mirror of
https://github.com/lancedb/lancedb.git
synced 2025-12-23 05:19:58 +00:00
Compare commits
54 Commits
python-v0.
...
python-v0.
| Author | SHA1 | Date | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
38f0031d0b | ||
|
|
e118c37228 | ||
|
|
abeaae3d80 | ||
|
|
b3c0227065 | ||
|
|
521e665f57 | ||
|
|
ffb28dd4fc | ||
|
|
32af962c0c | ||
|
|
18484d0b6c | ||
|
|
c02ee3c80c | ||
|
|
dcd5f51036 | ||
|
|
9b8472850e | ||
|
|
36d05ea641 | ||
|
|
7ed86cadfb | ||
|
|
1c123b58d8 | ||
|
|
bf7d2d6fb0 | ||
|
|
c7732585bf | ||
|
|
b3bf6386c3 | ||
|
|
4b79db72bf | ||
|
|
622a2922e2 | ||
|
|
c91221d710 | ||
|
|
56da5ebd13 | ||
|
|
64eb43229d | ||
|
|
c31c92122f | ||
|
|
205fc530cf | ||
|
|
2bde5401eb | ||
|
|
a405847f9b | ||
|
|
bcc19665ce | ||
|
|
2a6586d6fb | ||
|
|
029b01bbbf | ||
|
|
cd32944e54 | ||
|
|
7eb3b52297 | ||
|
|
8dcd328dce | ||
|
|
1d61717d0e | ||
|
|
4ee7225e91 | ||
|
|
2bc7dca3ca | ||
|
|
b24810a011 | ||
|
|
2b8e872be0 | ||
|
|
03ef1dc081 | ||
|
|
fde636ca2e | ||
|
|
51966a84f5 | ||
|
|
38015ffa7c | ||
|
|
dc72ece847 | ||
|
|
1521435193 | ||
|
|
bfe8fccfab | ||
|
|
6f6eb170a9 | ||
|
|
dd1c16bbaf | ||
|
|
a76186ee83 | ||
|
|
ae85008714 | ||
|
|
a85f039352 | ||
|
|
9c25998110 | ||
|
|
549ca51a8a | ||
|
|
632007d0e2 | ||
|
|
02d85a4ea4 | ||
|
|
a9d0625e2b |
@@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
||||
[tool.bumpversion]
|
||||
current_version = "0.10.0-beta.0"
|
||||
current_version = "0.10.0"
|
||||
parse = """(?x)
|
||||
(?P<major>0|[1-9]\\d*)\\.
|
||||
(?P<minor>0|[1-9]\\d*)\\.
|
||||
@@ -24,34 +24,56 @@ commit = true
|
||||
message = "Bump version: {current_version} → {new_version}"
|
||||
commit_args = ""
|
||||
|
||||
# Java maven files
|
||||
pre_commit_hooks = [
|
||||
"""
|
||||
NEW_VERSION="${BVHOOK_NEW_MAJOR}.${BVHOOK_NEW_MINOR}.${BVHOOK_NEW_PATCH}"
|
||||
if [ ! -z "$BVHOOK_NEW_PRE_L" ] && [ ! -z "$BVHOOK_NEW_PRE_N" ]; then
|
||||
NEW_VERSION="${NEW_VERSION}-${BVHOOK_NEW_PRE_L}.${BVHOOK_NEW_PRE_N}"
|
||||
fi
|
||||
echo "Constructed new version: $NEW_VERSION"
|
||||
cd java && mvn versions:set -DnewVersion=$NEW_VERSION && mvn versions:commit
|
||||
|
||||
# Check for any modified but unstaged pom.xml files
|
||||
MODIFIED_POMS=$(git ls-files -m | grep pom.xml)
|
||||
if [ ! -z "$MODIFIED_POMS" ]; then
|
||||
echo "The following pom.xml files were modified but not staged. Adding them now:"
|
||||
echo "$MODIFIED_POMS" | while read -r file; do
|
||||
git add "$file"
|
||||
echo "Added: $file"
|
||||
done
|
||||
fi
|
||||
""",
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
[tool.bumpversion.parts.pre_l]
|
||||
values = ["beta", "final"]
|
||||
optional_value = "final"
|
||||
values = ["beta", "final"]
|
||||
|
||||
[[tool.bumpversion.files]]
|
||||
filename = "node/package.json"
|
||||
search = "\"version\": \"{current_version}\","
|
||||
replace = "\"version\": \"{new_version}\","
|
||||
search = "\"version\": \"{current_version}\","
|
||||
|
||||
[[tool.bumpversion.files]]
|
||||
filename = "nodejs/package.json"
|
||||
search = "\"version\": \"{current_version}\","
|
||||
replace = "\"version\": \"{new_version}\","
|
||||
search = "\"version\": \"{current_version}\","
|
||||
|
||||
# nodejs binary packages
|
||||
[[tool.bumpversion.files]]
|
||||
glob = "nodejs/npm/*/package.json"
|
||||
search = "\"version\": \"{current_version}\","
|
||||
replace = "\"version\": \"{new_version}\","
|
||||
search = "\"version\": \"{current_version}\","
