|
||||
"s3://bucket/path",
|
||||
storage_options={
|
||||
"region": "us-east-1",
|
||||
"endpoint": "http://minio:9000",
|
||||
}
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
async_db = await lancedb.connect_async(
|
||||
"s3://bucket/path",
|
||||
storage_options={
|
||||
"region": "us-east-1",
|
||||
"endpoint": "http://minio:9000",
|
||||
}
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
db = await lancedb.connect_async(
|
||||
"s3://bucket/path",
|
||||
storage_options={
|
||||
"region": "us-east-1",
|
||||
"endpoint": "http://minio:9000",
|
||||
}
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
=== "TypeScript"
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -590,30 +504,16 @@ To configure LanceDB to use an S3 Express endpoint, you must set the storage opt
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Python"
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
db = lancedb.connect(
|
||||
"s3://my-bucket--use1-az4--x-s3/path",
|
||||
storage_options={
|
||||
"region": "us-east-1",
|
||||
"s3_express": "true",
|
||||
}
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
async_db = await lancedb.connect_async(
|
||||
"s3://my-bucket--use1-az4--x-s3/path",
|
||||
storage_options={
|
||||
"region": "us-east-1",
|
||||
"s3_express": "true",
|
||||
}
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
db = await lancedb.connect_async(
|
||||
"s3://my-bucket--use1-az4--x-s3/path",
|
||||
storage_options={
|
||||
"region": "us-east-1",
|
||||
"s3_express": "true",
|
||||
}
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
=== "TypeScript"
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -654,29 +554,15 @@ GCS credentials are configured by setting the `GOOGLE_SERVICE_ACCOUNT` environme
|
||||
=== "Python"
|
||||
|
||||
<!-- skip-test -->
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
db = lancedb.connect(
|
||||
"gs://my-bucket/my-database",
|
||||
storage_options={
|
||||
"service_account": "path/to/service-account.json",
|
||||
}
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
<!-- skip-test -->
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
async_db = await lancedb.connect_async(
|
||||
"gs://my-bucket/my-database",
|
||||
storage_options={
|
||||
"service_account": "path/to/service-account.json",
|
||||
}
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
db = await lancedb.connect_async(
|
||||
"gs://my-bucket/my-database",
|
||||
storage_options={
|
||||
"service_account": "path/to/service-account.json",
|
||||
}
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
=== "TypeScript"
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -728,31 +614,16 @@ Azure Blob Storage credentials can be configured by setting the `AZURE_STORAGE_A
|
||||
=== "Python"
|
||||
|
||||
<!-- skip-test -->
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
db = lancedb.connect(
|
||||
"az://my-container/my-database",
|
||||
storage_options={
|
||||
account_name: "some-account",
|
||||
account_key: "some-key",
|
||||
}
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
<!-- skip-test -->
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
async_db = await lancedb.connect_async(
|
||||
"az://my-container/my-database",
|
||||
storage_options={
|
||||
account_name: "some-account",
|
||||
account_key: "some-key",
|
||||
}
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
db = await lancedb.connect_async(
|
||||
"az://my-container/my-database",
|
||||
storage_options={
|
||||
account_name: "some-account",
|
||||
account_key: "some-key",
|
||||
}
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
=== "TypeScript"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -12,18 +12,10 @@ Initialize a LanceDB connection and create a table
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Python"
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:import-lancedb"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:connect"
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:import-lancedb"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:connect_async"
|
||||
```
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
db = lancedb.connect("./.lancedb")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
LanceDB allows ingesting data from various sources - `dict`, `list[dict]`, `pd.DataFrame`, `pa.Table` or a `Iterator[pa.RecordBatch]`. Let's take a look at some of the these.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -55,16 +47,18 @@ Initialize a LanceDB connection and create a table
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Python"
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:create_table"
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
db = lancedb.connect("./.lancedb")
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:create_table_async"
|
||||
```
|
||||
data = [{"vector": [1.1, 1.2], "lat": 45.5, "long": -122.7},
|
||||
{"vector": [0.2, 1.8], "lat": 40.1, "long": -74.1}]
|
||||
|
||||
db.create_table("my_table", data)
|
||||
|
||||
db["my_table"].head()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! info "Note"
|
||||
If the table already exists, LanceDB will raise an error by default.
|
||||
@@ -73,30 +67,16 @@ Initialize a LanceDB connection and create a table
|
||||
and the table exists, then it simply opens the existing table. The data you
|
||||
passed in will NOT be appended to the table in that case.
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:create_table_exist_ok"
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:create_table_async_exist_ok"
|
||||
```
|
||||
```python
|
||||
db.create_table("name", data, exist_ok=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Sometimes you want to make sure that you start fresh. If you want to
|
||||
overwrite the table, you can pass in mode="overwrite" to the createTable function.
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:create_table_overwrite"
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:create_table_async_overwrite"
|
||||
```
|
||||
```python
|
||||
db.create_table("name", data, mode="overwrite")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Typescript[^1]"
|
||||
You can create a LanceDB table in JavaScript using an array of records as follows.
|
||||
@@ -166,37 +146,34 @@ Initialize a LanceDB connection and create a table
|
||||
|
||||
### From a Pandas DataFrame
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import pandas as pd
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
data = pd.DataFrame({
|
||||
"vector": [[1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 1.4], [0.2, 1.8, 0.4, 3.6]],
|
||||
"lat": [45.5, 40.1],
|
||||
"long": [-122.7, -74.1]
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:import-pandas"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:create_table_from_pandas"
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
db.create_table("my_table", data)
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:import-pandas"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:create_table_async_from_pandas"
|
||||
```
|
||||
db["my_table"].head()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! info "Note"
|
||||
Data is converted to Arrow before being written to disk. For maximum control over how data is saved, either provide the PyArrow schema to convert to or else provide a PyArrow Table directly.
|
||||
|
||||
The **`vector`** column needs to be a [Vector](../python/pydantic.md#vector-field) (defined as [pyarrow.FixedSizeList](https://arrow.apache.org/docs/python/generated/pyarrow.list_.html)) type.
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
```python
|
||||
custom_schema = pa.schema([
|
||||
pa.field("vector", pa.list_(pa.float32(), 4)),
|
||||
pa.field("lat", pa.float32()),
|
||||
pa.field("long", pa.float32())
|
||||
])
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:import-pyarrow"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:create_table_custom_schema"
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:import-pyarrow"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:create_table_async_custom_schema"
|
||||
```
|
||||
table = db.create_table("my_table", data, schema=custom_schema)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### From a Polars DataFrame
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -205,38 +182,45 @@ written in Rust. Just like in Pandas, the Polars integration is enabled by PyArr
|
||||
under the hood. A deeper integration between LanceDB Tables and Polars DataFrames
|
||||
is on the way.
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import polars as pl
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:import-polars"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:create_table_from_polars"
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:import-polars"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:create_table_async_from_polars"
|
||||
```
|
||||
data = pl.DataFrame({
|
||||
"vector": [[3.1, 4.1], [5.9, 26.5]],
|
||||
"item": ["foo", "bar"],
|
||||
"price": [10.0, 20.0]
|
||||
})
|
||||
table = db.create_table("pl_table", data=data)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### From an Arrow Table
|
||||
You can also create LanceDB tables directly from Arrow tables.
|
||||
LanceDB supports float16 data type!
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Python"
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:import-pyarrow"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:import-numpy"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:create_table_from_arrow_table"
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import pyarrows as pa
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:import-polars"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:import-numpy"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:create_table_async_from_arrow_table"
|
||||
```
|
||||
dim = 16
|
||||
total = 2
|
||||
schema = pa.schema(
|
||||
[
|
||||
pa.field("vector", pa.list_(pa.float16(), dim)),
|
||||
pa.field("text", pa.string())
|
||||
]
|
||||
)
|
||||
data = pa.Table.from_arrays(
|
||||
[
|
||||
pa.array([np.random.randn(dim).astype(np.float16) for _ in range(total)],
|
||||
pa.list_(pa.float16(), dim)),
|
||||
pa.array(["foo", "bar"])
|
||||
],
|
||||
["vector", "text"],
|
||||
)
|
||||
tbl = db.create_table("f16_tbl", data, schema=schema)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Typescript[^1]"
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -266,22 +250,25 @@ can be configured with the vector dimensions. It is also important to note that
|
||||
LanceDB only understands subclasses of `lancedb.pydantic.LanceModel`
|
||||
(which itself derives from `pydantic.BaseModel`).
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from lancedb.pydantic import Vector, LanceModel
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:import-lancedb-pydantic"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:import-pyarrow"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:class-Content"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:create_table_from_pydantic"
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
class Content(LanceModel):
|
||||
movie_id: int
|
||||
vector: Vector(128)
|
||||
genres: str
|
||||
title: str
|
||||
imdb_id: int
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:import-lancedb-pydantic"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:import-pyarrow"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:class-Content"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:create_table_async_from_pydantic"
|
||||
```
|
||||
@property
|
||||
def imdb_url(self) -> str:
|
||||
return f"https://www.imdb.com/title/tt{self.imdb_id}"
|
||||
|
||||
import pyarrow as pa
|
||||
db = lancedb.connect("~/.lancedb")
|
||||
table_name = "movielens_small"
|
||||
table = db.create_table(table_name, schema=Content)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Nested schemas
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -290,24 +277,22 @@ For example, you may want to store the document string
|
||||
and the document source name as a nested Document object:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:import-pydantic-basemodel"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:class-Document"
|
||||
class Document(BaseModel):
|
||||
content: str
|
||||
source: str
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This can be used as the type of a LanceDB table column:
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
```python
|
||||
class NestedSchema(LanceModel):
|
||||
id: str
|
||||
vector: Vector(1536)
|
||||
document: Document
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:class-NestedSchema"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:create_table_nested_schema"
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
tbl = db.create_table("nested_table", schema=NestedSchema, mode="overwrite")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:class-NestedSchema"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:create_table_async_nested_schema"
|
||||
```
|
||||
This creates a struct column called "document" that has two subfields
|
||||
called "content" and "source":
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -371,20 +356,29 @@ LanceDB additionally supports PyArrow's `RecordBatch` Iterators or other generat
|
||||
|
||||
Here's an example using using `RecordBatch` iterator for creating tables.
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import pyarrow as pa
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:import-pyarrow"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:make_batches"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:create_table_from_batch"
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
def make_batches():
|
||||
for i in range(5):
|
||||
yield pa.RecordBatch.from_arrays(
|
||||
[
|
||||
pa.array([[3.1, 4.1, 5.1, 6.1], [5.9, 26.5, 4.7, 32.8]],
|
||||
pa.list_(pa.float32(), 4)),
|
||||
pa.array(["foo", "bar"]),
|
||||
pa.array([10.0, 20.0]),
|
||||
],
|
||||
["vector", "item", "price"],
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:import-pyarrow"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:make_batches"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:create_table_async_from_batch"
|
||||
```
|
||||
schema = pa.schema([
|
||||
pa.field("vector", pa.list_(pa.float32(), 4)),
|
||||
pa.field("item", pa.utf8()),
|
||||
pa.field("price", pa.float32()),
|
||||
])
|
||||
|
||||
db.create_table("batched_tale", make_batches(), schema=schema)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can also use iterators of other types like Pandas DataFrame or Pylists directly in the above example.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -393,29 +387,15 @@ You can also use iterators of other types like Pandas DataFrame or Pylists direc
|
||||
=== "Python"
|
||||
If you forget the name of your table, you can always get a listing of all table names.
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:list_tables"
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:list_tables_async"
|
||||
```
|
||||
```python
|
||||
print(db.table_names())
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then, you can open any existing tables.
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:open_table"
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:open_table_async"
|
||||
```
|
||||
```python
|
||||
tbl = db.open_table("my_table")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Typescript[^1]"
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -438,41 +418,35 @@ You can create an empty table for scenarios where you want to add data to the ta
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
An empty table can be initialized via a PyArrow schema.
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:import-lancedb"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:import-pyarrow"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:create_empty_table"
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
import pyarrow as pa
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:import-lancedb"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:import-pyarrow"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:create_empty_table_async"
|
||||
```
|
||||
schema = pa.schema(
|
||||
[
|
||||
pa.field("vector", pa.list_(pa.float32(), 2)),
|
||||
pa.field("item", pa.string()),
|
||||
pa.field("price", pa.float32()),
|
||||
])
|
||||
tbl = db.create_table("empty_table_add", schema=schema)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Alternatively, you can also use Pydantic to specify the schema for the empty table. Note that we do not
|
||||
directly import `pydantic` but instead use `lancedb.pydantic` which is a subclass of `pydantic.BaseModel`
|
||||
that has been extended to support LanceDB specific types like `Vector`.
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
from lancedb.pydantic import LanceModel, vector
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:import-lancedb"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:import-lancedb-pydantic"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:class-Item"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:create_empty_table_pydantic"
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
class Item(LanceModel):
|
||||
vector: Vector(2)
|
||||
item: str
|
||||
price: float
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:import-lancedb"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:import-lancedb-pydantic"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:class-Item"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:create_empty_table_async_pydantic"
|
||||
```
|
||||
tbl = db.create_table("empty_table_add", schema=Item.to_arrow_schema())
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Once the empty table has been created, you can add data to it via the various methods listed in the [Adding to a table](#adding-to-a-table) section.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -499,96 +473,86 @@ After a table has been created, you can always add more data to it using the `ad
|
||||
|
||||
### Add a Pandas DataFrame
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:add_table_from_pandas"
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:add_table_async_from_pandas"
|
||||
```
|
||||
```python
|
||||
df = pd.DataFrame({
|
||||
"vector": [[1.3, 1.4], [9.5, 56.2]], "item": ["banana", "apple"], "price": [5.0, 7.0]
|
||||
})
|
||||
tbl.add(df)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Add a Polars DataFrame
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:add_table_from_polars"
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:add_table_async_from_polars"
|
||||
```
|
||||
```python
|
||||
df = pl.DataFrame({
|
||||
"vector": [[1.3, 1.4], [9.5, 56.2]], "item": ["banana", "apple"], "price": [5.0, 7.0]
|
||||
})
|
||||
tbl.add(df)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Add an Iterator
|
||||
|
||||
You can also add a large dataset batch in one go using Iterator of any supported data types.
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:make_batches_for_add"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:add_table_from_batch"
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:make_batches_for_add"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:add_table_async_from_batch"
|
||||
```
|
||||
```python
|
||||
def make_batches():
|
||||
for i in range(5):
|
||||
yield [
|
||||
{"vector": [3.1, 4.1], "item": "peach", "price": 6.0},
|
||||
{"vector": [5.9, 26.5], "item": "pear", "price": 5.0}
|
||||
]
|
||||
tbl.add(make_batches())
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Add a PyArrow table
|
||||
|
||||
If you have data coming in as a PyArrow table, you can add it directly to the LanceDB table.
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
```python
|
||||
pa_table = pa.Table.from_arrays(
|
||||
[
|
||||
pa.array([[9.1, 6.7], [9.9, 31.2]],
|
||||
pa.list_(pa.float32(), 2)),
|
||||
pa.array(["mango", "orange"]),
|
||||
pa.array([7.0, 4.0]),
|
||||
],
|
||||
["vector", "item", "price"],
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:add_table_from_pyarrow"
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:add_table_async_from_pyarrow"
|
||||
```
|
||||
tbl.add(pa_table)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Add a Pydantic Model
|
||||
|
||||
Assuming that a table has been created with the correct schema as shown [above](#creating-empty-table), you can add data items that are valid Pydantic models to the table.
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
```python
|
||||
pydantic_model_items = [
|
||||
Item(vector=[8.1, 4.7], item="pineapple", price=10.0),
|
||||
Item(vector=[6.9, 9.3], item="avocado", price=9.0)
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:add_table_from_pydantic"
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:add_table_async_from_pydantic"
|
||||
```
|
||||
tbl.add(pydantic_model_items)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
??? "Ingesting Pydantic models with LanceDB embedding API"
|
||||
When using LanceDB's embedding API, you can add Pydantic models directly to the table. LanceDB will automatically convert the `vector` field to a vector before adding it to the table. You need to specify the default value of `vector` field as None to allow LanceDB to automatically vectorize the data.
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
from lancedb.pydantic import LanceModel, Vector
|
||||
from lancedb.embeddings import get_registry
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:import-lancedb"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:import-lancedb-pydantic"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:import-embeddings"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:create_table_with_embedding"
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
db = lancedb.connect("~/tmp")
|
||||
embed_fcn = get_registry().get("huggingface").create(name="BAAI/bge-small-en-v1.5")
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:import-lancedb"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:import-lancedb-pydantic"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:import-embeddings"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:create_table_async_with_embedding"
|
||||
```
|
||||
class Schema(LanceModel):
|
||||
text: str = embed_fcn.SourceField()
|
||||
vector: Vector(embed_fcn.ndims()) = embed_fcn.VectorField(default=None)
|
||||
|
||||
tbl = db.create_table("my_table", schema=Schema, mode="overwrite")
|
||||
models = [Schema(text="hello"), Schema(text="world")]
|
||||
tbl.add(models)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Typescript[^1]"
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -607,41 +571,44 @@ Use the `delete()` method on tables to delete rows from a table. To choose which
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Python"
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:delete_row"
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:delete_row_async"
|
||||
```
|
||||
```python
|
||||
tbl.delete('item = "fizz"')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Deleting row with specific column value
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:delete_specific_row"
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
data = [{"x": 1, "vector": [1, 2]},
|
||||
{"x": 2, "vector": [3, 4]},
|
||||
{"x": 3, "vector": [5, 6]}]
|
||||
db = lancedb.connect("./.lancedb")
|
||||
table = db.create_table("my_table", data)
|
||||
table.to_pandas()
|
||||
# x vector
|
||||
# 0 1 [1.0, 2.0]
|
||||
# 1 2 [3.0, 4.0]
|
||||
# 2 3 [5.0, 6.0]
|
||||
|
||||
table.delete("x = 2")
|
||||
table.to_pandas()
|
||||
# x vector
|
||||
# 0 1 [1.0, 2.0]
|
||||
# 1 3 [5.0, 6.0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:delete_specific_row_async"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Delete from a list of values
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:delete_list_values"
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
```python
|
||||
to_remove = [1, 5]
|
||||
to_remove = ", ".join(str(v) for v in to_remove)
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:delete_list_values_async"
|
||||
```
|
||||
table.delete(f"x IN ({to_remove})")
|
||||
table.to_pandas()
|
||||
# x vector
|
||||
# 0 3 [5.0, 6.0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Typescript[^1]"
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -692,20 +659,27 @@ This can be used to update zero to all rows depending on how many rows match the
|
||||
=== "Python"
|
||||
|
||||
API Reference: [lancedb.table.Table.update][]
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:import-lancedb"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:import-pandas"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:update_table"
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
import pandas as pd
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:import-lancedb"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:import-pandas"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:update_table_async"
|
||||
```
|
||||
# Create a lancedb connection
|
||||
db = lancedb.connect("./.lancedb")
|
||||
|
||||
# Create a table from a pandas DataFrame
|
||||
data = pd.DataFrame({"x": [1, 2, 3], "vector": [[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]]})
|
||||
table = db.create_table("my_table", data)
|
||||
|
||||
# Update the table where x = 2
|
||||
table.update(where="x = 2", values={"vector": [10, 10]})
|
||||
|
||||
# Get the updated table as a pandas DataFrame
|
||||
df = table.to_pandas()
|
||||
|
||||
# Print the DataFrame
|
||||
print(df)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Output
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
@@ -760,16 +734,13 @@ This can be used to update zero to all rows depending on how many rows match the
|
||||
The `values` parameter is used to provide the new values for the columns as literal values. You can also use the `values_sql` / `valuesSql` parameter to provide SQL expressions for the new values. For example, you can use `values_sql="x + 1"` to increment the value of the `x` column by 1.
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Python"
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:update_table_sql"
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# Update the table where x = 2
|
||||
table.update(valuesSql={"x": "x + 1"})
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:update_table_sql_async"
|
||||
```
|
||||
print(table.to_pandas())
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Output
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
@@ -800,16 +771,11 @@ This can be used to update zero to all rows depending on how many rows match the
|
||||
Use the `drop_table()` method on the database to remove a table.
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Python"
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_basic.py:drop_table"
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_basic.py:drop_table_async"
|
||||
```
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_basic.py:drop_table"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_basic.py:drop_table_async"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This permanently removes the table and is not recoverable, unlike deleting rows.
|
||||
By default, if the table does not exist an exception is raised. To suppress this,
|
||||
@@ -824,123 +790,6 @@ Use the `drop_table()` method on the database to remove a table.
|
||||
This permanently removes the table and is not recoverable, unlike deleting rows.
|
||||
If the table does not exist an exception is raised.
|
||||
|
||||
## Changing schemas
|
||||
|
||||
While tables must have a schema specified when they are created, you can
|
||||
change the schema over time. There's three methods to alter the schema of
|
||||
a table:
|
||||
|
||||
* `add_columns`: Add new columns to the table
|
||||
* `alter_columns`: Alter the name, nullability, or data type of a column
|
||||
* `drop_columns`: Drop columns from the table
|
||||
|
||||
### Adding new columns
|
||||
|
||||
You can add new columns to the table with the `add_columns` method. New columns
|
||||
are filled with values based on a SQL expression. For example, you can add a new
|
||||
column `y` to the table, fill it with the value of `x * 2` and set the expected
|
||||
data type for it.
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Python"
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_basic.py:add_columns"
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_basic.py:add_columns_async"
|
||||
```
|
||||
**API Reference:** [lancedb.table.Table.add_columns][]
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Typescript"
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
--8<-- "nodejs/examples/basic.test.ts:add_columns"
|
||||
```
|
||||
**API Reference:** [lancedb.Table.addColumns](../js/classes/Table.md/#addcolumns)
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to fill it with null, you can use `cast(NULL as <data_type>)` as
|
||||
the SQL expression to fill the column with nulls, while controlling the data
|
||||
type of the column. Available data types are base on the
|
||||
[DataFusion data types](https://datafusion.apache.org/user-guide/sql/data_types.html).
|
||||
You can use any of the SQL types, such as `BIGINT`:
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
cast(NULL as BIGINT)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Using Arrow data types and the `arrow_typeof` function is not yet supported.
|
||||
|
||||
<!-- TODO: we could provide a better formula for filling with nulls:
|
||||
https://github.com/lancedb/lance/issues/3175
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
### Altering existing columns
|
||||
|
||||
You can alter the name, nullability, or data type of a column with the `alter_columns`
|
||||
method.
|
||||
|
||||
Changing the name or nullability of a column just updates the metadata. Because
|
||||
of this, it's a fast operation. Changing the data type of a column requires
|
||||
rewriting the column, which can be a heavy operation.