|
||||
|
||||
# Cargo files
|
||||
# ------------
|
||||
[[tool.bumpversion.files]]
|
||||
filename = "rust/ffi/node/Cargo.toml"
|
||||
search = "\nversion = \"{current_version}\""
|
||||
replace = "\nversion = \"{new_version}\""
|
||||
search = "\nversion = \"{current_version}\""
|
||||
|
||||
[[tool.bumpversion.files]]
|
||||
filename = "rust/lancedb/Cargo.toml"
|
||||
search = "\nversion = \"{current_version}\""
|
||||
replace = "\nversion = \"{new_version}\""
|
||||
search = "\nversion = \"{current_version}\""
|
||||
|
||||
12
.github/workflows/docs_test.yml
vendored
12
.github/workflows/docs_test.yml
vendored
@@ -30,9 +30,13 @@ jobs:
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
- name: Print CPU capabilities
|
||||
run: cat /proc/cpuinfo
|
||||
- name: Install protobuf
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
sudo apt update
|
||||
sudo apt install -y protobuf-compiler
|
||||
- name: Install dependecies needed for ubuntu
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
sudo apt install -y protobuf-compiler libssl-dev
|
||||
sudo apt install -y libssl-dev
|
||||
rustup update && rustup default
|
||||
- name: Set up Python
|
||||
uses: actions/setup-python@v5
|
||||
@@ -72,9 +76,13 @@ jobs:
|
||||
uses: actions/setup-node@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
node-version: 20
|
||||
- name: Install protobuf
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
sudo apt update
|
||||
sudo apt install -y protobuf-compiler
|
||||
- name: Install dependecies needed for ubuntu
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
sudo apt install -y protobuf-compiler libssl-dev
|
||||
sudo apt install -y libssl-dev
|
||||
rustup update && rustup default
|
||||
- name: Rust cache
|
||||
uses: swatinem/rust-cache@v2
|
||||
|
||||
114
.github/workflows/java-publish.yml
vendored
Normal file
114
.github/workflows/java-publish.yml
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,114 @@
|
||||
name: Build and publish Java packages
|
||||
on:
|
||||
release:
|
||||
types: [released]
|
||||
pull_request:
|
||||
paths:
|
||||
- .github/workflows/java-publish.yml
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
macos-arm64:
|
||||
name: Build on MacOS Arm64
|
||||
runs-on: macos-14
|
||||
timeout-minutes: 45
|
||||
defaults:
|
||||
run:
|
||||
working-directory: ./java/core/lancedb-jni
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Checkout repository
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
- uses: Swatinem/rust-cache@v2
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
brew install protobuf
|
||||
- name: Build release
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
cargo build --release
|
||||
- uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: liblancedb_jni_darwin_aarch64.zip
|
||||
path: target/release/liblancedb_jni.dylib
|
||||
retention-days: 1
|
||||
if-no-files-found: error
|
||||
linux-arm64:
|
||||
name: Build on Linux Arm64
|
||||
runs-on: warp-ubuntu-2204-arm64-8x
|
||||
timeout-minutes: 45
|
||||
defaults:
|
||||
run:
|
||||
working-directory: ./java/core/lancedb-jni
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Checkout repository
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
- uses: Swatinem/rust-cache@v2
|
||||
- uses: actions-rust-lang/setup-rust-toolchain@v1
|
||||
with:
|
||||
toolchain: "1.79.0"
|
||||
cache-workspaces: "./java/core/lancedb-jni"
|
||||
# Disable full debug symbol generation to speed up CI build and keep memory down
|
||||
# "1" means line tables only, which is useful for panic tracebacks.
|
||||
rustflags: "-C debuginfo=1"
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
sudo apt -y -qq update
|
||||
sudo apt install -y protobuf-compiler libssl-dev pkg-config
|
||||
- name: Build release
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
cargo build --release
|
||||
- uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: liblancedb_jni_linux_aarch64.zip
|
||||
path: target/release/liblancedb_jni.so
|
||||
retention-days: 1
|
||||
if-no-files-found: error
|
||||
linux-x86:
|
||||
runs-on: warp-ubuntu-2204-x64-8x
|
||||
timeout-minutes: 30
|
||||
needs: [macos-arm64, linux-arm64]
|
||||
defaults:
|
||||
run:
|
||||
working-directory: ./java
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Checkout repository
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
- uses: Swatinem/rust-cache@v2
|
||||
- name: Set up Java 8
|
||||
uses: actions/setup-java@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
distribution: temurin
|
||||
java-version: 8
|
||||
cache: "maven"
|
||||
server-id: ossrh
|
||||
server-username: SONATYPE_USER
|
||||
server-password: SONATYPE_TOKEN
|
||||
gpg-private-key: ${{ secrets.GPG_PRIVATE_KEY }}
|
||||
gpg-passphrase: ${{ secrets.GPG_PASSPHRASE }}
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
sudo apt -y -qq update
|
||||
sudo apt install -y protobuf-compiler libssl-dev pkg-config
|
||||
- name: Download artifact
|
||||
uses: actions/download-artifact@v4
|
||||
- name: Copy native libs
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
mkdir -p ./core/target/classes/nativelib/darwin-aarch64 ./core/target/classes/nativelib/linux-aarch64
|
||||
cp ../liblancedb_jni_darwin_aarch64.zip/liblancedb_jni.dylib ./core/target/classes/nativelib/darwin-aarch64/liblancedb_jni.dylib
|
||||
cp ../liblancedb_jni_linux_aarch64.zip/liblancedb_jni.so ./core/target/classes/nativelib/linux-aarch64/liblancedb_jni.so
|
||||
- name: Dry run
|
||||
if: github.event_name == 'pull_request'
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
mvn --batch-mode -DskipTests package
|
||||
- name: Set github
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
git config --global user.email "LanceDB Github Runner"
|
||||
git config --global user.name "dev+gha@lancedb.com"
|
||||
- name: Publish with Java 8
|
||||
if: github.event_name == 'release'
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "use-agent" >> ~/.gnupg/gpg.conf
|
||||
echo "pinentry-mode loopback" >> ~/.gnupg/gpg.conf
|
||||
export GPG_TTY=$(tty)
|
||||
mvn --batch-mode -DskipTests -DpushChanges=false -Dgpg.passphrase=${{ secrets.GPG_PASSPHRASE }} deploy -P deploy-to-ossrh
|
||||
env:
|
||||
SONATYPE_USER: ${{ secrets.SONATYPE_USER }}
|
||||
SONATYPE_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.SONATYPE_TOKEN }}
|
||||
2
.github/workflows/make-release-commit.yml
vendored
2
.github/workflows/make-release-commit.yml
vendored
@@ -30,7 +30,7 @@ on:
|
||||
default: true
|
||||
type: boolean
|
||||
other:
|
||||
description: 'Make a Node/Rust release'
|
||||
description: 'Make a Node/Rust/Java release'
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
default: true
|
||||
type: boolean
|
||||
|
||||
13
Cargo.toml
13
Cargo.toml
@@ -20,12 +20,13 @@ keywords = ["lancedb", "lance", "database", "vector", "search"]
|
||||
categories = ["database-implementations"]
|
||||
|
||||
[workspace.dependencies]
|
||||
lance = { "version" = "=0.16.1", "features" = ["dynamodb"] }
|
||||
lance-index = { "version" = "=0.16.1" }
|
||||
lance-linalg = { "version" = "=0.16.1" }
|
||||
lance-testing = { "version" = "=0.16.1" }
|
||||
lance-datafusion = { "version" = "=0.16.1" }
|
||||
lance-encoding = { "version" = "=0.16.1" }
|
||||
lance = { "version" = "=0.18.0", "features" = ["dynamodb"] }
|
||||
lance-index = { "version" = "=0.18.0" }
|
||||
lance-linalg = { "version" = "=0.18.0" }
|
||||
lance-table = { "version" = "=0.18.0" }
|
||||
lance-testing = { "version" = "=0.18.0" }
|
||||
lance-datafusion = { "version" = "=0.18.0" }
|
||||
lance-encoding = { "version" = "=0.18.0" }
|
||||
# Note that this one does not include pyarrow
|
||||
arrow = { version = "52.2", optional = false }
|
||||
arrow-array = "52.2"
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -26,6 +26,7 @@ theme:
|
||||
- content.code.copy
|
||||