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Python"
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:import-pyarrow"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_basic.py:alter_columns"
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:import-pyarrow"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_basic.py:alter_columns_async"
|
||||
```
|
||||
**API Reference:** [lancedb.table.Table.alter_columns][]
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Typescript"
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
--8<-- "nodejs/examples/basic.test.ts:alter_columns"
|
||||
```
|
||||
**API Reference:** [lancedb.Table.alterColumns](../js/classes/Table.md/#altercolumns)
|
||||
|
||||
### Dropping columns
|
||||
|
||||
You can drop columns from the table with the `drop_columns` method. This will
|
||||
will remove the column from the schema.
|
||||
|
||||
<!-- TODO: Provide guidance on how to reduce disk usage once optimize helps here
|
||||
waiting on: https://github.com/lancedb/lance/issues/3177
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Python"
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_basic.py:drop_columns"
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_basic.py:drop_columns_async"
|
||||
```
|
||||
**API Reference:** [lancedb.table.Table.drop_columns][]
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Typescript"
|
||||
|
||||
```typescript
|
||||
--8<-- "nodejs/examples/basic.test.ts:drop_columns"
|
||||
```
|
||||
**API Reference:** [lancedb.Table.dropColumns](../js/classes/Table.md/#altercolumns)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Handling bad vectors
|
||||
|
||||
In LanceDB Python, you can use the `on_bad_vectors` parameter to choose how
|
||||
@@ -981,46 +830,31 @@ There are three possible settings for `read_consistency_interval`:
|
||||
|
||||
To set strong consistency, use `timedelta(0)`:
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:import-datetime"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:table_strong_consistency"
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:import-datetime"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:table_async_strong_consistency"
|
||||
```
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from datetime import timedelta
|
||||
db = lancedb.connect("./.lancedb",. read_consistency_interval=timedelta(0))
|
||||
table = db.open_table("my_table")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For eventual consistency, use a custom `timedelta`:
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:import-datetime"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:table_eventual_consistency"
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:import-datetime"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:table_async_eventual_consistency"
|
||||
```
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from datetime import timedelta
|
||||
db = lancedb.connect("./.lancedb", read_consistency_interval=timedelta(seconds=5))
|
||||
table = db.open_table("my_table")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
By default, a `Table` will never check for updates from other writers. To manually check for updates you can use `checkout_latest`:
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
```python
|
||||
db = lancedb.connect("./.lancedb")
|
||||
table = db.open_table("my_table")
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:table_checkout_latest"
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
# (Other writes happen to my_table from another process)
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_guide_tables.py:table_async_checkout_latest"
|
||||
```
|
||||
# Check for updates
|
||||
table.checkout_latest()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Typescript[^1]"
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1028,14 +862,14 @@ There are three possible settings for `read_consistency_interval`:
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
const db = await lancedb.connect({ uri: "./.lancedb", readConsistencyInterval: 0 });
|
||||
const tbl = await db.openTable("my_table");
|
||||
const table = await db.openTable("my_table");
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For eventual consistency, specify the update interval as seconds:
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
const db = await lancedb.connect({ uri: "./.lancedb", readConsistencyInterval: 5 });
|
||||
const tbl = await db.openTable("my_table");
|
||||
const table = await db.openTable("my_table");
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<!-- Node doesn't yet support the version time travel: https://github.com/lancedb/lancedb/issues/1007
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,8 +1,8 @@
|
||||
## Improving retriever performance
|
||||
|
||||
Try it yourself: <a href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/lancedb/lancedb/blob/main/docs/src/notebooks/lancedb_reranking.ipynb"><img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" alt="Open In Colab"></a><br/>
|
||||
Try it yourself - <a href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/lancedb/lancedb/blob/main/docs/src/notebooks/lancedb_reranking.ipynb"><img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" alt="Open In Colab"></a><br/>
|
||||
|
||||
VectorDBs are used as retrievers in recommender or chatbot-based systems for retrieving relevant data based on user queries. For example, retrievers are a critical component of Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) acrhitectures. In this section, we will discuss how to improve the performance of retrievers.
|
||||
VectorDBs are used as retreivers in recommender or chatbot-based systems for retrieving relevant data based on user queries. For example, retriever is a critical component of Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) acrhitectures. In this section, we will discuss how to improve the performance of retrievers.
|
||||
|
||||
There are serveral ways to improve the performance of retrievers. Some of the common techniques are:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -19,7 +19,7 @@ Using different embedding models is something that's very specific to the use ca
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## The dataset
|
||||
We'll be using a QA dataset generated using a LLama2 review paper. The dataset contains 221 query, context and answer triplets. The queries and answers are generated using GPT-4 based on a given query. Full script used to generate the dataset can be found on this [repo](https://github.com/lancedb/ragged). It can be downloaded from [here](https://github.com/AyushExel/assets/blob/main/data_qa.csv).
|
||||
We'll be using a QA dataset generated using a LLama2 review paper. The dataset contains 221 query, context and answer triplets. The queries and answers are generated using GPT-4 based on a given query. Full script used to generate the dataset can be found on this [repo](https://github.com/lancedb/ragged). It can be downloaded from [here](https://github.com/AyushExel/assets/blob/main/data_qa.csv)
|
||||
|
||||
### Using different query types
|
||||
Let's setup the embeddings and the dataset first. We'll use the LanceDB's `huggingface` embeddings integration for this guide.
|
||||
@@ -45,14 +45,14 @@ table.add(df[["context"]].to_dict(orient="records"))
|
||||
queries = df["query"].tolist()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now that we have the dataset and embeddings table set up, here's how you can run different query types on the dataset:
|
||||
Now that we have the dataset and embeddings table set up, here's how you can run different query types on the dataset.
|
||||
|
||||
* <b> Vector Search: </b>
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
table.search(quries[0], query_type="vector").limit(5).to_pandas()
|
||||
```
|
||||
By default, LanceDB uses vector search query type for searching and it automatically converts the input query to a vector before searching when using embedding API. So, the following statement is equivalent to the above statement:
|
||||
By default, LanceDB uses vector search query type for searching and it automatically converts the input query to a vector before searching when using embedding API. So, the following statement is equivalent to the above statement.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
table.search(quries[0]).limit(5).to_pandas()
|
||||
@@ -77,7 +77,7 @@ Now that we have the dataset and embeddings table set up, here's how you can run
|
||||
|
||||
* <b> Hybrid Search: </b>
|
||||
|
||||
Hybrid search is a combination of vector and full-text search. Here's how you can run a hybrid search query on the dataset:
|
||||
Hybrid search is a combination of vector and full-text search. Here's how you can run a hybrid search query on the dataset.
|
||||
```python
|
||||
table.search(quries[0], query_type="hybrid").limit(5).to_pandas()
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -87,7 +87,7 @@ Now that we have the dataset and embeddings table set up, here's how you can run
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note "Note"
|
||||
By default, it uses `LinearCombinationReranker` that combines the scores from vector and full-text search using a weighted linear combination. It is the simplest reranker implementation available in LanceDB. You can also use other rerankers like `CrossEncoderReranker` or `CohereReranker` for reranking the results.
|
||||
Learn more about rerankers [here](https://lancedb.github.io/lancedb/reranking/).
|
||||
Learn more about rerankers [here](https://lancedb.github.io/lancedb/reranking/)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
|
||||
Continuing from the previous section, we can now rerank the results using more complex rerankers.
|
||||
|
||||
Try it yourself: <a href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/lancedb/lancedb/blob/main/docs/src/notebooks/lancedb_reranking.ipynb"><img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" alt="Open In Colab"></a><br/>
|
||||
Try it yourself - <a href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/lancedb/lancedb/blob/main/docs/src/notebooks/lancedb_reranking.ipynb"><img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" alt="Open In Colab"></a><br/>
|
||||
|
||||
## Reranking search results
|
||||
You can rerank any search results using a reranker. The syntax for reranking is as follows:
|
||||
@@ -62,6 +62,9 @@ Let us take a look at the same datasets from the previous sections, using the sa
|
||||
| Reranked fts | 0.672 |
|
||||
| Hybrid | 0.759 |
|
||||
|
||||
### SQuAD Dataset
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Uber10K sec filing Dataset
|
||||
|
||||
| Query Type | Hit-rate@5 |
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
||||
## Finetuning the Embedding Model
|
||||
Try it yourself: <a href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/lancedb/lancedb/blob/main/docs/src/notebooks/embedding_tuner.ipynb"><img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" alt="Open In Colab"></a><br/>
|
||||
Try it yourself - <a href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/lancedb/lancedb/blob/main/docs/src/notebooks/embedding_tuner.ipynb"><img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" alt="Open In Colab"></a><br/>
|
||||
|
||||
Another way to improve retriever performance is to fine-tune the embedding model itself. Fine-tuning the embedding model can help in learning better representations for the documents and queries in the dataset. This can be particularly useful when the dataset is very different from the pre-trained data used to train the embedding model.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -16,7 +16,7 @@ validation_df.to_csv("data_val.csv", index=False)
|
||||
You can use any tuning API to fine-tune embedding models. In this example, we'll utilise Llama-index as it also comes with utilities for synthetic data generation and training the model.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
We parse the dataset as llama-index text nodes and generate synthetic QA pairs from each node:
|
||||
Then parse the dataset as llama-index text nodes and generate synthetic QA pairs from each node.
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from llama_index.core.node_parser import SentenceSplitter
|
||||
from llama_index.readers.file import PagedCSVReader
|
||||
@@ -43,7 +43,7 @@ val_dataset = generate_qa_embedding_pairs(
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now we'll use `SentenceTransformersFinetuneEngine` engine to fine-tune the model. You can also use `sentence-transformers` or `transformers` library to fine-tune the model:
|
||||
Now we'll use `SentenceTransformersFinetuneEngine` engine to fine-tune the model. You can also use `sentence-transformers` or `transformers` library to fine-tune the model.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from llama_index.finetuning import SentenceTransformersFinetuneEngine
|
||||
@@ -57,7 +57,7 @@ finetune_engine = SentenceTransformersFinetuneEngine(
|
||||
finetune_engine.finetune()
|
||||
embed_model = finetune_engine.get_finetuned_model()
|
||||
```
|
||||
This saves the fine tuned embedding model in `tuned_model` folder.
|
||||
This saves the fine tuned embedding model in `tuned_model` folder. This al
|
||||
|
||||
# Evaluation results
|
||||
In order to eval the retriever, you can either use this model to ingest the data into LanceDB directly or llama-index's LanceDB integration to create a `VectorStoreIndex` and use it as a retriever.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -3,22 +3,22 @@
|
||||
Hybrid Search is a broad (often misused) term. It can mean anything from combining multiple methods for searching, to applying ranking methods to better sort the results. In this blog, we use the definition of "hybrid search" to mean using a combination of keyword-based and vector search.
|
||||
|
||||
## The challenge of (re)ranking search results
|
||||
Once you have a group of the most relevant search results from multiple search sources, you'd likely standardize the score and rank them accordingly. This process can also be seen as another independent step: reranking.
|
||||
Once you have a group of the most relevant search results from multiple search sources, you'd likely standardize the score and rank them accordingly. This process can also be seen as another independent step - reranking.
|
||||
There are two approaches for reranking search results from multiple sources.
|
||||
|
||||
* <b>Score-based</b>: Calculate final relevance scores based on a weighted linear combination of individual search algorithm scores. Example: Weighted linear combination of semantic search & keyword-based search results.
|
||||
* <b>Score-based</b>: Calculate final relevance scores based on a weighted linear combination of individual search algorithm scores. Example - Weighted linear combination of semantic search & keyword-based search results.
|
||||
|
||||
* <b>Relevance-based</b>: Discards the existing scores and calculates the relevance of each search result-query pair. Example: Cross Encoder models
|
||||
* <b>Relevance-based</b>: Discards the existing scores and calculates the relevance of each search result - query pair. Example - Cross Encoder models
|
||||
|
||||
Even though there are many strategies for reranking search results, none works for all cases. Moreover, evaluating them itself is a challenge. Also, reranking can be dataset or application specific so it's hard to generalize.
|
||||
Even though there are many strategies for reranking search results, none works for all cases. Moreover, evaluating them itself is a challenge. Also, reranking can be dataset, application specific so it's hard to generalize.
|
||||
|
||||
### Example evaluation of hybrid search with Reranking
|
||||
|
||||
Here's some evaluation numbers from an experiment comparing these rerankers on about 800 queries. It is modified version of an evaluation script from [llama-index](https://github.com/run-llama/finetune-embedding/blob/main/evaluate.ipynb) that measures hit-rate at top-k.
|
||||
Here's some evaluation numbers from experiment comparing these re-rankers on about 800 queries. It is modified version of an evaluation script from [llama-index](https://github.com/run-llama/finetune-embedding/blob/main/evaluate.ipynb) that measures hit-rate at top-k.
|
||||
|
||||
<b> With OpenAI ada2 embedding </b>
|
||||
|
||||
Vector Search baseline: `0.64`
|
||||
Vector Search baseline - `0.64`
|
||||
|
||||
| Reranker | Top-3 | Top-5 | Top-10 |
|
||||
| --- | --- | --- | --- |
|
||||
@@ -33,7 +33,7 @@ Vector Search baseline: `0.64`
|
||||
|
||||
<b> With OpenAI embedding-v3-small </b>
|
||||
|
||||
Vector Search baseline: `0.59`
|
||||
Vector Search baseline - `0.59`
|
||||
|
||||
| Reranker | Top-3 | Top-5 | Top-10 |
|
||||
| --- | --- | --- | --- |
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -5,46 +5,57 @@ LanceDB supports both semantic and keyword-based search (also termed full-text s
|
||||
## Hybrid search in LanceDB
|
||||
You can perform hybrid search in LanceDB by combining the results of semantic and full-text search via a reranking algorithm of your choice. LanceDB provides multiple rerankers out of the box. However, you can always write a custom reranker if your use case need more sophisticated logic .
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import os
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_search.py:import-os"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_search.py:import-openai"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_search.py:import-lancedb"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_search.py:import-embeddings"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_search.py:import-pydantic"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_search.py:import-lancedb-fts"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_search.py:import-openai-embeddings"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_search.py:class-Documents"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_search.py:basic_hybrid_search"
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
import openai
|
||||
from lancedb.embeddings import get_registry
|
||||
from lancedb.pydantic import LanceModel, Vector
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_search.py:import-os"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_search.py:import-openai"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_search.py:import-lancedb"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_search.py:import-embeddings"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_search.py:import-pydantic"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_search.py:import-lancedb-fts"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_search.py:import-openai-embeddings"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_search.py:class-Documents"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_search.py:basic_hybrid_search_async"
|
||||
```
|
||||
db = lancedb.connect("~/.lancedb")
|
||||
|
||||
# Ingest embedding function in LanceDB table
|
||||
# Configuring the environment variable OPENAI_API_KEY
|
||||
if "OPENAI_API_KEY" not in os.environ:
|
||||
# OR set the key here as a variable
|
||||
openai.api_key = "sk-..."
|
||||
embeddings = get_registry().get("openai").create()
|
||||
|
||||
class Documents(LanceModel):
|
||||
vector: Vector(embeddings.ndims()) = embeddings.VectorField()
|
||||
text: str = embeddings.SourceField()
|
||||
|
||||
table = db.create_table("documents", schema=Documents)
|
||||
|
||||
data = [
|
||||
{ "text": "rebel spaceships striking from a hidden base"},
|
||||
{ "text": "have won their first victory against the evil Galactic Empire"},
|
||||
{ "text": "during the battle rebel spies managed to steal secret plans"},
|
||||
{ "text": "to the Empire's ultimate weapon the Death Star"}
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
# ingest docs with auto-vectorization
|
||||
table.add(data)
|
||||
|
||||
# Create a fts index before the hybrid search
|
||||
table.create_fts_index("text")
|
||||
# hybrid search with default re-ranker
|
||||
results = table.search("flower moon", query_type="hybrid").to_pandas()
|
||||
```
|
||||
!!! Note
|
||||
You can also pass the vector and text query manually. This is useful if you're not using the embedding API or if you're using a separate embedder service.
|
||||
### Explicitly passing the vector and text query
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
```python
|
||||
vector_query = [0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5]
|
||||
text_query = "flower moon"
|
||||
results = table.search(query_type="hybrid")
|
||||
.vector(vector_query)
|
||||
.text(text_query)
|
||||
.limit(5)
|
||||
.to_pandas()
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_search.py:hybrid_search_pass_vector_text"
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_search.py:hybrid_search_pass_vector_text_async"
|
||||
```
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
By default, LanceDB uses `RRFReranker()`, which uses reciprocal rank fusion score, to combine and rerank the results of semantic and full-text search. You can customize the hyperparameters as needed or write your own custom reranker. Here's how you can use any of the available rerankers:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -57,7 +68,7 @@ By default, LanceDB uses `RRFReranker()`, which uses reciprocal rank fusion scor
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Available Rerankers
|
||||
LanceDB provides a number of rerankers out of the box. You can use any of these rerankers by passing them to the `rerank()` method.
|
||||
LanceDB provides a number of re-rankers out of the box. You can use any of these re-rankers by passing them to the `rerank()` method.
|
||||
Go to [Rerankers](../reranking/index.md) to learn more about using the available rerankers and implementing custom rerankers.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
1
docs/src/js/.nojekyll
Normal file
1
docs/src/js/.nojekyll
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
|
||||
TypeDoc added this file to prevent GitHub Pages from using Jekyll. You can turn off this behavior by setting the `githubPages` option to false.
|
||||
@@ -27,9 +27,7 @@ the underlying connection has been closed.
|
||||
|
||||
### new Connection()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
new Connection(): Connection
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **new Connection**(): [`Connection`](Connection.md)
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -39,9 +37,7 @@ new Connection(): Connection
|
||||
|
||||
### close()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
abstract close(): void
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `abstract` **close**(): `void`
|
||||
|
||||
Close the connection, releasing any underlying resources.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -57,24 +53,21 @@ Any attempt to use the connection after it is closed will result in an error.
|
||||
|
||||
### createEmptyTable()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
abstract createEmptyTable(
|
||||
name,
|
||||
schema,
|
||||
options?): Promise<Table>
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `abstract` **createEmptyTable**(`name`, `schema`, `options`?): `Promise`<[`Table`](Table.md)>
|
||||
|
||||
Creates a new empty Table
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **name**: `string`
|
||||
The name of the table.
|
||||
• **name**: `string`
|
||||
|
||||
* **schema**: `SchemaLike`
|
||||
The schema of the table
|
||||
The name of the table.
|
||||
|
||||
* **options?**: `Partial`<[`CreateTableOptions`](../interfaces/CreateTableOptions.md)>
|
||||
• **schema**: `SchemaLike`
|
||||
|
||||
The schema of the table
|
||||
|
||||
• **options?**: `Partial`<[`CreateTableOptions`](../interfaces/CreateTableOptions.md)>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -86,16 +79,15 @@ Creates a new empty Table
|
||||
|
||||
#### createTable(options)
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
abstract createTable(options): Promise<Table>
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `abstract` **createTable**(`options`): `Promise`<[`Table`](Table.md)>
|
||||
|
||||
Creates a new Table and initialize it with new data.
|
||||
|
||||
##### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **options**: `object` & `Partial`<[`CreateTableOptions`](../interfaces/CreateTableOptions.md)>
|
||||
The options object.
|
||||
• **options**: `object` & `Partial`<[`CreateTableOptions`](../interfaces/CreateTableOptions.md)>
|
||||
|
||||
The options object.
|
||||
|
||||
##### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -103,25 +95,22 @@ Creates a new Table and initialize it with new data.
|
||||
|
||||
#### createTable(name, data, options)
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
abstract createTable(
|
||||
name,
|
||||
data,
|
||||
options?): Promise<Table>
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `abstract` **createTable**(`name`, `data`, `options`?): `Promise`<[`Table`](Table.md)>
|
||||
|
||||
Creates a new Table and initialize it with new data.
|
||||
|
||||
##### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **name**: `string`
|
||||
The name of the table.
|
||||
• **name**: `string`
|
||||
|
||||
* **data**: `TableLike` \| `Record`<`string`, `unknown`>[]
|
||||
Non-empty Array of Records
|
||||
to be inserted into the table
|
||||
The name of the table.
|
||||
|
||||
* **options?**: `Partial`<[`CreateTableOptions`](../interfaces/CreateTableOptions.md)>
|
||||
• **data**: `TableLike` \| `Record`<`string`, `unknown`>[]
|
||||
|
||||
Non-empty Array of Records
|
||||
to be inserted into the table
|
||||
|
||||
• **options?**: `Partial`<[`CreateTableOptions`](../interfaces/CreateTableOptions.md)>
|
||||
|
||||
##### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -131,9 +120,7 @@ Creates a new Table and initialize it with new data.
|
||||
|
||||
### display()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
abstract display(): string
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `abstract` **display**(): `string`
|
||||
|
||||
Return a brief description of the connection
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -145,16 +132,15 @@ Return a brief description of the connection
|
||||
|
||||
### dropTable()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
abstract dropTable(name): Promise<void>
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `abstract` **dropTable**(`name`): `Promise`<`void`>
|
||||
|
||||
Drop an existing table.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **name**: `string`
|
||||
The name of the table to drop.
|
||||
• **name**: `string`
|
||||
|
||||
The name of the table to drop.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -164,9 +150,7 @@ Drop an existing table.
|
||||
|
||||
### isOpen()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
abstract isOpen(): boolean
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `abstract` **isOpen**(): `boolean`
|
||||
|
||||
Return true if the connection has not been closed
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -178,18 +162,17 @@ Return true if the connection has not been closed
|
||||
|
||||
### openTable()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
abstract openTable(name, options?): Promise<Table>
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `abstract` **openTable**(`name`, `options`?): `Promise`<[`Table`](Table.md)>
|
||||
|
||||
Open a table in the database.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **name**: `string`
|
||||
The name of the table
|
||||
• **name**: `string`
|
||||
|
||||
* **options?**: `Partial`<`OpenTableOptions`>
|
||||
The name of the table
|
||||
|
||||
• **options?**: `Partial`<`OpenTableOptions`>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -199,9 +182,7 @@ Open a table in the database.
|
||||
|
||||
### tableNames()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
abstract tableNames(options?): Promise<string[]>
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `abstract` **tableNames**(`options`?): `Promise`<`string`[]>
|
||||
|
||||
List all the table names in this database.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -209,9 +190,10 @@ Tables will be returned in lexicographical order.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **options?**: `Partial`<[`TableNamesOptions`](../interfaces/TableNamesOptions.md)>
|
||||
options to control the
|
||||
paging / start point
|
||||
• **options?**: `Partial`<[`TableNamesOptions`](../interfaces/TableNamesOptions.md)>
|
||||
|
||||
options to control the
|
||||
paging / start point
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -8,30 +8,9 @@
|
||||
|
||||
## Methods
|
||||
|
||||
### bitmap()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
static bitmap(): Index
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Create a bitmap index.
|
||||
|
||||
A `Bitmap` index stores a bitmap for each distinct value in the column for every row.
|
||||
|
||||
This index works best for low-cardinality columns, where the number of unique values
|
||||
is small (i.e., less than a few hundreds).
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
[`Index`](Index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### btree()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
static btree(): Index
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `static` **btree**(): [`Index`](Index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Create a btree index
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -57,82 +36,9 @@ block size may be added in the future.
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### fts()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
static fts(options?): Index
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Create a full text search index
|
||||
|
||||
A full text search index is an index on a string column, so that you can conduct full
|
||||
text searches on the column.
|
||||
|
||||
The results of a full text search are ordered by relevance measured by BM25.
|
||||
|
||||
You can combine filters with full text search.
|
||||
|
||||
For now, the full text search index only supports English, and doesn't support phrase search.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **options?**: `Partial`<`FtsOptions`>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
[`Index`](Index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### hnswPq()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
static hnswPq(options?): Index
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Create a hnswPq index
|
||||
|
||||
HNSW-PQ stands for Hierarchical Navigable Small World - Product Quantization.
|
||||
It is a variant of the HNSW algorithm that uses product quantization to compress
|
||||
the vectors.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **options?**: `Partial`<`HnswPqOptions`>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
[`Index`](Index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### hnswSq()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
static hnswSq(options?): Index
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Create a hnswSq index
|
||||
|
||||
HNSW-SQ stands for Hierarchical Navigable Small World - Scalar Quantization.
|
||||
It is a variant of the HNSW algorithm that uses scalar quantization to compress
|
||||
the vectors.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **options?**: `Partial`<`HnswSqOptions`>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
[`Index`](Index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### ivfPq()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
static ivfPq(options?): Index
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `static` **ivfPq**(`options`?): [`Index`](Index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Create an IvfPq index
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -157,25 +63,29 @@ currently is also a memory intensive operation.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **options?**: `Partial`<[`IvfPqOptions`](../interfaces/IvfPqOptions.md)>
|
||||
• **options?**: `Partial`<[`IvfPqOptions`](../interfaces/IvfPqOptions.md)>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
[`Index`](Index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
### fts()
|
||||
|
||||
### labelList()
|
||||
> `static` **fts**(`options`?): [`Index`](Index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
static labelList(): Index
|
||||
```
|
||||
Create a full text search index
|
||||
|
||||
Create a label list index.
|
||||
This index is used to search for text data. The index is created by tokenizing the text
|
||||
into words and then storing occurrences of these words in a data structure called inverted index
|
||||
that allows for fast search.
|
||||
|
||||
LabelList index is a scalar index that can be used on `List<T>` columns to
|
||||
support queries with `array_contains_all` and `array_contains_any`
|
||||
using an underlying bitmap index.
|
||||
During a search the query is tokenized and the inverted index is used to find the rows that
|
||||
contain the query words. The rows are then scored based on BM25 and the top scoring rows are
|
||||
sorted and returned.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
• **options?**: `Partial`<[`FtsOptions`](../interfaces/FtsOptions.md)>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -12,13 +12,11 @@ Options to control the makeArrowTable call.
|
||||
|
||||
### new MakeArrowTableOptions()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
new MakeArrowTableOptions(values?): MakeArrowTableOptions
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **new MakeArrowTableOptions**(`values`?): [`MakeArrowTableOptions`](MakeArrowTableOptions.md)
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **values?**: `Partial`<[`MakeArrowTableOptions`](MakeArrowTableOptions.md)>
|
||||
• **values?**: `Partial`<[`MakeArrowTableOptions`](MakeArrowTableOptions.md)>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -28,9 +26,7 @@ new MakeArrowTableOptions(values?): MakeArrowTableOptions
|
||||
|
||||
### dictionaryEncodeStrings
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
dictionaryEncodeStrings: boolean = false;
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **dictionaryEncodeStrings**: `boolean` = `false`
|
||||
|
||||
If true then string columns will be encoded with dictionary encoding
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -44,30 +40,22 @@ If `schema` is provided then this property is ignored.
|
||||
|
||||
### embeddingFunction?
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
optional embeddingFunction: EmbeddingFunctionConfig;
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `optional` **embeddingFunction**: [`EmbeddingFunctionConfig`](../namespaces/embedding/interfaces/EmbeddingFunctionConfig.md)
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### embeddings?
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
optional embeddings: EmbeddingFunction<unknown, FunctionOptions>;
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `optional` **embeddings**: [`EmbeddingFunction`](../namespaces/embedding/classes/EmbeddingFunction.md)<`unknown`, `FunctionOptions`>
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### schema?
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
optional schema: SchemaLike;
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `optional` **schema**: `SchemaLike`
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### vectorColumns
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
vectorColumns: Record<string, VectorColumnOptions>;
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **vectorColumns**: `Record`<`string`, [`VectorColumnOptions`](VectorColumnOptions.md)>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -16,13 +16,11 @@ A builder for LanceDB queries.
|
||||
|
||||
### new Query()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
new Query(tbl): Query
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **new Query**(`tbl`): [`Query`](Query.md)
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **tbl**: `Table`
|
||||
• **tbl**: `Table`
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -36,9 +34,7 @@ new Query(tbl): Query
|
||||
|
||||
### inner
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
protected inner: Query | Promise<Query>;
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `protected` **inner**: `Query` \| `Promise`<`Query`>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Inherited from
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -48,9 +44,7 @@ protected inner: Query | Promise<Query>;
|
||||
|
||||
### \[asyncIterator\]()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
asyncIterator: AsyncIterator<RecordBatch<any>, any, undefined>
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **\[asyncIterator\]**(): `AsyncIterator`<`RecordBatch`<`any`>, `any`, `undefined`>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -64,13 +58,11 @@ asyncIterator: AsyncIterator<RecordBatch<any>, any, undefined>
|
||||
|
||||
### doCall()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
protected doCall(fn): void
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `protected` **doCall**(`fn`): `void`
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **fn**
|
||||
• **fn**
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -84,15 +76,13 @@ protected doCall(fn): void
|
||||
|
||||
### execute()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
protected execute(options?): RecordBatchIterator
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `protected` **execute**(`options`?): [`RecordBatchIterator`](RecordBatchIterator.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Execute the query and return the results as an
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **options?**: `Partial`<`QueryExecutionOptions`>
|
||||
• **options?**: `Partial`<`QueryExecutionOptions`>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -118,16 +108,15 @@ single query)
|
||||
|
||||
### explainPlan()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
explainPlan(verbose): Promise<string>
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **explainPlan**(`verbose`): `Promise`<`string`>
|
||||
|
||||
Generates an explanation of the query execution plan.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **verbose**: `boolean` = `false`
|
||||
If true, provides a more detailed explanation. Defaults to false.
|
||||
• **verbose**: `boolean` = `false`
|
||||
|
||||
If true, provides a more detailed explanation. Defaults to false.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -152,38 +141,15 @@ const plan = await table.query().nearestTo([0.5, 0.2]).explainPlan();
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### fastSearch()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
fastSearch(): this
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Skip searching un-indexed data. This can make search faster, but will miss
|
||||
any data that is not yet indexed.
|
||||
|
||||
Use lancedb.Table#optimize to index all un-indexed data.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
`this`
|
||||
|
||||
#### Inherited from
|
||||
|
||||
[`QueryBase`](QueryBase.md).[`fastSearch`](QueryBase.md#fastsearch)
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### ~~filter()~~
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
filter(predicate): this
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **filter**(`predicate`): `this`
|
||||
|
||||
A filter statement to be applied to this query.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **predicate**: `string`
|
||||
• **predicate**: `string`
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -203,33 +169,9 @@ Use `where` instead
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### fullTextSearch()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
fullTextSearch(query, options?): this
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **query**: `string`
|
||||
|
||||
* **options?**: `Partial`<`FullTextSearchOptions`>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
`this`
|
||||
|
||||
#### Inherited from
|
||||
|
||||
[`QueryBase`](QueryBase.md).[`fullTextSearch`](QueryBase.md#fulltextsearch)
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### limit()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
limit(limit): this
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **limit**(`limit`): `this`
|
||||
|
||||
Set the maximum number of results to return.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -238,7 +180,7 @@ called then every valid row from the table will be returned.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **limit**: `number`
|
||||
• **limit**: `number`
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -252,13 +194,11 @@ called then every valid row from the table will be returned.
|
||||
|
||||
### nativeExecute()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
protected nativeExecute(options?): Promise<RecordBatchIterator>
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `protected` **nativeExecute**(`options`?): `Promise`<`RecordBatchIterator`>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **options?**: `Partial`<`QueryExecutionOptions`>
|
||||
• **options?**: `Partial`<`QueryExecutionOptions`>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -272,9 +212,7 @@ protected nativeExecute(options?): Promise<RecordBatchIterator>
|
||||
|
||||
### nearestTo()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
nearestTo(vector): VectorQuery
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **nearestTo**(`vector`): [`VectorQuery`](VectorQuery.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Find the nearest vectors to the given query vector.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -294,7 +232,7 @@ If there is more than one vector column you must use
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **vector**: `IntoVector`
|
||||
• **vector**: `IntoVector`
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -326,49 +264,9 @@ a default `limit` of 10 will be used.
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### nearestToText()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
nearestToText(query, columns?): Query
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **query**: `string`
|
||||
|
||||
* **columns?**: `string`[]
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
[`Query`](Query.md)
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### offset()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
offset(offset): this
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **offset**: `number`
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
`this`
|
||||
|
||||
#### Inherited from
|
||||
|
||||
[`QueryBase`](QueryBase.md).[`offset`](QueryBase.md#offset)
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### select()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
select(columns): this
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **select**(`columns`): `this`
|
||||
|
||||
Return only the specified columns.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -392,7 +290,7 @@ input to this method would be:
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **columns**: `string` \| `string`[] \| `Record`<`string`, `string`> \| `Map`<`string`, `string`>
|
||||
• **columns**: `string` \| `string`[] \| `Record`<`string`, `string`> \| `Map`<`string`, `string`>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -419,15 +317,13 @@ object insertion order is easy to get wrong and `Map` is more foolproof.
|
||||
|
||||
### toArray()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
toArray(options?): Promise<any[]>
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **toArray**(`options`?): `Promise`<`any`[]>
|
||||
|
||||
Collect the results as an array of objects.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **options?**: `Partial`<`QueryExecutionOptions`>
|
||||
• **options?**: `Partial`<`QueryExecutionOptions`>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -441,15 +337,13 @@ Collect the results as an array of objects.
|
||||
|
||||
### toArrow()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
toArrow(options?): Promise<Table<any>>
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **toArrow**(`options`?): `Promise`<`Table`<`any`>>
|
||||
|
||||
Collect the results as an Arrow
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **options?**: `Partial`<`QueryExecutionOptions`>
|
||||
• **options?**: `Partial`<`QueryExecutionOptions`>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -467,9 +361,7 @@ ArrowTable.
|
||||
|
||||
### where()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
where(predicate): this
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **where**(`predicate`): `this`
|
||||
|
||||
A filter statement to be applied to this query.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -477,7 +369,7 @@ The filter should be supplied as an SQL query string. For example:
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **predicate**: `string`
|
||||
• **predicate**: `string`
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -497,25 +389,3 @@ on the filter column(s).
|
||||
#### Inherited from
|
||||
|
||||
[`QueryBase`](QueryBase.md).[`where`](QueryBase.md#where)
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### withRowId()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
withRowId(): this
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Whether to return the row id in the results.
|
||||
|
||||
This column can be used to match results between different queries. For
|
||||
example, to match results from a full text search and a vector search in
|
||||
order to perform hybrid search.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
`this`
|
||||
|
||||
#### Inherited from
|
||||
|
||||
[`QueryBase`](QueryBase.md).[`withRowId`](QueryBase.md#withrowid)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -25,13 +25,11 @@ Common methods supported by all query types
|
||||
|
||||
### new QueryBase()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
protected new QueryBase<NativeQueryType>(inner): QueryBase<NativeQueryType>
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `protected` **new QueryBase**<`NativeQueryType`>(`inner`): [`QueryBase`](QueryBase.md)<`NativeQueryType`>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **inner**: `NativeQueryType` \| `Promise`<`NativeQueryType`>
|
||||
• **inner**: `NativeQueryType` \| `Promise`<`NativeQueryType`>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -41,17 +39,13 @@ protected new QueryBase<NativeQueryType>(inner): QueryBase<NativeQueryType>
|
||||
|
||||
### inner
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
protected inner: NativeQueryType | Promise<NativeQueryType>;
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `protected` **inner**: `NativeQueryType` \| `Promise`<`NativeQueryType`>
|
||||
|
||||
## Methods
|
||||
|
||||
### \[asyncIterator\]()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
asyncIterator: AsyncIterator<RecordBatch<any>, any, undefined>
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **\[asyncIterator\]**(): `AsyncIterator`<`RecordBatch`<`any`>, `any`, `undefined`>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -65,13 +59,11 @@ asyncIterator: AsyncIterator<RecordBatch<any>, any, undefined>
|
||||
|
||||
### doCall()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
protected doCall(fn): void
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `protected` **doCall**(`fn`): `void`
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **fn**
|
||||
• **fn**
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -81,15 +73,13 @@ protected doCall(fn): void
|
||||
|
||||
### execute()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
protected execute(options?): RecordBatchIterator
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `protected` **execute**(`options`?): [`RecordBatchIterator`](RecordBatchIterator.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Execute the query and return the results as an
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **options?**: `Partial`<`QueryExecutionOptions`>
|
||||
• **options?**: `Partial`<`QueryExecutionOptions`>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -111,16 +101,15 @@ single query)
|
||||
|
||||
### explainPlan()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
explainPlan(verbose): Promise<string>
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **explainPlan**(`verbose`): `Promise`<`string`>
|
||||
|
||||
Generates an explanation of the query execution plan.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **verbose**: `boolean` = `false`
|
||||
If true, provides a more detailed explanation. Defaults to false.
|
||||
• **verbose**: `boolean` = `false`
|
||||
|
||||
If true, provides a more detailed explanation. Defaults to false.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -141,34 +130,15 @@ const plan = await table.query().nearestTo([0.5, 0.2]).explainPlan();
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### fastSearch()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
fastSearch(): this
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Skip searching un-indexed data. This can make search faster, but will miss
|
||||
any data that is not yet indexed.
|
||||
|
||||
Use lancedb.Table#optimize to index all un-indexed data.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
`this`
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### ~~filter()~~
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
filter(predicate): this
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **filter**(`predicate`): `this`
|
||||
|
||||
A filter statement to be applied to this query.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **predicate**: `string`
|
||||
• **predicate**: `string`
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -184,29 +154,9 @@ Use `where` instead
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### fullTextSearch()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
fullTextSearch(query, options?): this
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **query**: `string`
|
||||
|
||||
* **options?**: `Partial`<`FullTextSearchOptions`>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
`this`
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### limit()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
limit(limit): this
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **limit**(`limit`): `this`
|
||||
|
||||
Set the maximum number of results to return.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -215,7 +165,7 @@ called then every valid row from the table will be returned.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **limit**: `number`
|
||||
• **limit**: `number`
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -225,13 +175,11 @@ called then every valid row from the table will be returned.
|
||||
|
||||
### nativeExecute()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
protected nativeExecute(options?): Promise<RecordBatchIterator>
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `protected` **nativeExecute**(`options`?): `Promise`<`RecordBatchIterator`>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **options?**: `Partial`<`QueryExecutionOptions`>
|
||||
• **options?**: `Partial`<`QueryExecutionOptions`>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -239,27 +187,9 @@ protected nativeExecute(options?): Promise<RecordBatchIterator>
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### offset()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
offset(offset): this
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **offset**: `number`
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
`this`
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### select()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
select(columns): this
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **select**(`columns`): `this`
|
||||
|
||||
Return only the specified columns.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -283,7 +213,7 @@ input to this method would be:
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **columns**: `string` \| `string`[] \| `Record`<`string`, `string`> \| `Map`<`string`, `string`>
|
||||
• **columns**: `string` \| `string`[] \| `Record`<`string`, `string`> \| `Map`<`string`, `string`>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -306,15 +236,13 @@ object insertion order is easy to get wrong and `Map` is more foolproof.
|
||||
|
||||
### toArray()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
toArray(options?): Promise<any[]>
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **toArray**(`options`?): `Promise`<`any`[]>
|
||||
|
||||
Collect the results as an array of objects.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **options?**: `Partial`<`QueryExecutionOptions`>
|
||||
• **options?**: `Partial`<`QueryExecutionOptions`>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -324,15 +252,13 @@ Collect the results as an array of objects.
|
||||
|
||||
### toArrow()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
toArrow(options?): Promise<Table<any>>
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **toArrow**(`options`?): `Promise`<`Table`<`any`>>
|
||||
|
||||
Collect the results as an Arrow
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **options?**: `Partial`<`QueryExecutionOptions`>
|
||||
• **options?**: `Partial`<`QueryExecutionOptions`>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -346,9 +272,7 @@ ArrowTable.
|
||||
|
||||
### where()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
where(predicate): this
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **where**(`predicate`): `this`
|
||||
|
||||
A filter statement to be applied to this query.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -356,7 +280,7 @@ The filter should be supplied as an SQL query string. For example:
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **predicate**: `string`
|
||||
• **predicate**: `string`
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -372,21 +296,3 @@ x > 5 OR y = 'test'
|
||||
Filtering performance can often be improved by creating a scalar index
|
||||
on the filter column(s).
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### withRowId()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
withRowId(): this
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Whether to return the row id in the results.
|
||||
|
||||
This column can be used to match results between different queries. For
|
||||
example, to match results from a full text search and a vector search in
|
||||
order to perform hybrid search.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
`this`
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -14,13 +14,11 @@
|
||||
|
||||
### new RecordBatchIterator()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
new RecordBatchIterator(promise?): RecordBatchIterator
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **new RecordBatchIterator**(`promise`?): [`RecordBatchIterator`](RecordBatchIterator.md)
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **promise?**: `Promise`<`RecordBatchIterator`>
|
||||
• **promise?**: `Promise`<`RecordBatchIterator`>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -30,9 +28,7 @@ new RecordBatchIterator(promise?): RecordBatchIterator
|
||||
|
||||
### next()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
next(): Promise<IteratorResult<RecordBatch<any>, any>>
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **next**(): `Promise`<`IteratorResult`<`RecordBatch`<`any`>, `any`>>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -21,9 +21,7 @@ collected.
|
||||
|
||||
### new Table()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
new Table(): Table
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **new Table**(): [`Table`](Table.md)
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -33,9 +31,7 @@ new Table(): Table
|
||||
|
||||
### name
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
get abstract name(): string
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `get` `abstract` **name**(): `string`
|
||||
|
||||
Returns the name of the table
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -47,18 +43,17 @@ Returns the name of the table
|
||||
|
||||
### add()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
abstract add(data, options?): Promise<void>
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `abstract` **add**(`data`, `options`?): `Promise`<`void`>
|
||||
|
||||
Insert records into this Table.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **data**: [`Data`](../type-aliases/Data.md)
|
||||
Records to be inserted into the Table
|
||||
• **data**: [`Data`](../type-aliases/Data.md)
|
||||
|
||||
* **options?**: `Partial`<[`AddDataOptions`](../interfaces/AddDataOptions.md)>
|
||||
Records to be inserted into the Table
|
||||
|
||||
• **options?**: `Partial`<[`AddDataOptions`](../interfaces/AddDataOptions.md)>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -68,19 +63,18 @@ Insert records into this Table.
|
||||
|
||||
### addColumns()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
abstract addColumns(newColumnTransforms): Promise<void>
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `abstract` **addColumns**(`newColumnTransforms`): `Promise`<`void`>
|
||||
|
||||
Add new columns with defined values.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **newColumnTransforms**: [`AddColumnsSql`](../interfaces/AddColumnsSql.md)[]
|
||||
pairs of column names and
|
||||
the SQL expression to use to calculate the value of the new column. These
|
||||
expressions will be evaluated for each row in the table, and can
|
||||
reference existing columns in the table.
|
||||
• **newColumnTransforms**: [`AddColumnsSql`](../interfaces/AddColumnsSql.md)[]
|
||||
|
||||
pairs of column names and
|
||||
the SQL expression to use to calculate the value of the new column. These
|
||||
expressions will be evaluated for each row in the table, and can
|
||||
reference existing columns in the table.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -90,17 +84,16 @@ Add new columns with defined values.
|
||||
|
||||
### alterColumns()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
abstract alterColumns(columnAlterations): Promise<void>
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `abstract` **alterColumns**(`columnAlterations`): `Promise`<`void`>
|
||||
|
||||
Alter the name or nullability of columns.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **columnAlterations**: [`ColumnAlteration`](../interfaces/ColumnAlteration.md)[]
|
||||
One or more alterations to
|
||||
apply to columns.
|
||||
• **columnAlterations**: [`ColumnAlteration`](../interfaces/ColumnAlteration.md)[]
|
||||
|
||||
One or more alterations to
|
||||
apply to columns.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -110,9 +103,7 @@ Alter the name or nullability of columns.
|
||||
|
||||
### checkout()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
abstract checkout(version): Promise<void>
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `abstract` **checkout**(`version`): `Promise`<`void`>
|
||||
|
||||
Checks out a specific version of the table _This is an in-place operation._
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -125,8 +116,9 @@ wish to return to standard mode, call `checkoutLatest`.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **version**: `number`
|
||||
The version to checkout
|
||||
• **version**: `number`
|
||||
|
||||
The version to checkout
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -152,9 +144,7 @@ console.log(await table.version()); // 2
|
||||
|
||||
### checkoutLatest()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
abstract checkoutLatest(): Promise<void>
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `abstract` **checkoutLatest**(): `Promise`<`void`>
|
||||
|
||||
Checkout the latest version of the table. _This is an in-place operation._
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -169,9 +159,7 @@ version of the table.
|
||||
|
||||
### close()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
abstract close(): void
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `abstract` **close**(): `void`
|
||||
|
||||
Close the table, releasing any underlying resources.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -187,15 +175,13 @@ Any attempt to use the table after it is closed will result in an error.
|
||||
|
||||
### countRows()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
abstract countRows(filter?): Promise<number>
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `abstract` **countRows**(`filter`?): `Promise`<`number`>
|
||||
|
||||
Count the total number of rows in the dataset.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **filter?**: `string`
|
||||
• **filter?**: `string`
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -205,9 +191,7 @@ Count the total number of rows in the dataset.
|
||||
|
||||
### createIndex()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
abstract createIndex(column, options?): Promise<void>
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `abstract` **createIndex**(`column`, `options`?): `Promise`<`void`>
|
||||
|
||||
Create an index to speed up queries.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -218,9 +202,9 @@ vector and non-vector searches)
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **column**: `string`
|
||||
• **column**: `string`
|
||||
|
||||
* **options?**: `Partial`<[`IndexOptions`](../interfaces/IndexOptions.md)>
|
||||
• **options?**: `Partial`<[`IndexOptions`](../interfaces/IndexOptions.md)>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -261,15 +245,13 @@ await table.createIndex("my_float_col");
|
||||
|
||||
### delete()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
abstract delete(predicate): Promise<void>
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `abstract` **delete**(`predicate`): `Promise`<`void`>
|
||||
|
||||
Delete the rows that satisfy the predicate.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **predicate**: `string`
|
||||
• **predicate**: `string`
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -279,9 +261,7 @@ Delete the rows that satisfy the predicate.
|
||||
|
||||
### display()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
abstract display(): string
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `abstract` **display**(): `string`
|
||||
|
||||
Return a brief description of the table
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -293,9 +273,7 @@ Return a brief description of the table
|
||||
|
||||
### dropColumns()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
abstract dropColumns(columnNames): Promise<void>
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `abstract` **dropColumns**(`columnNames`): `Promise`<`void`>
|
||||
|
||||
Drop one or more columns from the dataset
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -306,10 +284,11 @@ then call ``cleanup_files`` to remove the old files.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **columnNames**: `string`[]
|
||||
The names of the columns to drop. These can
|
||||
be nested column references (e.g. "a.b.c") or top-level column names
|
||||
(e.g. "a").
|
||||
• **columnNames**: `string`[]
|
||||
|
||||
The names of the columns to drop. These can
|
||||
be nested column references (e.g. "a.b.c") or top-level column names
|
||||
(e.g. "a").
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -319,16 +298,15 @@ then call ``cleanup_files`` to remove the old files.
|
||||
|
||||
### indexStats()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
abstract indexStats(name): Promise<undefined | IndexStatistics>
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `abstract` **indexStats**(`name`): `Promise`<`undefined` \| [`IndexStatistics`](../interfaces/IndexStatistics.md)>
|
||||
|
||||
List all the stats of a specified index
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **name**: `string`
|
||||
The name of the index.
|
||||
• **name**: `string`
|
||||
|
||||
The name of the index.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -340,9 +318,7 @@ The stats of the index. If the index does not exist, it will return undefined
|
||||
|
||||
### isOpen()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
abstract isOpen(): boolean
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `abstract` **isOpen**(): `boolean`
|
||||
|
||||
Return true if the table has not been closed
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -354,9 +330,7 @@ Return true if the table has not been closed
|
||||
|
||||
### listIndices()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
abstract listIndices(): Promise<IndexConfig[]>
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `abstract` **listIndices**(): `Promise`<[`IndexConfig`](../interfaces/IndexConfig.md)[]>
|
||||
|
||||
List all indices that have been created with [Table.createIndex](Table.md#createindex)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -366,29 +340,13 @@ List all indices that have been created with [Table.createIndex](Table.md#create
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### listVersions()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
abstract listVersions(): Promise<Version[]>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
List all the versions of the table
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
`Promise`<`Version`[]>
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### mergeInsert()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
abstract mergeInsert(on): MergeInsertBuilder
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `abstract` **mergeInsert**(`on`): `MergeInsertBuilder`
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **on**: `string` \| `string`[]
|
||||
• **on**: `string` \| `string`[]
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -398,9 +356,7 @@ abstract mergeInsert(on): MergeInsertBuilder
|
||||
|
||||
### optimize()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
abstract optimize(options?): Promise<OptimizeStats>
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `abstract` **optimize**(`options`?): `Promise`<`OptimizeStats`>
|
||||
|
||||
Optimize the on-disk data and indices for better performance.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -432,7 +388,7 @@ Modeled after ``VACUUM`` in PostgreSQL.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **options?**: `Partial`<[`OptimizeOptions`](../interfaces/OptimizeOptions.md)>
|
||||
• **options?**: `Partial`<`OptimizeOptions`>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -442,9 +398,7 @@ Modeled after ``VACUUM`` in PostgreSQL.
|
||||
|
||||
### query()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
abstract query(): Query
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `abstract` **query**(): [`Query`](Query.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Create a [Query](Query.md) Builder.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -512,9 +466,7 @@ for await (const batch of table.query()) {
|
||||
|
||||
### restore()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
abstract restore(): Promise<void>
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `abstract` **restore**(): `Promise`<`void`>
|
||||
|
||||
Restore the table to the currently checked out version
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -535,9 +487,7 @@ out state and the read_consistency_interval, if any, will apply.
|
||||
|
||||
### schema()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
abstract schema(): Promise<Schema<any>>
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `abstract` **schema**(): `Promise`<`Schema`<`any`>>
|
||||
|
||||
Get the schema of the table.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -549,41 +499,61 @@ Get the schema of the table.
|
||||
|
||||
### search()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
abstract search(
|
||||
query,
|
||||
queryType?,
|
||||
ftsColumns?): VectorQuery | Query
|
||||
```
|
||||
#### search(query)
|
||||
|
||||
> `abstract` **search**(`query`, `queryType`, `ftsColumns`): [`VectorQuery`](VectorQuery.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Create a search query to find the nearest neighbors
|
||||
of the given query
|
||||
of the given query vector, or the documents
|
||||
with the highest relevance to the query string.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
##### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **query**: `string` \| `IntoVector`
|
||||
the query, a vector or string
|
||||
• **query**: `string`
|
||||
|
||||
* **queryType?**: `string`
|
||||
the type of the query, "vector", "fts", or "auto"
|
||||
the query. This will be converted to a vector using the table's provided embedding function,
|
||||
or the query string for full-text search if `queryType` is "fts".
|
||||
|
||||
* **ftsColumns?**: `string` \| `string`[]
|
||||
the columns to search in for full text search
|
||||
for now, only one column can be searched at a time.
|
||||
when "auto" is used, if the query is a string and an embedding function is defined, it will be treated as a vector query
|
||||
if the query is a string and no embedding function is defined, it will be treated as a full text search query
|
||||
• **queryType**: `string` = `"auto"` \| `"fts"`
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
the type of query to run. If "auto", the query type will be determined based on the query.
|
||||
|
||||
[`VectorQuery`](VectorQuery.md) \| [`Query`](Query.md)
|
||||
• **ftsColumns**: `string[] | str` = undefined
|
||||
|
||||
the columns to search in. If not provided, all indexed columns will be searched.
|
||||
|
||||
For now, this can support to search only one column.
|
||||
|
||||
##### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
[`VectorQuery`](VectorQuery.md)
|
||||
|
||||
##### Note
|
||||
|
||||
If no embedding functions are defined in the table, this will error when collecting the results.
|
||||
|
||||
#### search(query)
|
||||
|
||||
> `abstract` **search**(`query`): [`VectorQuery`](VectorQuery.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Create a search query to find the nearest neighbors
|
||||
of the given query vector
|
||||
|
||||
##### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
• **query**: `IntoVector`
|
||||
|
||||
the query vector
|
||||
|
||||
##### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
[`VectorQuery`](VectorQuery.md)
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### toArrow()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
abstract toArrow(): Promise<Table<any>>
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `abstract` **toArrow**(): `Promise`<`Table`<`any`>>
|
||||
|
||||
Return the table as an arrow table
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -597,15 +567,13 @@ Return the table as an arrow table
|
||||
|
||||
#### update(opts)
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
abstract update(opts): Promise<void>
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `abstract` **update**(`opts`): `Promise`<`void`>
|
||||
|
||||
Update existing records in the Table
|
||||
|
||||
##### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **opts**: `object` & `Partial`<[`UpdateOptions`](../interfaces/UpdateOptions.md)>
|
||||
• **opts**: `object` & `Partial`<[`UpdateOptions`](../interfaces/UpdateOptions.md)>
|
||||
|
||||
##### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -619,15 +587,13 @@ table.update({where:"x = 2", values:{"vector": [10, 10]}})
|
||||
|
||||
#### update(opts)
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
abstract update(opts): Promise<void>
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `abstract` **update**(`opts`): `Promise`<`void`>
|
||||
|
||||
Update existing records in the Table
|
||||
|
||||
##### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **opts**: `object` & `Partial`<[`UpdateOptions`](../interfaces/UpdateOptions.md)>
|
||||
• **opts**: `object` & `Partial`<[`UpdateOptions`](../interfaces/UpdateOptions.md)>
|
||||
|
||||
##### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -641,9 +607,7 @@ table.update({where:"x = 2", valuesSql:{"x": "x + 1"}})
|
||||
|
||||
#### update(updates, options)
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
abstract update(updates, options?): Promise<void>
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `abstract` **update**(`updates`, `options`?): `Promise`<`void`>
|
||||
|
||||
Update existing records in the Table
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -662,17 +626,20 @@ repeatedly calilng this method.
|
||||
|
||||
##### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **updates**: `Record`<`string`, `string`> \| `Map`<`string`, `string`>
|
||||
the
|
||||
columns to update
|
||||
Keys in the map should specify the name of the column to update.
|
||||
Values in the map provide the new value of the column. These can
|
||||
be SQL literal strings (e.g. "7" or "'foo'") or they can be expressions
|
||||
based on the row being updated (e.g. "my_col + 1")
|
||||
• **updates**: `Record`<`string`, `string`> \| `Map`<`string`, `string`>
|
||||
|
||||
* **options?**: `Partial`<[`UpdateOptions`](../interfaces/UpdateOptions.md)>
|
||||
additional options to control
|
||||
the update behavior
|
||||
the
|
||||
columns to update
|
||||
|
||||
Keys in the map should specify the name of the column to update.
|
||||
Values in the map provide the new value of the column. These can
|
||||
be SQL literal strings (e.g. "7" or "'foo'") or they can be expressions
|
||||
based on the row being updated (e.g. "my_col + 1")
|
||||
|
||||
• **options?**: `Partial`<[`UpdateOptions`](../interfaces/UpdateOptions.md)>
|
||||
|
||||
additional options to control
|
||||
the update behavior
|
||||
|
||||
##### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -682,9 +649,7 @@ repeatedly calilng this method.
|
||||
|
||||
### vectorSearch()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
abstract vectorSearch(vector): VectorQuery
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `abstract` **vectorSearch**(`vector`): [`VectorQuery`](VectorQuery.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Search the table with a given query vector.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -694,7 +659,7 @@ by `query`.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **vector**: `IntoVector`
|
||||
• **vector**: `IntoVector`
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -708,9 +673,7 @@ by `query`.
|
||||
|
||||
### version()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
abstract version(): Promise<number>
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `abstract` **version**(): `Promise`<`number`>
|
||||
|
||||
Retrieve the version of the table
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -722,20 +685,15 @@ Retrieve the version of the table
|
||||
|
||||
### parseTableData()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
static parseTableData(
|
||||
data,
|
||||
options?,
|
||||
streaming?): Promise<object>
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `static` **parseTableData**(`data`, `options`?, `streaming`?): `Promise`<`object`>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **data**: `TableLike` \| `Record`<`string`, `unknown`>[]
|
||||
• **data**: `TableLike` \| `Record`<`string`, `unknown`>[]
|
||||
|
||||
* **options?**: `Partial`<[`CreateTableOptions`](../interfaces/CreateTableOptions.md)>
|
||||
• **options?**: `Partial`<[`CreateTableOptions`](../interfaces/CreateTableOptions.md)>
|
||||
|
||||
* **streaming?**: `boolean` = `false`
|
||||
• **streaming?**: `boolean` = `false`
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -743,12 +701,8 @@ static parseTableData(
|
||||
|
||||
##### buf
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
buf: Buffer;
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **buf**: `Buffer`
|
||||
|
||||
##### mode
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
mode: string;
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **mode**: `string`
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -10,13 +10,11 @@
|
||||
|
||||
### new VectorColumnOptions()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
new VectorColumnOptions(values?): VectorColumnOptions
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **new VectorColumnOptions**(`values`?): [`VectorColumnOptions`](VectorColumnOptions.md)
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **values?**: `Partial`<[`VectorColumnOptions`](VectorColumnOptions.md)>
|
||||
• **values?**: `Partial`<[`VectorColumnOptions`](VectorColumnOptions.md)>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -26,8 +24,6 @@ new VectorColumnOptions(values?): VectorColumnOptions
|
||||
|
||||
### type
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
type: Float<Floats>;
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **type**: `Float`<`Floats`>
|
||||
|
||||
Vector column type.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -18,13 +18,11 @@ This builder can be reused to execute the query many times.
|
||||
|
||||
### new VectorQuery()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
new VectorQuery(inner): VectorQuery
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **new VectorQuery**(`inner`): [`VectorQuery`](VectorQuery.md)
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **inner**: `VectorQuery` \| `Promise`<`VectorQuery`>
|
||||
• **inner**: `VectorQuery` \| `Promise`<`VectorQuery`>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -38,9 +36,7 @@ new VectorQuery(inner): VectorQuery
|
||||
|
||||
### inner
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
protected inner: VectorQuery | Promise<VectorQuery>;
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `protected` **inner**: `VectorQuery` \| `Promise`<`VectorQuery`>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Inherited from
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -50,9 +46,7 @@ protected inner: VectorQuery | Promise<VectorQuery>;
|
||||
|
||||
### \[asyncIterator\]()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
asyncIterator: AsyncIterator<RecordBatch<any>, any, undefined>
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **\[asyncIterator\]**(): `AsyncIterator`<`RecordBatch`<`any`>, `any`, `undefined`>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -64,27 +58,9 @@ asyncIterator: AsyncIterator<RecordBatch<any>, any, undefined>
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### addQueryVector()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
addQueryVector(vector): VectorQuery
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **vector**: `IntoVector`
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
[`VectorQuery`](VectorQuery.md)
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### bypassVectorIndex()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
bypassVectorIndex(): VectorQuery
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **bypassVectorIndex**(): [`VectorQuery`](VectorQuery.md)
|
||||
|
||||
If this is called then any vector index is skipped
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -102,9 +78,7 @@ calculate your recall to select an appropriate value for nprobes.
|
||||
|
||||
### column()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
column(column): VectorQuery
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **column**(`column`): [`VectorQuery`](VectorQuery.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Set the vector column to query
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -113,7 +87,7 @@ the call to
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **column**: `string`
|
||||
• **column**: `string`
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -130,9 +104,7 @@ whose data type is a fixed-size-list of floats.
|
||||
|
||||
### distanceType()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
distanceType(distanceType): VectorQuery
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **distanceType**(`distanceType`): [`VectorQuery`](VectorQuery.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Set the distance metric to use
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -142,7 +114,7 @@ use. See
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **distanceType**: `"l2"` \| `"cosine"` \| `"dot"`
|
||||
• **distanceType**: `"l2"` \| `"cosine"` \| `"dot"`
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -163,13 +135,11 @@ By default "l2" is used.
|
||||
|
||||
### doCall()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
protected doCall(fn): void
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `protected` **doCall**(`fn`): `void`
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **fn**
|
||||
• **fn**
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -181,41 +151,15 @@ protected doCall(fn): void
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### ef()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
ef(ef): VectorQuery
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Set the number of candidates to consider during the search
|
||||
|
||||
This argument is only used when the vector column has an HNSW index.
|
||||
If there is no index then this value is ignored.
|
||||
|
||||
Increasing this value will increase the recall of your query but will
|
||||
also increase the latency of your query. The default value is 1.5*limit.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **ef**: `number`
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
[`VectorQuery`](VectorQuery.md)
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### execute()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
protected execute(options?): RecordBatchIterator
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `protected` **execute**(`options`?): [`RecordBatchIterator`](RecordBatchIterator.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Execute the query and return the results as an
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **options?**: `Partial`<`QueryExecutionOptions`>
|
||||
• **options?**: `Partial`<`QueryExecutionOptions`>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -241,16 +185,15 @@ single query)
|
||||
|
||||
### explainPlan()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
explainPlan(verbose): Promise<string>
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **explainPlan**(`verbose`): `Promise`<`string`>
|
||||
|
||||
Generates an explanation of the query execution plan.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **verbose**: `boolean` = `false`
|
||||
If true, provides a more detailed explanation. Defaults to false.
|
||||
• **verbose**: `boolean` = `false`
|
||||
|
||||
If true, provides a more detailed explanation. Defaults to false.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -275,38 +218,15 @@ const plan = await table.query().nearestTo([0.5, 0.2]).explainPlan();
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### fastSearch()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
fastSearch(): this
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Skip searching un-indexed data. This can make search faster, but will miss
|
||||
any data that is not yet indexed.
|
||||
|
||||
Use lancedb.Table#optimize to index all un-indexed data.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
`this`
|
||||
|
||||
#### Inherited from
|
||||
|
||||
[`QueryBase`](QueryBase.md).[`fastSearch`](QueryBase.md#fastsearch)
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### ~~filter()~~
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
filter(predicate): this
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **filter**(`predicate`): `this`
|
||||
|
||||
A filter statement to be applied to this query.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **predicate**: `string`
|
||||
• **predicate**: `string`
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -326,33 +246,9 @@ Use `where` instead
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### fullTextSearch()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
fullTextSearch(query, options?): this
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **query**: `string`
|
||||
|
||||
* **options?**: `Partial`<`FullTextSearchOptions`>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
`this`
|
||||
|
||||
#### Inherited from
|
||||
|
||||
[`QueryBase`](QueryBase.md).[`fullTextSearch`](QueryBase.md#fulltextsearch)
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### limit()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
limit(limit): this
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **limit**(`limit`): `this`
|
||||
|
||||
Set the maximum number of results to return.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -361,7 +257,7 @@ called then every valid row from the table will be returned.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **limit**: `number`
|
||||
• **limit**: `number`
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -375,13 +271,11 @@ called then every valid row from the table will be returned.
|
||||
|
||||
### nativeExecute()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
protected nativeExecute(options?): Promise<RecordBatchIterator>
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `protected` **nativeExecute**(`options`?): `Promise`<`RecordBatchIterator`>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **options?**: `Partial`<`QueryExecutionOptions`>
|
||||
• **options?**: `Partial`<`QueryExecutionOptions`>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -395,9 +289,7 @@ protected nativeExecute(options?): Promise<RecordBatchIterator>
|
||||
|
||||
### nprobes()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
nprobes(nprobes): VectorQuery
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **nprobes**(`nprobes`): [`VectorQuery`](VectorQuery.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Set the number of partitions to search (probe)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -422,7 +314,7 @@ you the desired recall.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **nprobes**: `number`
|
||||
• **nprobes**: `number`
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -430,31 +322,9 @@ you the desired recall.
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### offset()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
offset(offset): this
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **offset**: `number`
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
`this`
|
||||
|
||||
#### Inherited from
|
||||
|
||||
[`QueryBase`](QueryBase.md).[`offset`](QueryBase.md#offset)
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### postfilter()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
postfilter(): VectorQuery
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **postfilter**(): [`VectorQuery`](VectorQuery.md)
|
||||
|
||||
If this is called then filtering will happen after the vector search instead of
|
||||
before.
|
||||
@@ -486,9 +356,7 @@ factor can often help restore some of the results lost by post filtering.
|
||||
|
||||
### refineFactor()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
refineFactor(refineFactor): VectorQuery
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **refineFactor**(`refineFactor`): [`VectorQuery`](VectorQuery.md)
|
||||
|
||||
A multiplier to control how many additional rows are taken during the refine step
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -520,7 +388,7 @@ distance between the query vector and the actual uncompressed vector.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **refineFactor**: `number`
|
||||
• **refineFactor**: `number`
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -530,9 +398,7 @@ distance between the query vector and the actual uncompressed vector.
|
||||
|
||||
### select()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
select(columns): this
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **select**(`columns`): `this`
|
||||
|
||||
Return only the specified columns.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -556,7 +422,7 @@ input to this method would be:
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **columns**: `string` \| `string`[] \| `Record`<`string`, `string`> \| `Map`<`string`, `string`>
|
||||
• **columns**: `string` \| `string`[] \| `Record`<`string`, `string`> \| `Map`<`string`, `string`>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -583,15 +449,13 @@ object insertion order is easy to get wrong and `Map` is more foolproof.
|
||||
|
||||
### toArray()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
toArray(options?): Promise<any[]>
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **toArray**(`options`?): `Promise`<`any`[]>
|
||||
|
||||
Collect the results as an array of objects.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **options?**: `Partial`<`QueryExecutionOptions`>
|
||||
• **options?**: `Partial`<`QueryExecutionOptions`>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -605,15 +469,13 @@ Collect the results as an array of objects.
|
||||
|
||||
### toArrow()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
toArrow(options?): Promise<Table<any>>
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **toArrow**(`options`?): `Promise`<`Table`<`any`>>
|
||||
|
||||
Collect the results as an Arrow
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **options?**: `Partial`<`QueryExecutionOptions`>
|
||||
• **options?**: `Partial`<`QueryExecutionOptions`>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -631,9 +493,7 @@ ArrowTable.
|
||||
|
||||
### where()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
where(predicate): this
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **where**(`predicate`): `this`
|
||||
|
||||
A filter statement to be applied to this query.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -641,7 +501,7 @@ The filter should be supplied as an SQL query string. For example:
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **predicate**: `string`
|
||||
• **predicate**: `string`
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -661,25 +521,3 @@ on the filter column(s).
|
||||
#### Inherited from
|
||||
|
||||
[`QueryBase`](QueryBase.md).[`where`](QueryBase.md#where)
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### withRowId()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
withRowId(): this
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Whether to return the row id in the results.
|
||||
|
||||
This column can be used to match results between different queries. For
|
||||
example, to match results from a full text search and a vector search in
|
||||
order to perform hybrid search.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
`this`
|
||||
|
||||
#### Inherited from
|
||||
|
||||
[`QueryBase`](QueryBase.md).[`withRowId`](QueryBase.md#withrowid)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -12,22 +12,16 @@ Write mode for writing a table.
|
||||
|
||||
### Append
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
Append: "Append";
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **Append**: `"Append"`
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### Create
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
Create: "Create";
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **Create**: `"Create"`
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### Overwrite
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
Overwrite: "Overwrite";
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **Overwrite**: `"Overwrite"`
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -8,9 +8,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
## connect(uri, opts)
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
function connect(uri, opts?): Promise<Connection>
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **connect**(`uri`, `opts`?): `Promise`<[`Connection`](../classes/Connection.md)>
|
||||
|
||||
Connect to a LanceDB instance at the given URI.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -22,11 +20,12 @@ Accepted formats:
|
||||
|
||||
### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **uri**: `string`
|
||||
The uri of the database. If the database uri starts
|
||||
with `db://` then it connects to a remote database.
|
||||
• **uri**: `string`
|
||||
|
||||
* **opts?**: `Partial`<[`ConnectionOptions`](../interfaces/ConnectionOptions.md)>
|
||||
The uri of the database. If the database uri starts
|
||||
with `db://` then it connects to a remote database.
|
||||
|
||||
• **opts?**: `Partial`<[`ConnectionOptions`](../interfaces/ConnectionOptions.md) \| `RemoteConnectionOptions`>
|
||||
|
||||
### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -51,9 +50,7 @@ const conn = await connect(
|
||||
|
||||
## connect(opts)
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
function connect(opts): Promise<Connection>
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **connect**(`opts`): `Promise`<[`Connection`](../classes/Connection.md)>
|
||||
|
||||
Connect to a LanceDB instance at the given URI.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -65,7 +62,7 @@ Accepted formats:
|
||||
|
||||
### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **opts**: `Partial`<[`ConnectionOptions`](../interfaces/ConnectionOptions.md)> & `object`
|
||||
• **opts**: `Partial`<[`ConnectionOptions`](../interfaces/ConnectionOptions.md) \| `RemoteConnectionOptions`> & `object`
|
||||
|
||||
### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -6,12 +6,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# Function: makeArrowTable()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
function makeArrowTable(
|
||||
data,
|
||||
options?,
|
||||
metadata?): ArrowTable
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **makeArrowTable**(`data`, `options`?, `metadata`?): `ArrowTable`
|
||||
|
||||
An enhanced version of the makeTable function from Apache Arrow
|
||||
that supports nested fields and embeddings columns.
|
||||
@@ -45,11 +40,11 @@ rules are as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
## Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **data**: `Record`<`string`, `unknown`>[]
|
||||
• **data**: `Record`<`string`, `unknown`>[]
|
||||
|
||||
* **options?**: `Partial`<[`MakeArrowTableOptions`](../classes/MakeArrowTableOptions.md)>
|
||||
• **options?**: `Partial`<[`MakeArrowTableOptions`](../classes/MakeArrowTableOptions.md)>
|
||||
|
||||
* **metadata?**: `Map`<`string`, `string`>
|
||||
• **metadata?**: `Map`<`string`, `string`>
|
||||
|
||||
## Returns
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -28,19 +28,17 @@
|
||||
|
||||
- [AddColumnsSql](interfaces/AddColumnsSql.md)
|
||||
- [AddDataOptions](interfaces/AddDataOptions.md)
|
||||
- [ClientConfig](interfaces/ClientConfig.md)
|
||||
- [ColumnAlteration](interfaces/ColumnAlteration.md)
|
||||
- [ConnectionOptions](interfaces/ConnectionOptions.md)
|
||||
- [CreateTableOptions](interfaces/CreateTableOptions.md)
|
||||
- [ExecutableQuery](interfaces/ExecutableQuery.md)
|
||||
- [IndexConfig](interfaces/IndexConfig.md)
|
||||
- [IndexMetadata](interfaces/IndexMetadata.md)
|
||||
- [IndexOptions](interfaces/IndexOptions.md)
|
||||
- [IndexStatistics](interfaces/IndexStatistics.md)
|
||||
- [IvfPqOptions](interfaces/IvfPqOptions.md)
|
||||
- [OptimizeOptions](interfaces/OptimizeOptions.md)
|
||||
- [RetryConfig](interfaces/RetryConfig.md)
|
||||
- [FtsOptions](interfaces/FtsOptions.md)
|
||||
- [TableNamesOptions](interfaces/TableNamesOptions.md)
|
||||
- [TimeoutConfig](interfaces/TimeoutConfig.md)
|
||||
- [UpdateOptions](interfaces/UpdateOptions.md)
|
||||
- [WriteOptions](interfaces/WriteOptions.md)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -12,9 +12,7 @@ A definition of a new column to add to a table.
|
||||
|
||||
### name
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
name: string;
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **name**: `string`
|
||||
|
||||
The name of the new column.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -22,9 +20,7 @@ The name of the new column.
|
||||
|
||||
### valueSql
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
valueSql: string;
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **valueSql**: `string`
|
||||
|
||||
The values to populate the new column with, as a SQL expression.
|
||||
The expression can reference other columns in the table.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -12,9 +12,7 @@ Options for adding data to a table.
|
||||
|
||||
### mode
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
mode: "append" | "overwrite";
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **mode**: `"append"` \| `"overwrite"`
|
||||
|
||||
If "append" (the default) then the new data will be added to the table
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,31 +0,0 @@
|
||||
[**@lancedb/lancedb**](../README.md) • **Docs**
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
[@lancedb/lancedb](../globals.md) / ClientConfig
|
||||
|
||||
# Interface: ClientConfig
|
||||
|
||||
## Properties
|
||||
|
||||
### retryConfig?
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
optional retryConfig: RetryConfig;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### timeoutConfig?
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
optional timeoutConfig: TimeoutConfig;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### userAgent?
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
optional userAgent: string;
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -13,29 +13,9 @@ must be provided.
|
||||
|
||||
## Properties
|
||||
|
||||
### dataType?
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
optional dataType: string;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
A new data type for the column. If not provided then the data type will not be changed.
|
||||
Changing data types is limited to casting to the same general type. For example, these
|
||||
changes are valid:
|
||||
* `int32` -> `int64` (integers)
|
||||
* `double` -> `float` (floats)
|
||||
* `string` -> `large_string` (strings)
|
||||
But these changes are not:
|
||||
* `int32` -> `double` (mix integers and floats)
|
||||
* `string` -> `int32` (mix strings and integers)
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### nullable?
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
optional nullable: boolean;
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `optional` **nullable**: `boolean`
|
||||
|
||||
Set the new nullability. Note that a nullable column cannot be made non-nullable.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -43,9 +23,7 @@ Set the new nullability. Note that a nullable column cannot be made non-nullable
|
||||
|
||||
### path
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
path: string;
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **path**: `string`
|
||||
|
||||
The path to the column to alter. This is a dot-separated path to the column.
|
||||
If it is a top-level column then it is just the name of the column. If it is
|
||||
@@ -56,9 +34,7 @@ a nested column then it is the path to the column, e.g. "a.b.c" for a column
|
||||
|
||||
### rename?
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
optional rename: string;
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `optional` **rename**: `string`
|
||||
|
||||
The new name of the column. If not provided then the name will not be changed.
|
||||
This must be distinct from the names of all other columns in the table.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -8,44 +8,9 @@
|
||||
|
||||
## Properties
|
||||
|
||||
### apiKey?
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
optional apiKey: string;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
(For LanceDB cloud only): the API key to use with LanceDB Cloud.
|
||||
|
||||
Can also be set via the environment variable `LANCEDB_API_KEY`.
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### clientConfig?
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
optional clientConfig: ClientConfig;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
(For LanceDB cloud only): configuration for the remote HTTP client.
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### hostOverride?
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
optional hostOverride: string;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
(For LanceDB cloud only): the host to use for LanceDB cloud. Used
|
||||
for testing purposes.
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### readConsistencyInterval?
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
optional readConsistencyInterval: number;
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `optional` **readConsistencyInterval**: `number`
|
||||
|
||||
(For LanceDB OSS only): The interval, in seconds, at which to check for
|
||||
updates to the table from other processes. If None, then consistency is not
|
||||
@@ -59,22 +24,9 @@ always consistent.
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### region?
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
optional region: string;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
(For LanceDB cloud only): the region to use for LanceDB cloud.
|
||||
Defaults to 'us-east-1'.
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### storageOptions?
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
optional storageOptions: Record<string, string>;
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `optional` **storageOptions**: `Record`<`string`, `string`>
|
||||
|
||||
(For LanceDB OSS only): configuration for object storage.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -8,46 +8,15 @@
|
||||
|
||||
## Properties
|
||||
|
||||
### dataStorageVersion?
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
optional dataStorageVersion: string;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The version of the data storage format to use.
|
||||
|
||||
The default is `stable`.
|
||||
Set to "legacy" to use the old format.
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### embeddingFunction?
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
optional embeddingFunction: EmbeddingFunctionConfig;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### enableV2ManifestPaths?
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
optional enableV2ManifestPaths: boolean;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Use the new V2 manifest paths. These paths provide more efficient
|
||||
opening of datasets with many versions on object stores. WARNING:
|
||||
turning this on will make the dataset unreadable for older versions
|
||||
of LanceDB (prior to 0.10.0). To migrate an existing dataset, instead
|
||||
use the LocalTable#migrateManifestPathsV2 method.
|
||||
> `optional` **embeddingFunction**: [`EmbeddingFunctionConfig`](../namespaces/embedding/interfaces/EmbeddingFunctionConfig.md)
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### existOk
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
existOk: boolean;
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **existOk**: `boolean`
|
||||
|
||||
If this is true and the table already exists and the mode is "create"
|
||||
then no error will be raised.
|
||||
@@ -56,9 +25,7 @@ then no error will be raised.
|
||||
|
||||
### mode
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
mode: "overwrite" | "create";
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **mode**: `"overwrite"` \| `"create"`
|
||||
|
||||
The mode to use when creating the table.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -72,17 +39,13 @@ If this is set to "overwrite" then any existing table will be replaced.
|
||||
|
||||
### schema?
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
optional schema: SchemaLike;
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `optional` **schema**: `SchemaLike`
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### storageOptions?
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
optional storageOptions: Record<string, string>;
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `optional` **storageOptions**: `Record`<`string`, `string`>
|
||||
|
||||
Configuration for object storage.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -95,12 +58,8 @@ The available options are described at https://lancedb.github.io/lancedb/guides/
|
||||
|
||||
### useLegacyFormat?
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
optional useLegacyFormat: boolean;
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `optional` **useLegacyFormat**: `boolean`
|
||||
|
||||
If true then data files will be written with the legacy format
|
||||
|
||||
The default is false.
|
||||
|
||||
Deprecated. Use data storage version instead.
|
||||
The default is true while the new format is in beta
|
||||
|
||||
25
docs/src/js/interfaces/FtsOptions.md
Normal file
25
docs/src/js/interfaces/FtsOptions.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,25 @@
|
||||
[**@lancedb/lancedb**](../README.md) • **Docs**
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
[@lancedb/lancedb](../globals.md) / FtsOptions
|
||||
|
||||
# Interface: FtsOptions
|
||||
|
||||
Options to create an `FTS` index
|
||||
|
||||
## Properties
|
||||
|
||||
### withPosition?
|
||||
|
||||
> `optional` **withPosition**: `boolean`
|
||||
|
||||
Whether to store the positions of the term in the document.
|
||||
|
||||
If this is true then the index will store the positions of the term in the document.
|
||||
This allows phrase queries to be run. But it also increases the size of the index,
|
||||
and the time to build the index.
|
||||
|
||||
The default value is true.
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
@@ -12,9 +12,7 @@ A description of an index currently configured on a column
|
||||
|
||||
### columns
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
columns: string[];
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **columns**: `string`[]
|
||||
|
||||
The columns in the index
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -25,9 +23,7 @@ be more columns to represent composite indices.
|
||||
|
||||
### indexType
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
indexType: string;
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **indexType**: `string`
|
||||
|
||||
The type of the index
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -35,8 +31,6 @@ The type of the index
|
||||
|
||||
### name
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
name: string;
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **name**: `string`
|
||||
|
||||
The name of the index
|
||||
|
||||
19
docs/src/js/interfaces/IndexMetadata.md
Normal file
19
docs/src/js/interfaces/IndexMetadata.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,19 @@
|
||||
[**@lancedb/lancedb**](../README.md) • **Docs**
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
[@lancedb/lancedb](../globals.md) / IndexMetadata
|
||||
|
||||
# Interface: IndexMetadata
|
||||
|
||||
## Properties
|
||||
|
||||
### indexType?
|
||||
|
||||
> `optional` **indexType**: `string`
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### metricType?
|
||||
|
||||
> `optional` **metricType**: `string`
|
||||
@@ -10,9 +10,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
### config?
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
optional config: Index;
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `optional` **config**: [`Index`](../classes/Index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Advanced index configuration
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -28,9 +26,7 @@ will be used to determine the most useful kind of index to create.
|
||||
|
||||
### replace?
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
optional replace: boolean;
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `optional` **replace**: `boolean`
|
||||
|
||||
Whether to replace the existing index
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -8,52 +8,32 @@
|
||||
|
||||
## Properties
|
||||
|
||||
### distanceType?
|
||||
### indexType?
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
optional distanceType: string;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The type of the distance function used by the index. This is only
|
||||
present for vector indices. Scalar and full text search indices do
|
||||
not have a distance function.
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### indexType
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
indexType: string;
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `optional` **indexType**: `string`
|
||||
|
||||
The type of the index
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### indices
|
||||
|
||||
> **indices**: [`IndexMetadata`](IndexMetadata.md)[]
|
||||
|
||||
The metadata for each index
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### numIndexedRows
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
numIndexedRows: number;
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **numIndexedRows**: `number`
|
||||
|
||||
The number of rows indexed by the index
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### numIndices?
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
optional numIndices: number;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The number of parts this index is split into.
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### numUnindexedRows
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
numUnindexedRows: number;
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **numUnindexedRows**: `number`
|
||||
|
||||
The number of rows not indexed
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -12,9 +12,7 @@ Options to create an `IVF_PQ` index
|
||||
|
||||
### distanceType?
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
optional distanceType: "l2" | "cosine" | "dot";
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `optional` **distanceType**: `"l2"` \| `"cosine"` \| `"dot"`
|
||||
|
||||
Distance type to use to build the index.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -52,9 +50,7 @@ L2 norm is 1), then dot distance is equivalent to the cosine distance.
|
||||
|
||||
### maxIterations?
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
optional maxIterations: number;
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `optional` **maxIterations**: `number`
|
||||
|
||||
Max iteration to train IVF kmeans.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -70,9 +66,7 @@ The default value is 50.
|
||||
|
||||
### numPartitions?
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
optional numPartitions: number;
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `optional` **numPartitions**: `number`
|
||||
|
||||
The number of IVF partitions to create.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -88,9 +82,7 @@ part of the search (searching within a partition) will be slow.
|
||||
|
||||
### numSubVectors?
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
optional numSubVectors: number;
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `optional` **numSubVectors**: `number`
|
||||
|
||||
Number of sub-vectors of PQ.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -109,9 +101,7 @@ will likely result in poor performance.
|
||||
|
||||
### sampleRate?
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
optional sampleRate: number;
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `optional` **sampleRate**: `number`
|
||||
|
||||
The number of vectors, per partition, to sample when training IVF kmeans.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,39 +0,0 @@
|
||||
[**@lancedb/lancedb**](../README.md) • **Docs**
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
[@lancedb/lancedb](../globals.md) / OptimizeOptions
|
||||
|
||||
# Interface: OptimizeOptions
|
||||
|
||||
## Properties
|
||||
|
||||
### cleanupOlderThan
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
cleanupOlderThan: Date;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If set then all versions older than the given date
|
||||
be removed. The current version will never be removed.
|
||||
The default is 7 days
|
||||
|
||||
#### Example
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
// Delete all versions older than 1 day
|
||||
const olderThan = new Date();
|
||||
olderThan.setDate(olderThan.getDate() - 1));
|
||||
tbl.cleanupOlderVersions(olderThan);
|
||||
|
||||
// Delete all versions except the current version
|
||||
tbl.cleanupOlderVersions(new Date());
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### deleteUnverified
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
deleteUnverified: boolean;
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -1,90 +0,0 @@
|
||||
[**@lancedb/lancedb**](../README.md) • **Docs**
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
[@lancedb/lancedb](../globals.md) / RetryConfig
|
||||
|
||||
# Interface: RetryConfig
|
||||
|
||||
Retry configuration for the remote HTTP client.
|
||||
|
||||
## Properties
|
||||
|
||||
### backoffFactor?
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
optional backoffFactor: number;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The backoff factor to apply between retries. Default is 0.25. Between each retry
|
||||
the client will wait for the amount of seconds:
|
||||
`{backoff factor} * (2 ** ({number of previous retries}))`. So for the default
|
||||
of 0.25, the first retry will wait 0.25 seconds, the second retry will wait 0.5
|
||||
seconds, the third retry will wait 1 second, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
You can also set this via the environment variable
|
||||
`LANCE_CLIENT_RETRY_BACKOFF_FACTOR`.
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### backoffJitter?
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
optional backoffJitter: number;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The jitter to apply to the backoff factor, in seconds. Default is 0.25.
|
||||
|
||||
A random value between 0 and `backoff_jitter` will be added to the backoff
|
||||
factor in seconds. So for the default of 0.25 seconds, between 0 and 250
|
||||
milliseconds will be added to the sleep between each retry.
|
||||
|
||||
You can also set this via the environment variable
|
||||
`LANCE_CLIENT_RETRY_BACKOFF_JITTER`.
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### connectRetries?
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
optional connectRetries: number;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The maximum number of retries for connection errors. Default is 3. You
|
||||
can also set this via the environment variable `LANCE_CLIENT_CONNECT_RETRIES`.
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### readRetries?
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
optional readRetries: number;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The maximum number of retries for read errors. Default is 3. You can also
|
||||
set this via the environment variable `LANCE_CLIENT_READ_RETRIES`.
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### retries?
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
optional retries: number;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The maximum number of retries for a request. Default is 3. You can also
|
||||
set this via the environment variable `LANCE_CLIENT_MAX_RETRIES`.
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### statuses?
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
optional statuses: number[];
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The HTTP status codes for which to retry the request. Default is
|
||||
[429, 500, 502, 503].
|
||||
|
||||
You can also set this via the environment variable
|
||||
`LANCE_CLIENT_RETRY_STATUSES`. Use a comma-separated list of integers.
|
||||
@@ -10,9 +10,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
### limit?
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
optional limit: number;
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `optional` **limit**: `number`
|
||||
|
||||
An optional limit to the number of results to return.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -20,9 +18,7 @@ An optional limit to the number of results to return.
|
||||
|
||||
### startAfter?
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
optional startAfter: string;
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `optional` **startAfter**: `string`
|
||||
|
||||
If present, only return names that come lexicographically after the
|
||||
supplied value.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,46 +0,0 @@
|
||||
[**@lancedb/lancedb**](../README.md) • **Docs**
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
[@lancedb/lancedb](../globals.md) / TimeoutConfig
|
||||
|
||||
# Interface: TimeoutConfig
|
||||
|
||||
Timeout configuration for remote HTTP client.
|
||||
|
||||
## Properties
|
||||
|
||||
### connectTimeout?
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
optional connectTimeout: number;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The timeout for establishing a connection in seconds. Default is 120
|
||||
seconds (2 minutes). This can also be set via the environment variable
|
||||
`LANCE_CLIENT_CONNECT_TIMEOUT`, as an integer number of seconds.
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### poolIdleTimeout?
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
optional poolIdleTimeout: number;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The timeout for keeping idle connections in the connection pool in seconds.
|
||||
Default is 300 seconds (5 minutes). This can also be set via the
|
||||
environment variable `LANCE_CLIENT_CONNECTION_TIMEOUT`, as an integer
|
||||
number of seconds.
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### readTimeout?
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
optional readTimeout: number;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The timeout for reading data from the server in seconds. Default is 300
|
||||
seconds (5 minutes). This can also be set via the environment variable
|
||||
`LANCE_CLIENT_READ_TIMEOUT`, as an integer number of seconds.
|
||||
@@ -10,9 +10,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
### where
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
where: string;
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **where**: `string`
|
||||
|
||||
A filter that limits the scope of the update.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -12,8 +12,6 @@ Write options when creating a Table.
|
||||
|
||||
### mode?
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
optional mode: WriteMode;
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `optional` **mode**: [`WriteMode`](../enumerations/WriteMode.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Write mode for writing to a table.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -12,12 +12,16 @@
|
||||
|
||||
- [EmbeddingFunction](classes/EmbeddingFunction.md)
|
||||
- [EmbeddingFunctionRegistry](classes/EmbeddingFunctionRegistry.md)
|
||||
- [TextEmbeddingFunction](classes/TextEmbeddingFunction.md)
|
||||
- [OpenAIEmbeddingFunction](classes/OpenAIEmbeddingFunction.md)
|
||||
|
||||
### Interfaces
|
||||
|
||||
- [EmbeddingFunctionConfig](interfaces/EmbeddingFunctionConfig.md)
|
||||
|
||||
### Type Aliases
|
||||
|
||||
- [OpenAIOptions](type-aliases/OpenAIOptions.md)
|
||||
|
||||
### Functions
|
||||
|
||||
- [LanceSchema](functions/LanceSchema.md)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -10,7 +10,7 @@ An embedding function that automatically creates vector representation for a giv
|
||||
|
||||
## Extended by
|
||||
|
||||
- [`TextEmbeddingFunction`](TextEmbeddingFunction.md)
|
||||
- [`OpenAIEmbeddingFunction`](OpenAIEmbeddingFunction.md)
|
||||
|
||||
## Type Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -22,9 +22,7 @@ An embedding function that automatically creates vector representation for a giv
|
||||
|
||||
### new EmbeddingFunction()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
new EmbeddingFunction<T, M>(): EmbeddingFunction<T, M>
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **new EmbeddingFunction**<`T`, `M`>(): [`EmbeddingFunction`](EmbeddingFunction.md)<`T`, `M`>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -34,15 +32,13 @@ new EmbeddingFunction<T, M>(): EmbeddingFunction<T, M>
|
||||
|
||||
### computeQueryEmbeddings()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
computeQueryEmbeddings(data): Promise<number[] | Float32Array | Float64Array>
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **computeQueryEmbeddings**(`data`): `Promise`<`number`[] \| `Float32Array` \| `Float64Array`>
|
||||
|
||||
Compute the embeddings for a single query
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **data**: `T`
|
||||
• **data**: `T`
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -52,15 +48,13 @@ Compute the embeddings for a single query
|
||||
|
||||
### computeSourceEmbeddings()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
abstract computeSourceEmbeddings(data): Promise<number[][] | Float32Array[] | Float64Array[]>
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `abstract` **computeSourceEmbeddings**(`data`): `Promise`<`number`[][] \| `Float32Array`[] \| `Float64Array`[]>
|
||||
|
||||
Creates a vector representation for the given values.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **data**: `T`[]
|
||||
• **data**: `T`[]
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -70,9 +64,7 @@ Creates a vector representation for the given values.
|
||||
|
||||
### embeddingDataType()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
abstract embeddingDataType(): Float<Floats>
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `abstract` **embeddingDataType**(): `Float`<`Floats`>
|
||||
|
||||
The datatype of the embeddings
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -82,23 +74,9 @@ The datatype of the embeddings
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### init()?
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
optional init(): Promise<void>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
`Promise`<`void`>
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### ndims()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
ndims(): undefined | number
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **ndims**(): `undefined` \| `number`
|
||||
|
||||
The number of dimensions of the embeddings
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -110,16 +88,15 @@ The number of dimensions of the embeddings
|
||||
|
||||
### sourceField()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
sourceField(optionsOrDatatype): [DataType<Type, any>, Map<string, EmbeddingFunction<any, FunctionOptions>>]
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **sourceField**(`optionsOrDatatype`): [`DataType`<`Type`, `any`>, `Map`<`string`, [`EmbeddingFunction`](EmbeddingFunction.md)<`any`, `FunctionOptions`>>]
|
||||
|
||||
sourceField is used in combination with `LanceSchema` to provide a declarative data model
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **optionsOrDatatype**: `DataType`<`Type`, `any`> \| `Partial`<`FieldOptions`<`DataType`<`Type`, `any`>>>
|
||||
The options for the field or the datatype
|
||||
• **optionsOrDatatype**: `DataType`<`Type`, `any`> \| `Partial`<`FieldOptions`<`DataType`<`Type`, `any`>>>
|
||||
|
||||
The options for the field or the datatype
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -133,9 +110,7 @@ lancedb.LanceSchema
|
||||
|
||||
### toJSON()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
abstract toJSON(): Partial<M>
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `abstract` **toJSON**(): `Partial`<`M`>
|
||||
|
||||
Convert the embedding function to a JSON object
|
||||
It is used to serialize the embedding function to the schema
|
||||
@@ -170,15 +145,13 @@ class MyEmbeddingFunction extends EmbeddingFunction {
|
||||
|
||||
### vectorField()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
vectorField(optionsOrDatatype?): [DataType<Type, any>, Map<string, EmbeddingFunction<any, FunctionOptions>>]
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **vectorField**(`optionsOrDatatype`?): [`DataType`<`Type`, `any`>, `Map`<`string`, [`EmbeddingFunction`](EmbeddingFunction.md)<`any`, `FunctionOptions`>>]
|
||||
|
||||
vectorField is used in combination with `LanceSchema` to provide a declarative data model
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **optionsOrDatatype?**: `DataType`<`Type`, `any`> \| `Partial`<`FieldOptions`<`DataType`<`Type`, `any`>>>
|
||||
• **optionsOrDatatype?**: `DataType`<`Type`, `any`> \| `Partial`<`FieldOptions`<`DataType`<`Type`, `any`>>>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -15,9 +15,7 @@ or TextEmbeddingFunction and registering it with the registry
|
||||
|
||||
### new EmbeddingFunctionRegistry()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
new EmbeddingFunctionRegistry(): EmbeddingFunctionRegistry
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **new EmbeddingFunctionRegistry**(): [`EmbeddingFunctionRegistry`](EmbeddingFunctionRegistry.md)
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -27,13 +25,11 @@ new EmbeddingFunctionRegistry(): EmbeddingFunctionRegistry
|
||||
|
||||
### functionToMetadata()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
functionToMetadata(conf): Record<string, any>
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **functionToMetadata**(`conf`): `Record`<`string`, `any`>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **conf**: [`EmbeddingFunctionConfig`](../interfaces/EmbeddingFunctionConfig.md)
|
||||
• **conf**: [`EmbeddingFunctionConfig`](../interfaces/EmbeddingFunctionConfig.md)
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -43,9 +39,7 @@ functionToMetadata(conf): Record<string, any>
|
||||
|
||||
### get()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
get<T>(name): undefined | EmbeddingFunctionCreate<T>
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **get**<`T`, `Name`>(`name`): `Name` *extends* `"openai"` ? `EmbeddingFunctionCreate`<[`OpenAIEmbeddingFunction`](OpenAIEmbeddingFunction.md)> : `undefined` \| `EmbeddingFunctionCreate`<`T`>
|
||||
|
||||
Fetch an embedding function by name
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -53,26 +47,27 @@ Fetch an embedding function by name
|
||||
|
||||
• **T** *extends* [`EmbeddingFunction`](EmbeddingFunction.md)<`unknown`, `FunctionOptions`>
|
||||
|
||||
• **Name** *extends* `string` = `""`
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **name**: `string`
|
||||
The name of the function
|
||||
• **name**: `Name` *extends* `"openai"` ? `"openai"` : `string`
|
||||
|
||||
The name of the function
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
`undefined` \| `EmbeddingFunctionCreate`<`T`>
|
||||
`Name` *extends* `"openai"` ? `EmbeddingFunctionCreate`<[`OpenAIEmbeddingFunction`](OpenAIEmbeddingFunction.md)> : `undefined` \| `EmbeddingFunctionCreate`<`T`>
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### getTableMetadata()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
getTableMetadata(functions): Map<string, string>
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **getTableMetadata**(`functions`): `Map`<`string`, `string`>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **functions**: [`EmbeddingFunctionConfig`](../interfaces/EmbeddingFunctionConfig.md)[]
|
||||
• **functions**: [`EmbeddingFunctionConfig`](../interfaces/EmbeddingFunctionConfig.md)[]
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -80,25 +75,9 @@ getTableMetadata(functions): Map<string, string>
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### length()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
length(): number
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Get the number of registered functions
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
`number`
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### register()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
register<T>(this, alias?): (ctor) => any
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **register**<`T`>(`this`, `alias`?): (`ctor`) => `any`
|
||||
|
||||
Register an embedding function
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -108,9 +87,9 @@ Register an embedding function
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **this**: [`EmbeddingFunctionRegistry`](EmbeddingFunctionRegistry.md)
|
||||
• **this**: [`EmbeddingFunctionRegistry`](EmbeddingFunctionRegistry.md)
|
||||
|
||||
* **alias?**: `string`
|
||||
• **alias?**: `string`
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -118,7 +97,7 @@ Register an embedding function
|
||||
|
||||
##### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **ctor**: `T`
|
||||
• **ctor**: `T`
|
||||
|
||||
##### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -132,15 +111,13 @@ Error if the function is already registered
|
||||
|
||||
### reset()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
reset(this): void
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **reset**(`this`): `void`
|
||||
|
||||
reset the registry to the initial state
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **this**: [`EmbeddingFunctionRegistry`](EmbeddingFunctionRegistry.md)
|
||||
• **this**: [`EmbeddingFunctionRegistry`](EmbeddingFunctionRegistry.md)
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -2,33 +2,31 @@
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
[@lancedb/lancedb](../../../globals.md) / [embedding](../README.md) / TextEmbeddingFunction
|
||||
[@lancedb/lancedb](../../../globals.md) / [embedding](../README.md) / OpenAIEmbeddingFunction
|
||||
|
||||
# Class: `abstract` TextEmbeddingFunction<M>
|
||||
# Class: OpenAIEmbeddingFunction
|
||||
|
||||
an abstract class for implementing embedding functions that take text as input
|
||||
An embedding function that automatically creates vector representation for a given column.
|
||||
|
||||
## Extends
|
||||
|
||||
- [`EmbeddingFunction`](EmbeddingFunction.md)<`string`, `M`>
|
||||
|
||||
## Type Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
• **M** *extends* `FunctionOptions` = `FunctionOptions`
|
||||
- [`EmbeddingFunction`](EmbeddingFunction.md)<`string`, `Partial`<[`OpenAIOptions`](../type-aliases/OpenAIOptions.md)>>
|
||||
|
||||
## Constructors
|
||||
|
||||
### new TextEmbeddingFunction()
|
||||
### new OpenAIEmbeddingFunction()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
new TextEmbeddingFunction<M>(): TextEmbeddingFunction<M>
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **new OpenAIEmbeddingFunction**(`options`): [`OpenAIEmbeddingFunction`](OpenAIEmbeddingFunction.md)
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
• **options**: `Partial`<[`OpenAIOptions`](../type-aliases/OpenAIOptions.md)> = `...`
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
[`TextEmbeddingFunction`](TextEmbeddingFunction.md)<`M`>
|
||||
[`OpenAIEmbeddingFunction`](OpenAIEmbeddingFunction.md)
|
||||
|
||||
#### Inherited from
|
||||
#### Overrides
|
||||
|
||||
[`EmbeddingFunction`](EmbeddingFunction.md).[`constructor`](EmbeddingFunction.md#constructors)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -36,19 +34,17 @@ new TextEmbeddingFunction<M>(): TextEmbeddingFunction<M>
|
||||
|
||||
### computeQueryEmbeddings()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
computeQueryEmbeddings(data): Promise<number[] | Float32Array | Float64Array>
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **computeQueryEmbeddings**(`data`): `Promise`<`number`[]>
|
||||
|
||||
Compute the embeddings for a single query
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **data**: `string`
|
||||
• **data**: `string`
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
`Promise`<`number`[] \| `Float32Array` \| `Float64Array`>
|
||||
`Promise`<`number`[]>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Overrides
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -58,19 +54,17 @@ Compute the embeddings for a single query
|
||||
|
||||
### computeSourceEmbeddings()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
computeSourceEmbeddings(data): Promise<number[][] | Float32Array[] | Float64Array[]>
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **computeSourceEmbeddings**(`data`): `Promise`<`number`[][]>
|
||||
|
||||
Creates a vector representation for the given values.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **data**: `string`[]
|
||||
• **data**: `string`[]
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
`Promise`<`number`[][] \| `Float32Array`[] \| `Float64Array`[]>
|
||||
`Promise`<`number`[][]>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Overrides
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -80,9 +74,7 @@ Creates a vector representation for the given values.
|
||||
|
||||
### embeddingDataType()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
embeddingDataType(): Float<Floats>
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **embeddingDataType**(): `Float`<`Floats`>
|
||||
|
||||
The datatype of the embeddings
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -96,53 +88,17 @@ The datatype of the embeddings
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### generateEmbeddings()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
abstract generateEmbeddings(texts, ...args): Promise<number[][] | Float32Array[] | Float64Array[]>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **texts**: `string`[]
|
||||
|
||||
* ...**args**: `any`[]
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
`Promise`<`number`[][] \| `Float32Array`[] \| `Float64Array`[]>
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### init()?
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
optional init(): Promise<void>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
`Promise`<`void`>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Inherited from
|
||||
|
||||
[`EmbeddingFunction`](EmbeddingFunction.md).[`init`](EmbeddingFunction.md#init)
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### ndims()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
ndims(): undefined | number
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **ndims**(): `number`
|
||||
|
||||
The number of dimensions of the embeddings
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
`undefined` \| `number`
|
||||
`number`
|
||||
|
||||
#### Inherited from
|
||||
#### Overrides
|
||||
|
||||
[`EmbeddingFunction`](EmbeddingFunction.md).[`ndims`](EmbeddingFunction.md#ndims)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -150,12 +106,16 @@ The number of dimensions of the embeddings
|
||||
|
||||
### sourceField()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
sourceField(): [DataType<Type, any>, Map<string, EmbeddingFunction<any, FunctionOptions>>]
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **sourceField**(`optionsOrDatatype`): [`DataType`<`Type`, `any`>, `Map`<`string`, [`EmbeddingFunction`](EmbeddingFunction.md)<`any`, `FunctionOptions`>>]
|
||||
|
||||
sourceField is used in combination with `LanceSchema` to provide a declarative data model
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
• **optionsOrDatatype**: `DataType`<`Type`, `any`> \| `Partial`<`FieldOptions`<`DataType`<`Type`, `any`>>>
|
||||
|
||||
The options for the field or the datatype
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
[`DataType`<`Type`, `any`>, `Map`<`string`, [`EmbeddingFunction`](EmbeddingFunction.md)<`any`, `FunctionOptions`>>]
|
||||
@@ -164,7 +124,7 @@ sourceField is used in combination with `LanceSchema` to provide a declarative d
|
||||
|
||||
lancedb.LanceSchema
|
||||
|
||||
#### Overrides
|
||||
#### Inherited from
|
||||
|
||||
[`EmbeddingFunction`](EmbeddingFunction.md).[`sourceField`](EmbeddingFunction.md#sourcefield)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -172,9 +132,7 @@ lancedb.LanceSchema
|
||||
|
||||
### toJSON()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
abstract toJSON(): Partial<M>
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **toJSON**(): `object`
|
||||
|
||||
Convert the embedding function to a JSON object
|
||||
It is used to serialize the embedding function to the schema
|
||||
@@ -186,7 +144,11 @@ If it does not, the embedding function will not be able to be recreated, or coul
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
`Partial`<`M`>
|
||||
`object`
|
||||
|
||||
##### model
|
||||
|
||||
> **model**: `string` & `object` \| `"text-embedding-ada-002"` \| `"text-embedding-3-small"` \| `"text-embedding-3-large"`
|
||||
|
||||
#### Example
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -205,7 +167,7 @@ class MyEmbeddingFunction extends EmbeddingFunction {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Inherited from
|
||||
#### Overrides
|
||||
|
||||
[`EmbeddingFunction`](EmbeddingFunction.md).[`toJSON`](EmbeddingFunction.md#tojson)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -213,15 +175,13 @@ class MyEmbeddingFunction extends EmbeddingFunction {
|
||||
|
||||
### vectorField()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
vectorField(optionsOrDatatype?): [DataType<Type, any>, Map<string, EmbeddingFunction<any, FunctionOptions>>]
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **vectorField**(`optionsOrDatatype`?): [`DataType`<`Type`, `any`>, `Map`<`string`, [`EmbeddingFunction`](EmbeddingFunction.md)<`any`, `FunctionOptions`>>]
|
||||
|
||||
vectorField is used in combination with `LanceSchema` to provide a declarative data model
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **optionsOrDatatype?**: `DataType`<`Type`, `any`> \| `Partial`<`FieldOptions`<`DataType`<`Type`, `any`>>>
|
||||
• **optionsOrDatatype?**: `DataType`<`Type`, `any`> \| `Partial`<`FieldOptions`<`DataType`<`Type`, `any`>>>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -6,15 +6,13 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# Function: LanceSchema()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
function LanceSchema(fields): Schema
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **LanceSchema**(`fields`): `Schema`
|
||||
|
||||
Create a schema with embedding functions.
|
||||
|
||||
## Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **fields**: `Record`<`string`, `object` \| [`object`, `Map`<`string`, [`EmbeddingFunction`](../classes/EmbeddingFunction.md)<`any`, `FunctionOptions`>>]>
|
||||
• **fields**: `Record`<`string`, `object` \| [`object`, `Map`<`string`, [`EmbeddingFunction`](../classes/EmbeddingFunction.md)<`any`, `FunctionOptions`>>]>
|
||||
|
||||
## Returns
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -6,9 +6,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# Function: getRegistry()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
function getRegistry(): EmbeddingFunctionRegistry
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **getRegistry**(): [`EmbeddingFunctionRegistry`](../classes/EmbeddingFunctionRegistry.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Utility function to get the global instance of the registry
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -6,13 +6,11 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# Function: register()
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
function register(name?): (ctor) => any
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **register**(`name`?): (`ctor`) => `any`
|
||||
|
||||
## Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **name?**: `string`
|
||||
• **name?**: `string`
|
||||
|
||||
## Returns
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -20,7 +18,7 @@ function register(name?): (ctor) => any
|
||||
|
||||
### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
* **ctor**: `EmbeddingFunctionConstructor`<[`EmbeddingFunction`](../classes/EmbeddingFunction.md)<`any`, `FunctionOptions`>>
|
||||
• **ctor**: `EmbeddingFunctionConstructor`<[`EmbeddingFunction`](../classes/EmbeddingFunction.md)<`any`, `FunctionOptions`>>
|
||||
|
||||
### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -10,22 +10,16 @@
|
||||
|
||||
### function
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
function: EmbeddingFunction<any, FunctionOptions>;
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **function**: [`EmbeddingFunction`](../classes/EmbeddingFunction.md)<`any`, `FunctionOptions`>
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### sourceColumn
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
sourceColumn: string;
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **sourceColumn**: `string`
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
### vectorColumn?
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
optional vectorColumn: string;
|
||||
```
|
||||
> `optional` **vectorColumn**: `string`
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,19 @@
|
||||
[**@lancedb/lancedb**](../../../README.md) • **Docs**
|
||||
|
||||
***
|
||||
|
||||
[@lancedb/lancedb](../../../globals.md) / [embedding](../README.md) / OpenAIOptions
|
||||
|
||||
# Type Alias: OpenAIOptions
|
||||
|
||||
> **OpenAIOptions**: `object`
|
||||
|
||||
## Type declaration
|
||||
|
||||
### apiKey
|
||||
|
||||
> **apiKey**: `string`
|
||||
|
||||
### model
|
||||
|
||||
> **model**: `EmbeddingCreateParams`\[`"model"`\]
|
||||
@@ -6,8 +6,6 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# Type Alias: Data
|
||||
|
||||
```ts
|
||||
type Data: Record<string, unknown>[] | TableLike;
|
||||
```
|
||||
> **Data**: `Record`<`string`, `unknown`>[] \| `TableLike`
|
||||
|
||||
Data type accepted by NodeJS SDK
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,14 +1,81 @@
|
||||
# Rust-backed Client Migration Guide
|
||||
|
||||
In an effort to ensure all clients have the same set of capabilities we have
|
||||
migrated the Python and Node clients onto a common Rust base library. In Python,
|
||||
both the synchronous and asynchronous clients are based on this implementation.
|
||||
In Node, the new client is available as `@lancedb/lancedb`, which replaces
|
||||
the existing `vectordb` package.
|
||||
In an effort to ensure all clients have the same set of capabilities we have begun migrating the
|
||||
python and node clients onto a common Rust base library. In python, this new client is part of
|
||||
the same lancedb package, exposed as an asynchronous client. Once the asynchronous client has
|
||||
reached full functionality we will begin migrating the synchronous library to be a thin wrapper
|
||||
around the asynchronous client.
|
||||
|
||||
This guide describes the differences between the two Node APIs and will hopefully assist users
|
||||
This guide describes the differences between the two APIs and will hopefully assist users
|
||||
that would like to migrate to the new API.
|
||||
|
||||
## Python
|
||||
### Closeable Connections
|
||||
|
||||
The Connection now has a `close` method. You can call this when
|
||||
you are done with the connection to eagerly free resources. Currently
|
||||
this is limited to freeing/closing the HTTP connection for remote
|
||||
connections. In the future we may add caching or other resources to
|
||||
native connections so this is probably a good practice even if you
|
||||
aren't using remote connections.
|
||||
|
||||
In addition, the connection can be used as a context manager which may
|
||||
be a more convenient way to ensure the connection is closed.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
|
||||
async def my_async_fn():
|
||||
with await lancedb.connect_async("my_uri") as db:
|
||||
print(await db.table_names())
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
It is not mandatory to call the `close` method. If you do not call it
|
||||
then the connection will be closed when the object is garbage collected.
|
||||
|
||||
### Closeable Table
|
||||
|
||||
The Table now also has a `close` method, similar to the connection. This
|
||||
can be used to eagerly free the cache used by a Table object. Similar to
|
||||
the connection, it can be used as a context manager and it is not mandatory
|
||||
to call the `close` method.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Changes to Table APIs
|
||||
|
||||
- Previously `Table.schema` was a property. Now it is an async method.
|
||||
- The method `Table.__len__` was removed and `len(table)` will no longer
|
||||
work. Use `Table.count_rows` instead.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Creating Indices
|
||||
|
||||
The `Table.create_index` method is now used for creating both vector indices
|
||||
and scalar indices. It currently requires a column name to be specified (the
|
||||
column to index). Vector index defaults are now smarter and scale better with
|
||||
the size of the data.
|
||||
|
||||
To specify index configuration details you will need to specify which kind of
|
||||
index you are using.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Querying
|
||||
|
||||
The `Table.search` method has been renamed to `AsyncTable.vector_search` for
|
||||
clarity.
|
||||
|
||||
### Features not yet supported
|
||||
|
||||
The following features are not yet supported by the asynchronous API. However,
|
||||
we plan to support them soon.
|
||||
|
||||
- You cannot specify an embedding function when creating or opening a table.
|
||||
You must calculate embeddings yourself if using the asynchronous API
|
||||
- The merge insert operation is not supported in the asynchronous API
|
||||
- Cleanup / compact / optimize indices are not supported in the asynchronous API
|
||||
- add / alter columns is not supported in the asynchronous API
|
||||
- The asynchronous API does not yet support any full text search or reranking
|
||||
search
|
||||
- Remote connections to LanceDb Cloud are not yet supported.
|
||||
- The method Table.head is not yet supported.
|
||||
|
||||
## TypeScript/JavaScript
|
||||
|
||||
For JS/TS users, we offer a brand new SDK [@lancedb/lancedb](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@lancedb/lancedb)
|
||||
@@ -66,7 +133,7 @@ the size of the data.
|
||||
|
||||
### Embedding Functions
|
||||
|
||||
The embedding API has been completely reworked, and it now more closely resembles the Python API, including the new [embedding registry](./js/classes/embedding.EmbeddingFunctionRegistry.md):
|
||||
The embedding API has been completely reworked, and it now more closely resembles the Python API, including the new [embedding registry](./js/classes/embedding.EmbeddingFunctionRegistry.md)
|
||||
|
||||
=== "vectordb (deprecated)"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -207,7 +207,7 @@
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## The dataset\n",
|
||||
"The dataset we'll use is a synthetic QA dataset generated from LLama2 review paper. The paper was divided into chunks, with each chunk being a unique context. An LLM was prompted to ask questions relevant to the context for testing a retriever.\n",
|
||||
"The dataset we'll use is a synthetic QA dataset generated from LLama2 review paper. The paper was divided into chunks, with each chunk being a unique context. An LLM was prompted to ask questions relevant to the context for testing a retreiver.\n",
|
||||
"The exact code and other utility functions for this can be found in [this](https://github.com/lancedb/ragged) repo\n"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -477,7 +477,7 @@
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Vector Search\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Average latency: `3.48 ms ± 71.6 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 100 loops each)`"
|
||||
"avg latency - `3.48 ms ± 71.6 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 100 loops each)`"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@@ -597,7 +597,7 @@
|
||||
"`LinearCombinationReranker(weight=0.7)` is used as the default reranker for reranking the hybrid search results if the reranker isn't specified explicitly.\n",
|
||||
"The `weight` param controls the weightage provided to vector search score. The weight of `1-weight` is applied to FTS scores when reranking.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Latency: `71 ms ± 25.4 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 100 loops each)`"
|
||||
"Latency - `71 ms ± 25.4 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 100 loops each)`"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@@ -675,9 +675,9 @@
|
||||
},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Cohere Reranker\n",
|
||||
"This uses Cohere's Reranking API to re-rank the results. It accepts the reranking model name as a parameter. By default it uses the english-v3 model but you can easily switch to a multi-lingual model.\n",
|
||||
"This uses Cohere's Reranking API to re-rank the results. It accepts the reranking model name as a parameter. By Default it uses the english-v3 model but you can easily switch to a multi-lingual model.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Latency: `605 ms ± 78.1 ms per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1 loop each)`"
|
||||
"latency - `605 ms ± 78.1 ms per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1 loop each)`"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@@ -1165,7 +1165,7 @@
|
||||
},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### ColBERT Reranker\n",
|
||||
"Colbert Reranker is powered by ColBERT model. It runs locally using the huggingface implementation.\n",
|
||||
"Colber Reranker is powered by ColBERT model. It runs locally using the huggingface implementation.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Latency - `950 ms ± 5.78 ms per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1 loop each)`\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
@@ -1489,9 +1489,9 @@
|
||||
},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Cross Encoder Reranker\n",
|
||||
"Uses cross encoder models are rerankers. Uses sentence transformer implementation locally\n",
|
||||
"Uses cross encoder models are rerankers. Uses sentence transformer implemntation locally\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Latency: `1.38 s ± 64.6 ms per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1 loop each)`"
|
||||
"Latency - `1.38 s ± 64.6 ms per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1 loop each)`"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@@ -1771,10 +1771,10 @@
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### (Experimental) OpenAI Reranker\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"This prompts a chat model to rerank results and is not a dedicated reranker model. This should be treated as experimental. You might exceed the token limit so set the search limits based on your token limit.\n",
|
||||
"NOTE: It is recommended to use `gpt-4-turbo-preview` as older models might lead to bad behaviour\n",
|
||||
"This prompts chat model to rerank results which is not a dedicated reranker model. This should be treated as experimental. You might run out of token limit so set the search limits based on your token limit.\n",
|
||||
"NOTE: It is recommended to use `gpt-4-turbo-preview`, older models might lead to bad behaviour\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Latency: `Can take 10s of seconds if using GPT-4 model`"
|
||||
"Latency - `Can take 10s of seconds if using GPT-4 model`"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@@ -1817,7 +1817,7 @@
|
||||
},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Use your custom Reranker\n",
|
||||
"Hybrid search in LanceDB is designed to be very flexible. You can easily plug in your own Re-reranking logic. To do so, you simply need to implement the base Reranker class:"
|
||||
"Hybrid search in LanceDB is designed to be very flexible. You can easily plug in your own Re-reranking logic. To do so, you simply need to implement the base Reranker class"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@@ -1849,9 +1849,9 @@
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Custom Reranker based on CohereReranker\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"For the sake of simplicity let's build a custom reranker that enhances the Cohere Reranker by accepting a filter query, and accepts other CohereReranker params as kwargs.\n",
|
||||
"For the sake of simplicity let's build custom reranker that just enchances the Cohere Reranker by accepting a filter query, and accept other CohereReranker params as kwags.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"For this toy example let's say we want to get rid of docs that represent a table of contents or appendix, as these are semantically close to representing costs but don't represent the specific reasons why operating costs were high."
|
||||
"For this toy example let's say we want to get rid of docs that represent a table of contents, appendix etc. as these are semantically close of representing costs but this isn't something we are interested in because they don't represent the specific reasons why operating costs were high. They simply represent the costs."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@@ -1969,7 +1969,7 @@
|
||||
"id": "b3b5464a-7252-4eab-aaac-9b0eae37496f"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"As you can see, the document containing the table of contents no longer shows up."
|
||||
"As you can see the document containing the Table of contetnts of spending no longer shows up"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -49,7 +49,7 @@
|
||||
},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## What is a retriever\n",
|
||||
"VectorDBs are used as retrievers in recommender or chatbot-based systems for retrieving relevant data based on user queries. For example, retriever is a critical component of Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) acrhitectures. In this section, we will discuss how to improve the performance of retrievers.\n",
|
||||
"VectorDBs are used as retreivers in recommender or chatbot-based systems for retrieving relevant data based on user queries. For example, retriever is a critical component of Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) acrhitectures. In this section, we will discuss how to improve the performance of retrievers.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"<img src=\"https://llmstack.ai/assets/images/rag-f517f1f834bdbb94a87765e0edd40ff2.png\" />\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
@@ -64,7 +64,7 @@
|
||||
"- Fine-tuning the embedding models\n",
|
||||
"- Using different embedding models\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Obviously, the above list is not exhaustive. There are other subtler ways that can improve retrieval performance like alternative chunking algorithms, using different distance/similarity metrics, and more. For brevity, we'll only cover high level and more impactful techniques here.\n",
|
||||
"Obviously, the above list is not exhaustive. There are other subtler ways that can improve retrieval performance like experimenting chunking algorithms, using different distance/similarity metrics etc. But for brevity, we'll only cover high level and more impactful techniques here.\n",
|
||||
"\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
@@ -77,7 +77,7 @@
|
||||
"# LanceDB\n",
|
||||
"- Multimodal DB for AI\n",
|
||||
"- Powered by an innovative & open-source in-house file format\n",
|
||||
"- Zero setup\n",
|
||||
"- 0 Setup\n",
|
||||
"- Scales up on disk storage\n",
|
||||
"- Native support for vector, full-text(BM25) and hybrid search\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
@@ -92,8 +92,8 @@
|
||||
},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## The dataset\n",
|
||||
"The dataset we'll use is a synthetic QA dataset generated from LLama2 review paper. The paper was divided into chunks, with each chunk being a unique context. An LLM was prompted to ask questions relevant to the context for testing a retriever.\n",
|
||||
"The exact code and other utility functions for this can be found in [this](https://github.com/lancedb/ragged) repo.\n"
|
||||
"The dataset we'll use is a synthetic QA dataset generated from LLama2 review paper. The paper was divided into chunks, with each chunk being a unique context. An LLM was prompted to ask questions relevant to the context for testing a retreiver.\n",
|
||||
"The exact code and other utility functions for this can be found in [this](https://github.com/lancedb/ragged) repo\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@@ -594,10 +594,10 @@
|
||||
},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Ingestion\n",
|
||||
"Let us now ingest the contexts in LanceDB. The steps will be:\n",
|
||||
"Let us now ingest the contexts in LanceDB\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"- Create a schema (Pydantic or Pyarrow)\n",
|
||||
"- Select an embedding model from LanceDB Embedding API (to allow automatic vectorization of data)\n",
|
||||
"- Select an embedding model from LanceDB Embedding API (Allows automatic vectorization of data)\n",
|
||||
"- Ingest the contexts\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
@@ -841,7 +841,7 @@
|
||||
},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Different Query types in LanceDB\n",
|
||||
"LanceDB allows switching query types with by setting `query_type` argument, which defaults to `vector` when using Embedding API. In this example we'll use `JinaReranker` which is one of many rerankers supported by LanceDB.\n",
|
||||
"LanceDB allows switching query types with by setting `query_type` argument, which defaults to `vector` when using Embedding API. In this example we'll use `JinaReranker` which is one of many rerankers supported by LanceDB\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"### Vector search:\n",
|
||||
"Vector search\n",
|
||||
@@ -1446,11 +1446,11 @@
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Takeaways & Tradeoffs\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"* **Rerankers significantly improve accuracy at little cost.** Using Hybrid search and/or rerankers can significantly improve retrieval performance without spending any additional time or effort on tuning embedding models, generators, or dissecting the dataset.\n",
|
||||
"* **Easiest method to significantly improve accuracy** Using Hybrid search and/or rerankers can significantly improve retrieval performance without spending any additional time or effort on tuning embedding models, generators, or dissecting the dataset.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"* **Reranking is an expensive operation.** Depending on the type of reranker you choose, they can incur significant latecy to query times. Although some API-based rerankers can be significantly faster.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"* **Pre-warmed GPU environments reduce latency.** When using models locally, having a warmed-up GPU environment will significantly reduce latency. This is especially useful if the application doesn't need to be strictly realtime. Pre-warming comes at the expense of GPU resources."
|
||||
"* When using models locally, having a warmed-up GPU environment will significantly reduce latency. This is specially useful if the application doesn't need to be strcitly realtime. The tradeoff being GPU resources."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@@ -1504,4 +1504,4 @@
|
||||
},
|
||||
"nbformat": 4,
|
||||
"nbformat_minor": 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
@@ -8,55 +8,54 @@ and PyArrow. The sequence of steps in a typical workflow is shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
First, we need to connect to a LanceDB database.
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
```py
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_python.py:import-lancedb"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_python.py:connect_to_lancedb"
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_python.py:import-lancedb"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_python.py:connect_to_lancedb_async"
|
||||
```
|
||||
db = lancedb.connect("data/sample-lancedb")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We can load a Pandas `DataFrame` to LanceDB directly.
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import pandas as pd
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_python.py:import-pandas"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_python.py:create_table_pandas"
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_python.py:import-pandas"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_python.py:create_table_pandas_async"
|
||||
```
|
||||
data = pd.DataFrame({
|
||||
"vector": [[3.1, 4.1], [5.9, 26.5]],
|
||||
"item": ["foo", "bar"],
|
||||
"price": [10.0, 20.0]
|
||||
})
|
||||
table = db.create_table("pd_table", data=data)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Similar to the [`pyarrow.write_dataset()`](https://arrow.apache.org/docs/python/generated/pyarrow.dataset.write_dataset.html) method, LanceDB's
|
||||
[`db.create_table()`](python.md/#lancedb.db.DBConnection.create_table) accepts data in a variety of forms.
|
||||
|
||||
If you have a dataset that is larger than memory, you can create a table with `Iterator[pyarrow.RecordBatch]` to lazily load the data:
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
```py
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_python.py:import-iterable"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_python.py:import-pyarrow"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_python.py:make_batches"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_python.py:create_table_iterable"
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
from typing import Iterable
|
||||
import pyarrow as pa
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_python.py:import-iterable"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_python.py:import-pyarrow"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_python.py:make_batches"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_python.py:create_table_iterable_async"
|
||||
```
|
||||
def make_batches() -> Iterable[pa.RecordBatch]:
|
||||
for i in range(5):
|
||||
yield pa.RecordBatch.from_arrays(
|
||||
[
|
||||
pa.array([[3.1, 4.1], [5.9, 26.5]]),
|
||||
pa.array(["foo", "bar"]),
|
||||
pa.array([10.0, 20.0]),
|
||||
],
|
||||
["vector", "item", "price"])
|
||||
|
||||
schema=pa.schema([
|
||||
pa.field("vector", pa.list_(pa.float32())),
|
||||
pa.field("item", pa.utf8()),
|
||||
pa.field("price", pa.float32()),
|
||||
])
|
||||
|
||||
table = db.create_table("iterable_table", data=make_batches(), schema=schema)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You will find detailed instructions of creating a LanceDB dataset in
|
||||
[Getting Started](../basic.md#quick-start) and [API](python.md/#lancedb.db.DBConnection.create_table)
|
||||
@@ -66,16 +65,15 @@ sections.
|
||||
|
||||
We can now perform similarity search via the LanceDB Python API.
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
```py
|
||||
# Open the table previously created.
|
||||
table = db.open_table("pd_table")
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_python.py:vector_search"
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_python.py:vector_search_async"
|
||||
```
|
||||
query_vector = [100, 100]
|
||||
# Pandas DataFrame
|
||||
df = table.search(query_vector).limit(1).to_pandas()
|
||||
print(df)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
vector item price _distance
|
||||
@@ -85,13 +83,16 @@ We can now perform similarity search via the LanceDB Python API.
|
||||
If you have a simple filter, it's faster to provide a `where` clause to LanceDB's `search` method.
|
||||
For more complex filters or aggregations, you can always resort to using the underlying `DataFrame` methods after performing a search.
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Sync API"
|
||||
```python
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_python.py:vector_search_with_filter"
|
||||
```
|
||||
=== "Async API"
|
||||
# Apply the filter via LanceDB
|
||||
results = table.search([100, 100]).where("price < 15").to_pandas()
|
||||
assert len(results) == 1
|
||||
assert results["item"].iloc[0] == "foo"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_python.py:vector_search_with_filter_async"
|
||||
```
|
||||
# Apply the filter via Pandas
|
||||
df = results = table.search([100, 100]).to_pandas()
|
||||
results = df[df.price < 15]
|
||||
assert len(results) == 1
|
||||
assert results["item"].iloc[0] == "foo"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -2,29 +2,38 @@
|
||||
|
||||
LanceDB supports [Polars](https://github.com/pola-rs/polars), a blazingly fast DataFrame library for Python written in Rust. Just like in Pandas, the Polars integration is enabled by PyArrow under the hood. A deeper integration between Lance Tables and Polars DataFrames is in progress, but at the moment, you can read a Polars DataFrame into LanceDB and output the search results from a query to a Polars DataFrame.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Create & Query LanceDB Table
|
||||
|
||||
### From Polars DataFrame
|
||||
|
||||
First, we connect to a LanceDB database.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_python.py:import-lancedb"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_python.py:connect_to_lancedb"
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
|
||||
db = lancedb.connect("data/polars-lancedb")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We can load a Polars `DataFrame` to LanceDB directly.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_python.py:import-polars"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_python.py:create_table_polars"
|
||||
import polars as pl
|
||||
|
||||
data = pl.DataFrame({
|
||||
"vector": [[3.1, 4.1], [5.9, 26.5]],
|
||||
"item": ["foo", "bar"],
|
||||
"price": [10.0, 20.0]
|
||||
})
|
||||
table = db.create_table("pl_table", data=data)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We can now perform similarity search via the LanceDB Python API.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_python.py:vector_search_polars"
|
||||
query = [3.0, 4.0]
|
||||
result = table.search(query).limit(1).to_polars()
|
||||
print(result)
|
||||
print(type(result))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In addition to the selected columns, LanceDB also returns a vector
|
||||
@@ -50,16 +59,33 @@ Note that the type of the result from a table search is a Polars DataFrame.
|
||||
Alternately, we can create an empty LanceDB Table using a Pydantic schema and populate it with a Polars DataFrame.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_python.py:import-polars"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_python.py:import-lancedb-pydantic"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_python.py:class_Item"
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_python.py:create_table_pydantic"
|
||||
import polars as pl
|
||||
from lancedb.pydantic import Vector, LanceModel
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Item(LanceModel):
|
||||
vector: Vector(2)
|
||||
item: str
|
||||
price: float
|
||||
|
||||
data = {
|
||||
"vector": [[3.1, 4.1]],
|
||||
"item": "foo",
|
||||
"price": 10.0,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
table = db.create_table("test_table", schema=Item)
|
||||
df = pl.DataFrame(data)
|
||||
# Add Polars DataFrame to table
|
||||
table.add(df)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The table can now be queried as usual.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_python.py:vector_search_polars"
|
||||
result = table.search([3.0, 4.0]).limit(1).to_polars()
|
||||
print(result)
|
||||
print(type(result))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -82,7 +108,8 @@ As you iterate on your application, you'll likely need to work with the whole ta
|
||||
LanceDB tables can also be converted directly into a polars LazyFrame for further processing.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_python.py:dump_table_lazyform"
|
||||
ldf = table.to_polars()
|
||||
print(type(ldf))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Unlike the search result from a query, we can see that the type of the result is a LazyFrame.
|
||||
@@ -94,7 +121,7 @@ Unlike the search result from a query, we can see that the type of the result is
|
||||
We can now work with the LazyFrame as we would in Polars, and collect the first result.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
--8<-- "python/python/tests/docs/test_python.py:print_table_lazyform"
|
||||
print(ldf.first().collect())
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,16 +1,6 @@
|
||||
# Python API Reference
|
||||
|
||||
This section contains the API reference for the Python API. There is a
|
||||
synchronous and an asynchronous API client.
|
||||
|
||||
The general flow of using the API is:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Use [lancedb.connect][] or [lancedb.connect_async][] to connect to a database.
|
||||
2. Use the returned [lancedb.DBConnection][] or [lancedb.AsyncConnection][] to
|
||||
create or open tables.
|
||||
3. Use the returned [lancedb.table.Table][] or [lancedb.AsyncTable][] to query
|
||||
or modify tables.
|
||||
|
||||
This section contains the API reference for the OSS Python API.
|
||||
|
||||
## Installation
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -47,8 +37,6 @@ is also an [asynchronous API client](#connections-asynchronous).
|
||||
|
||||
::: lancedb.embeddings.registry.EmbeddingFunctionRegistry
|
||||
|
||||
::: lancedb.embeddings.base.EmbeddingFunctionConfig
|
||||
|
||||
::: lancedb.embeddings.base.EmbeddingFunction
|
||||
|
||||
::: lancedb.embeddings.base.TextEmbeddingFunction
|
||||
@@ -137,8 +125,6 @@ lists the indices that LanceDb supports.
|
||||
|
||||
::: lancedb.index.HnswSq
|
||||
|
||||
::: lancedb.index.IvfFlat
|
||||
|
||||
## Querying (Asynchronous)
|
||||
|
||||
Queries allow you to return data from your database. Basic queries can be
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -17,8 +17,4 @@ pip install lancedb
|
||||
## Table
|
||||
|
||||
::: lancedb.remote.table.RemoteTable
|
||||
options:
|
||||
filters:
|
||||
- "!cleanup_old_versions"
|
||||
- "!compact_files"
|
||||
- "!optimize"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -2,7 +2,7 @@
|
||||
====================================================================
|
||||
Adaptive RAG introduces a RAG technique that combines query analysis with self-corrective RAG.
|
||||
|
||||
For Query Analysis, it uses a small classifier(LLM), to decide the query’s complexity. Query Analysis guides adjustment between different retrieval strategies: No retrieval, Single-shot RAG or Iterative RAG.
|
||||
For Query Analysis, it uses a small classifier(LLM), to decide the query’s complexity. Query Analysis helps routing smoothly to adjust between different retrieval strategies No retrieval, Single-shot RAG or Iterative RAG.
|
||||
|
||||
**[Official Paper](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2403.14403)**
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -12,9 +12,9 @@ For Query Analysis, it uses a small classifier(LLM), to decide the query’s com
|
||||
</figcaption>
|
||||
</figure>
|
||||
|
||||
**[Official Implementation](https://github.com/starsuzi/Adaptive-RAG)**
|
||||
**[Offical Implementation](https://github.com/starsuzi/Adaptive-RAG)**
|
||||
|
||||
Here’s a code snippet for query analysis:
|
||||
Here’s a code snippet for query analysis
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
|
||||
@@ -35,7 +35,7 @@ llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-3.5-turbo-0125", temperature=0)
|
||||
structured_llm_router = llm.with_structured_output(RouteQuery)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The following example defines and queries a retriever:
|
||||
For defining and querying retriever
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# add documents in LanceDB
|
||||
@@ -48,4 +48,4 @@ retriever = vectorstore.as_retriever()
|
||||
# query using defined retriever
|
||||
question = "How adaptive RAG works"
|
||||
docs = retriever.get_relevant_documents(question)
|
||||
```
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -11,7 +11,7 @@ FLARE, stands for Forward-Looking Active REtrieval augmented generation is a gen
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/examples/better-rag-FLAIR/main.ipynb)
|
||||
|
||||
Here’s a code snippet for using FLARE with Langchain:
|
||||
Here’s a code snippet for using FLARE with Langchain
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from langchain.vectorstores import LanceDB
|
||||
@@ -35,4 +35,4 @@ flare = FlareChain.from_llm(llm=llm,retriever=vector_store_retriever,max_generat
|
||||
result = flare.run(input_text)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/examples/better-rag-FLAIR/main.ipynb)
|
||||
[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/examples/better-rag-FLAIR/main.ipynb)
|
||||
@@ -11,7 +11,7 @@ HyDE, stands for Hypothetical Document Embeddings is an approach used for precis
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/examples/Advance-RAG-with-HyDE/main.ipynb)
|
||||
|
||||
Here’s a code snippet for using HyDE with Langchain:
|
||||
Here’s a code snippet for using HyDE with Langchain
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from langchain.llms import OpenAI
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
|
||||
**Agentic RAG 🤖**
|
||||
====================================================================
|
||||
Agentic RAG introduces an advanced framework for answering questions by using intelligent agents instead of just relying on large language models. These agents act like expert researchers, handling complex tasks such as detailed planning, multi-step reasoning, and using external tools. They navigate multiple documents, compare information, and generate accurate answers. This system is easily scalable, with each new document set managed by a sub-agent, making it a powerful tool for tackling a wide range of information needs.
|
||||
Agentic RAG is Agent-based RAG introduces an advanced framework for answering questions by using intelligent agents instead of just relying on large language models. These agents act like expert researchers, handling complex tasks such as detailed planning, multi-step reasoning, and using external tools. They navigate multiple documents, compare information, and generate accurate answers. This system is easily scalable, with each new document set managed by a sub-agent, making it a powerful tool for tackling a wide range of information needs.
|
||||
|
||||
<figure markdown="span">
|
||||
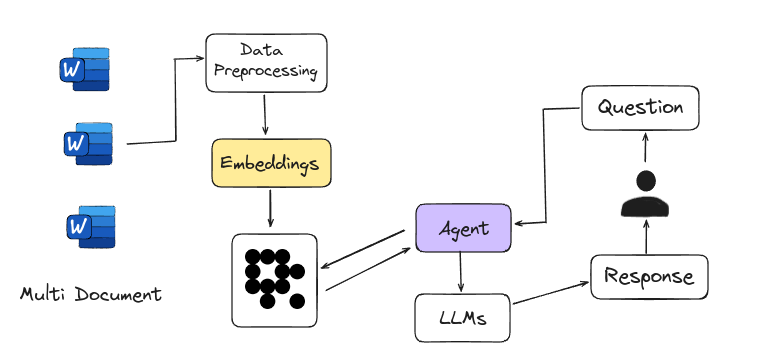
|
||||
@@ -9,7 +9,7 @@ Agentic RAG introduces an advanced framework for answering questions by using in
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/tutorials/Agentic_RAG/main.ipynb)
|
||||
|
||||
Here’s a code snippet for defining retriever using Langchain:
|
||||
Here’s a code snippet for defining retriever using Langchain
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from langchain.text_splitter import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
|
||||
@@ -41,7 +41,7 @@ retriever = vectorstore.as_retriever()
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Here is an agent that formulates an improved query for better retrieval results and then grades the retrieved documents:
|
||||
Agent that formulates an improved query for better retrieval results and then grades the retrieved documents
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
def grade_documents(state) -> Literal["generate", "rewrite"]:
|
||||
@@ -98,4 +98,4 @@ def rewrite(state):
|
||||
return {"messages": [response]}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/tutorials/Agentic_RAG/main.ipynb)
|
||||
[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/tutorials/Agentic_RAG/main.ipynb)
|
||||
@@ -4,7 +4,7 @@
|
||||
Corrective-RAG (CRAG) is a strategy for Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) that includes self-reflection and self-grading of retrieved documents. Here’s a simplified breakdown of the steps involved:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Relevance Check**: If at least one document meets the relevance threshold, the process moves forward to the generation phase.
|
||||
2. **Knowledge Refinement**: Before generating an answer, the process refines the knowledge by dividing the document into smaller segments called "knowledge strips".
|
||||
2. **Knowledge Refinement**: Before generating an answer, the process refines the knowledge by dividing the document into smaller segments called "knowledge strips."
|
||||
3. **Grading and Filtering**: Each "knowledge strip" is graded, and irrelevant ones are filtered out.
|
||||
4. **Additional Data Source**: If all documents are below the relevance threshold, or if the system is unsure about their relevance, it will seek additional information by performing a web search to supplement the retrieved data.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -19,11 +19,11 @@ Above steps are mentioned in
|
||||
|
||||
Corrective Retrieval-Augmented Generation (CRAG) is a method that works like a **built-in fact-checker**.
|
||||
|
||||
**[Official Implementation](https://github.com/HuskyInSalt/CRAG)**
|
||||
**[Offical Implementation](https://github.com/HuskyInSalt/CRAG)**
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/tutorials/Corrective-RAG-with_Langgraph/CRAG_with_Langgraph.ipynb)
|
||||
|
||||
Here’s a code snippet for defining a table with the [Embedding API](https://lancedb.github.io/lancedb/embeddings/embedding_functions/), and retrieves the relevant documents:
|
||||
Here’s a code snippet for defining a table with the [Embedding API](https://lancedb.github.io/lancedb/embeddings/embedding_functions/), and retrieves the relevant documents.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import pandas as pd
|
||||
@@ -115,6 +115,6 @@ def grade_documents(state):
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Check Colab for the Implementation of CRAG with Langgraph:
|
||||
Check Colab for the Implementation of CRAG with Langgraph
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/tutorials/Corrective-RAG-with_Langgraph/CRAG_with_Langgraph.ipynb)
|
||||
[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/tutorials/Corrective-RAG-with_Langgraph/CRAG_with_Langgraph.ipynb)
|
||||
@@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ One of the main benefits of Graph RAG is its ability to capture and represent co
|
||||
|
||||
**[Official Paper](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2404.16130)**
|
||||
|
||||
**[Official Implementation](https://github.com/microsoft/graphrag)**
|
||||
**[Offical Implementation](https://github.com/microsoft/graphrag)**
|
||||
|
||||
[Microsoft Research Blog](https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/blog/graphrag-unlocking-llm-discovery-on-narrative-private-data/)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -39,16 +39,16 @@ python3 -m graphrag.index --root dataset-dir
|
||||
|
||||
- **Execute Query**
|
||||
|
||||
Global Query Execution gives a broad overview of dataset:
|
||||
Global Query Execution gives a broad overview of dataset
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python3 -m graphrag.query --root dataset-dir --method global "query-question"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Local Query Execution gives a detailed and specific answers based on the context of the entities:
|
||||
Local Query Execution gives a detailed and specific answers based on the context of the entities
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python3 -m graphrag.query --root dataset-dir --method local "query-question"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/examples/Graphrag/main.ipynb)
|
||||
[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/examples/Graphrag/main.ipynb)
|
||||
@@ -15,7 +15,7 @@ MRAG is cost-effective and energy-efficient because it avoids extra LLM queries,
|
||||
|
||||
**[Official Implementation](https://github.com/spcl/MRAG)**
|
||||
|
||||
Here’s a code snippet for defining different embedding spaces with the [Embedding API](https://lancedb.github.io/lancedb/embeddings/embedding_functions/):
|
||||
Here’s a code snippet for defining different embedding spaces with the [Embedding API](https://lancedb.github.io/lancedb/embeddings/embedding_functions/)
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
@@ -44,6 +44,6 @@ class Space3(LanceModel):
|
||||
vector: Vector(model3.ndims()) = model3.VectorField()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Create different tables using defined embedding spaces, then make queries to each embedding space. Use the resulting closest documents from each embedding space to generate answers.
|
||||
Create different tables using defined embedding spaces, then make queries to each embedding space. Use the resulted closest documents from each embedding space to generate answers.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
|
||||
**Self RAG 🤳**
|
||||
====================================================================
|
||||
Self-RAG is a strategy for Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) to get better retrieved information, generated text, and validation, without loss of flexibility. Unlike the traditional Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) method, Self-RAG retrieves information as needed, can skip retrieval if not needed, and evaluates its own output while generating text. It also uses a process to pick the best output based on different preferences.
|
||||
Self-RAG is a strategy for Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) to get better retrieved information, generated text, and checking their own work, all without losing their flexibility. Unlike the traditional Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) method, Self-RAG retrieves information as needed, can skip retrieval if not needed, and evaluates its own output while generating text. It also uses a process to pick the best output based on different preferences.
|
||||
|
||||
**[Official Paper](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2310.11511)**
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -10,11 +10,11 @@ Self-RAG is a strategy for Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) to get better re
|
||||
</figcaption>
|
||||
</figure>
|
||||
|
||||
**[Official Implementation](https://github.com/AkariAsai/self-rag)**
|
||||
**[Offical Implementation](https://github.com/AkariAsai/self-rag)**
|
||||
|
||||
Self-RAG starts by generating a response without retrieving extra info if it's not needed. For questions that need more details, it retrieves to get the necessary information.
|
||||
|
||||
Here’s a code snippet for defining retriever using Langchain:
|
||||
Here’s a code snippet for defining retriever using Langchain
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from langchain.text_splitter import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
|
||||
@@ -46,7 +46,7 @@ retriever = vectorstore.as_retriever()
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The following functions grade the retrieved documents and formulate an improved query for better retrieval results, if required:
|
||||
Functions that grades the retrieved documents and if required formulates an improved query for better retrieval results
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
def grade_documents(state) -> Literal["generate", "rewrite"]:
|
||||
@@ -93,4 +93,4 @@ def rewrite(state):
|
||||
model = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0, model="gpt-4-0125-preview", streaming=True)
|
||||
response = model.invoke(msg)
|
||||
return {"messages": [response]}
|
||||
```
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -1,8 +1,8 @@
|
||||
**SFR RAG 📑**
|
||||
====================================================================
|
||||
Salesforce AI Research introduced SFR-RAG, a 9-billion-parameter language model trained with a significant emphasis on reliable, precise, and faithful contextual generation abilities specific to real-world RAG use cases and relevant agentic tasks. It targets precise factual knowledge extraction, distinction between relevant and distracting contexts, citation of appropriate sources along with answers, production of complex and multi-hop reasoning over multiple contexts, consistent format following, as well as minimization of hallucination over unanswerable queries.
|
||||
Salesforce AI Research introduces SFR-RAG, a 9-billion-parameter language model trained with a significant emphasis on reliable, precise, and faithful contextual generation abilities specific to real-world RAG use cases and relevant agentic tasks. They include precise factual knowledge extraction, distinguishing relevant against distracting contexts, citing appropriate sources along with answers, producing complex and multi-hop reasoning over multiple contexts, consistent format following, as well as refraining from hallucination over unanswerable queries.
|
||||
|
||||
**[Official Implementation](https://github.com/SalesforceAIResearch/SFR-RAG)**
|
||||
**[Offical Implementation](https://github.com/SalesforceAIResearch/SFR-RAG)**
|
||||
|
||||
<figure markdown="span">
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
|
||||
# AnswersDotAI Rerankers
|
||||
|
||||
This integration uses [AnswersDotAI's rerankers](https://github.com/AnswerDotAI/rerankers) to rerank the search results, providing a lightweight, low-dependency, unified API to use all common reranking and cross-encoder models.
|
||||
This integration allows using answersdotai's rerankers to rerank the search results. [Rerankers](https://github.com/AnswerDotAI/rerankers)
|
||||
A lightweight, low-dependency, unified API to use all common reranking and cross-encoder models.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note
|
||||
Supported Query Types: Hybrid, Vector, FTS
|
||||
@@ -44,10 +45,10 @@ Accepted Arguments
|
||||
----------------
|
||||
| Argument | Type | Default | Description |
|
||||
| --- | --- | --- | --- |
|
||||
| `model_type` | `str` | `"colbert"` | The type of model to use. Supported model types can be found here: https://github.com/AnswerDotAI/rerankers. |
|
||||
| `model_type` | `str` | `"colbert"` | The type of model to use. Supported model types can be found here - https://github.com/AnswerDotAI/rerankers |
|
||||
| `model_name` | `str` | `"answerdotai/answerai-colbert-small-v1"` | The name of the reranker model to use. |
|
||||
| `column` | `str` | `"text"` | The name of the column to use as input to the cross encoder model. |
|
||||
| `return_score` | str | `"relevance"` | Options are "relevance" or "all". The type of score to return. If "relevance", will return only the `_relevance_score. If "all" is supported, will return relevance score along with the vector and/or fts scores depending on query type. |
|
||||
| `return_score` | str | `"relevance"` | Options are "relevance" or "all". The type of score to return. If "relevance", will return only the `_relevance_score. If "all" is supported, will return relevance score along with the vector and/or fts scores depending on query type |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -57,17 +58,17 @@ You can specify the type of scores you want the reranker to return. The followin
|
||||
### Hybrid Search
|
||||
|`return_score`| Status | Description |
|
||||
| --- | --- | --- |
|
||||
| `relevance` | ✅ Supported | Results only have the `_relevance_score` column. |
|
||||
| `all` | ❌ Not Supported | Results have vector(`_distance`) and FTS(`score`) along with Hybrid Search score(`_relevance_score`). |
|
||||
| `relevance` | ✅ Supported | Returns only have the `_relevance_score` column |
|
||||
| `all` | ❌ Not Supported | Returns have vector(`_distance`) and FTS(`score`) along with Hybrid Search score(`_relevance_score`) |
|
||||
|
||||
### Vector Search
|
||||
|`return_score`| Status | Description |
|
||||
| --- | --- | --- |
|
||||
| `relevance` | ✅ Supported | Results only have the `_relevance_score` column. |
|
||||
| `all` | ✅ Supported | Results have vector(`_distance`) along with Hybrid Search score(`_relevance_score`). |
|
||||
| `relevance` | ✅ Supported | Returns only have the `_relevance_score` column |
|
||||
| `all` | ✅ Supported | Returns have vector(`_distance`) along with Hybrid Search score(`_relevance_score`) |
|
||||
|
||||
### FTS Search
|
||||
|`return_score`| Status | Description |
|
||||
| --- | --- | --- |
|
||||
| `relevance` | ✅ Supported | Results only have the `_relevance_score` column. |
|
||||
| `all` | ✅ Supported | Results have FTS(`score`) along with Hybrid Search score(`_relevance_score`). |
|
||||
| `relevance` | ✅ Supported | Returns only have the `_relevance_score` column |
|
||||
| `all` | ✅ Supported | Returns have FTS(`score`) along with Hybrid Search score(`_relevance_score`) |
|
||||
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
|
||||
# Cohere Reranker
|
||||
|
||||
This reranker uses the [Cohere](https://cohere.ai/) API to rerank the search results. You can use this reranker by passing `CohereReranker()` to the `rerank()` method. Note that you'll either need to set the `COHERE_API_KEY` environment variable or pass the `api_key` argument to use this reranker.
|
||||
This re-ranker uses the [Cohere](https://cohere.ai/) API to rerank the search results. You can use this re-ranker by passing `CohereReranker()` to the `rerank()` method. Note that you'll either need to set the `COHERE_API_KEY` environment variable or pass the `api_key` argument to use this re-ranker.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note
|
||||
@@ -62,17 +62,17 @@ You can specify the type of scores you want the reranker to return. The followin
|
||||
### Hybrid Search
|
||||
|`return_score`| Status | Description |
|
||||
| --- | --- | --- |
|
||||
| `relevance` | ✅ Supported | Results only have the `_relevance_score` column |
|
||||
| `all` | ❌ Not Supported | Results have vector(`_distance`) and FTS(`score`) along with Hybrid Search score(`_relevance_score`) |
|
||||
| `relevance` | ✅ Supported | Returns only have the `_relevance_score` column |
|
||||
| `all` | ❌ Not Supported | Returns have vector(`_distance`) and FTS(`score`) along with Hybrid Search score(`_relevance_score`) |
|
||||
|
||||
### Vector Search
|
||||
|`return_score`| Status | Description |
|
||||
| --- | --- | --- |
|
||||
| `relevance` | ✅ Supported | Results only have the `_relevance_score` column |
|
||||
| `all` | ✅ Supported | Results have vector(`_distance`) along with Hybrid Search score(`_relevance_score`) |
|
||||
| `relevance` | ✅ Supported | Returns only have the `_relevance_score` column |
|
||||
| `all` | ✅ Supported | Returns have vector(`_distance`) along with Hybrid Search score(`_relevance_score`) |
|
||||
|
||||
### FTS Search
|
||||
|`return_score`| Status | Description |
|
||||
| --- | --- | --- |
|
||||
| `relevance` | ✅ Supported | Results only have the `_relevance_score` column |
|
||||
| `all` | ✅ Supported | Results have FTS(`score`) along with Hybrid Search score(`_relevance_score`) |
|
||||
| `relevance` | ✅ Supported | Returns only have the `_relevance_score` column |
|
||||
| `all` | ✅ Supported | Returns have FTS(`score`) along with Hybrid Search score(`_relevance_score`) |
|
||||
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
|
||||
# ColBERT Reranker
|
||||
|
||||
This reranker uses ColBERT model to rerank the search results. You can use this reranker by passing `ColbertReranker()` to the `rerank()` method.
|
||||
This re-ranker uses ColBERT model to rerank the search results. You can use this re-ranker by passing `ColbertReranker()` to the `rerank()` method.
|
||||
!!! note
|
||||
Supported Query Types: Hybrid, Vector, FTS
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -46,7 +46,7 @@ Accepted Arguments
|
||||
| `model_name` | `str` | `"colbert-ir/colbertv2.0"` | The name of the reranker model to use.|
|
||||
| `column` | `str` | `"text"` | The name of the column to use as input to the cross encoder model. |
|
||||
| `device` | `str` | `None` | The device to use for the cross encoder model. If None, will use "cuda" if available, otherwise "cpu". |
|
||||
| `return_score` | str | `"relevance"` | Options are "relevance" or "all". The type of score to return. If "relevance", will return only the `_relevance_score. If "all" is supported, will return relevance score along with the vector and/or fts scores depending on query type. |
|
||||
| `return_score` | str | `"relevance"` | Options are "relevance" or "all". The type of score to return. If "relevance", will return only the `_relevance_score. If "all" is supported, will return relevance score along with the vector and/or fts scores depending on query type |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Supported Scores for each query type
|
||||
@@ -55,17 +55,17 @@ You can specify the type of scores you want the reranker to return. The followin
|
||||
### Hybrid Search
|
||||
|`return_score`| Status | Description |
|
||||
| --- | --- | --- |
|
||||
| `relevance` | ✅ Supported | Results only have the `_relevance_score` column. |
|
||||
| `all` | ❌ Not Supported | Results have vector(`_distance`) and FTS(`score`) along with Hybrid Search score(`_relevance_score`). |
|
||||
| `relevance` | ✅ Supported | Returns only have the `_relevance_score` column |
|
||||
| `all` | ❌ Not Supported | Returns have vector(`_distance`) and FTS(`score`) along with Hybrid Search score(`_relevance_score`) |
|
||||
|
||||
### Vector Search
|
||||
|`return_score`| Status | Description |
|
||||
| --- | --- | --- |
|
||||
| `relevance` | ✅ Supported | Results only have the `_relevance_score` column. |
|
||||
| `all` | ✅ Supported | Results have vector(`_distance`) along with Hybrid Search score(`_relevance_score`). |
|
||||
| `relevance` | ✅ Supported | Returns only have the `_relevance_score` column |
|
||||
| `all` | ✅ Supported | Returns have vector(`_distance`) along with Hybrid Search score(`_relevance_score`) |
|
||||
|
||||
### FTS Search
|
||||
|`return_score`| Status | Description |
|
||||
| --- | --- | --- |
|
||||
| `relevance` | ✅ Supported | Results only have the `_relevance_score` column. |
|
||||
| `all` | ✅ Supported | Results have FTS(`score`) along with Hybrid Search score(`_relevance_score`). |
|
||||
| `relevance` | ✅ Supported | Returns only have the `_relevance_score` column |
|
||||
| `all` | ✅ Supported | Returns have FTS(`score`) along with Hybrid Search score(`_relevance_score`) |
|
||||
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
|
||||
# Cross Encoder Reranker
|
||||
|
||||
This reranker uses Cross Encoder models from sentence-transformers to rerank the search results. You can use this reranker by passing `CrossEncoderReranker()` to the `rerank()` method.
|
||||
This re-ranker uses Cross Encoder models from sentence-transformers to rerank the search results. You can use this re-ranker by passing `CrossEncoderReranker()` to the `rerank()` method.
|
||||
!!! note
|
||||
Supported Query Types: Hybrid, Vector, FTS
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -46,7 +46,7 @@ Accepted Arguments
|
||||
| `model_name` | `str` | `""cross-encoder/ms-marco-TinyBERT-L-6"` | The name of the reranker model to use.|
|
||||
| `column` | `str` | `"text"` | The name of the column to use as input to the cross encoder model. |
|
||||
| `device` | `str` | `None` | The device to use for the cross encoder model. If None, will use "cuda" if available, otherwise "cpu". |
|
||||
| `return_score` | str | `"relevance"` | Options are "relevance" or "all". The type of score to return. If "relevance", will return only the `_relevance_score. If "all" is supported, will return relevance score along with the vector and/or fts scores depending on query type. |
|
||||
| `return_score` | str | `"relevance"` | Options are "relevance" or "all". The type of score to return. If "relevance", will return only the `_relevance_score. If "all" is supported, will return relevance score along with the vector and/or fts scores depending on query type |
|
||||
|
||||
## Supported Scores for each query type
|
||||
You can specify the type of scores you want the reranker to return. The following are the supported scores for each query type:
|
||||
@@ -54,17 +54,17 @@ You can specify the type of scores you want the reranker to return. The followin
|
||||
### Hybrid Search
|
||||
|`return_score`| Status | Description |
|
||||
| --- | --- | --- |
|
||||
| `relevance` | ✅ Supported | Results only have the `_relevance_score` column. |
|
||||
| `all` | ❌ Not Supported | Results have vector(`_distance`) and FTS(`score`) along with Hybrid Search score(`_relevance_score`). |
|
||||
| `relevance` | ✅ Supported | Returns only have the `_relevance_score` column |
|
||||
| `all` | ❌ Not Supported | Returns have vector(`_distance`) and FTS(`score`) along with Hybrid Search score(`_relevance_score`) |
|
||||
|
||||
### Vector Search
|
||||
|`return_score`| Status | Description |
|
||||
| --- | --- | --- |
|
||||
| `relevance` | ✅ Supported | Results only have the `_relevance_score` column. |
|
||||
| `all` | ✅ Supported | Results have vector(`_distance`) along with Hybrid Search score(`_relevance_score`). |
|
||||
| `relevance` | ✅ Supported | Returns only have the `_relevance_score` column |
|
||||
| `all` | ✅ Supported | Returns have vector(`_distance`) along with Hybrid Search score(`_relevance_score`) |
|
||||
|
||||
### FTS Search
|
||||
|`return_score`| Status | Description |
|
||||
| --- | --- | --- |
|
||||
| `relevance` | ✅ Supported | Results only have the `_relevance_score` column. |
|
||||
| `all` | ✅ Supported | Results have FTS(`score`) along with Hybrid Search score(`_relevance_score`). |
|
||||
| `relevance` | ✅ Supported | Returns only have the `_relevance_score` column |
|
||||
| `all` | ✅ Supported | Returns have FTS(`score`) along with Hybrid Search score(`_relevance_score`) |
|
||||
Some files were not shown because too many files have changed in this diff Show More
Reference in New Issue
Block a user