- content.tabs.link
|
||||
- content.action.edit
|
||||
- content.tooltips
|
||||
- toc.follow
|
||||
- navigation.top
|
||||
- navigation.tabs
|
||||
@@ -35,6 +36,7 @@ theme:
|
||||
- navigation.instant
|
||||
icon:
|
||||
repo: fontawesome/brands/github
|
||||
annotation: material/arrow-right-circle
|
||||
custom_dir: overrides
|
||||
|
||||
plugins:
|
||||
@@ -76,7 +78,12 @@ markdown_extensions:
|
||||
- pymdownx.tabbed:
|
||||
alternate_style: true
|
||||
- md_in_html
|
||||
- abbr
|
||||
- attr_list
|
||||
- pymdownx.snippets
|
||||
- pymdownx.emoji:
|
||||
emoji_index: !!python/name:material.extensions.emoji.twemoji
|
||||
emoji_generator: !!python/name:material.extensions.emoji.to_svg
|
||||
|
||||
nav:
|
||||
- Home:
|
||||
@@ -84,7 +91,9 @@ nav:
|
||||
- 🏃🏼♂️ Quick start: basic.md
|
||||
- 📚 Concepts:
|
||||
- Vector search: concepts/vector_search.md
|
||||
- Indexing: concepts/index_ivfpq.md
|
||||
- Indexing:
|
||||
- IVFPQ: concepts/index_ivfpq.md
|
||||
- HNSW: concepts/index_hnsw.md
|
||||
- Storage: concepts/storage.md
|
||||
- Data management: concepts/data_management.md
|
||||
- 🔨 Guides:
|
||||
@@ -97,6 +106,17 @@ nav:
|
||||
- Overview: hybrid_search/hybrid_search.md
|
||||
- Comparing Rerankers: hybrid_search/eval.md
|
||||
- Airbnb financial data example: notebooks/hybrid_search.ipynb
|
||||
- RAG:
|
||||
- Vanilla RAG: rag/vanilla_rag.md
|
||||
- Multi-head RAG: rag/multi_head_rag.md
|
||||
- Corrective RAG: rag/corrective_rag.md
|
||||
- Agentic RAG: rag/agentic_rag.md
|
||||
- Graph RAG: rag/graph_rag.md
|
||||
- Self RAG: rag/self_rag.md
|
||||
- Adaptive RAG: rag/adaptive_rag.md
|
||||
- Advanced Techniques:
|
||||
- HyDE: rag/advanced_techniques/hyde.md
|
||||
- FLARE: rag/advanced_techniques/flare.md
|
||||
- Reranking:
|
||||
- Quickstart: reranking/index.md
|
||||
- Cohere Reranker: reranking/cohere.md
|
||||
@@ -106,6 +126,7 @@ nav:
|
||||
- ColBERT Reranker: reranking/colbert.md
|
||||
- Jina Reranker: reranking/jina.md
|
||||
- OpenAI Reranker: reranking/openai.md
|
||||
- AnswerDotAi Rerankers: reranking/answerdotai.md
|
||||
- Building Custom Rerankers: reranking/custom_reranker.md
|
||||
- Example: notebooks/lancedb_reranking.ipynb
|
||||
- Filtering: sql.md
|
||||
@@ -117,9 +138,26 @@ nav:
|
||||
- Reranking: guides/tuning_retrievers/2_reranking.md
|
||||
- Embedding fine-tuning: guides/tuning_retrievers/3_embed_tuning.md
|
||||
- 🧬 Managing embeddings:
|
||||
- Overview: embeddings/index.md
|
||||
- Understand Embeddings: embeddings/understanding_embeddings.md
|
||||
- Get Started: embeddings/index.md
|
||||
- Embedding functions: embeddings/embedding_functions.md
|
||||
- Available models: embeddings/default_embedding_functions.md
|
||||
- Available models:
|
||||
- Overview: embeddings/default_embedding_functions.md
|
||||
- Text Embedding Functions:
|
||||
- Sentence Transformers: embeddings/available_embedding_models/text_embedding_functions/sentence_transformers.md
|
||||
- Huggingface Embedding Models: embeddings/available_embedding_models/text_embedding_functions/huggingface_embedding.md
|
||||
- Ollama Embeddings: embeddings/available_embedding_models/text_embedding_functions/ollama_embedding.md
|
||||
- OpenAI Embeddings: embeddings/available_embedding_models/text_embedding_functions/openai_embedding.md
|
||||
- Instructor Embeddings: embeddings/available_embedding_models/text_embedding_functions/instructor_embedding.md
|
||||
- Gemini Embeddings: embeddings/available_embedding_models/text_embedding_functions/gemini_embedding.md
|
||||
- Cohere Embeddings: embeddings/available_embedding_models/text_embedding_functions/cohere_embedding.md
|
||||
- Jina Embeddings: embeddings/available_embedding_models/text_embedding_functions/jina_embedding.md
|
||||
- AWS Bedrock Text Embedding Functions: embeddings/available_embedding_models/text_embedding_functions/aws_bedrock_embedding.md
|
||||
- IBM watsonx.ai Embeddings: embeddings/available_embedding_models/text_embedding_functions/ibm_watsonx_ai_embedding.md
|
||||
- Multimodal Embedding Functions:
|
||||
- OpenClip embeddings: embeddings/available_embedding_models/multimodal_embedding_functions/openclip_embedding.md
|
||||
- Imagebind embeddings: embeddings/available_embedding_models/multimodal_embedding_functions/imagebind_embedding.md
|
||||
- Jina Embeddings: embeddings/available_embedding_models/multimodal_embedding_functions/jina_multimodal_embedding.md
|
||||
- User-defined embedding functions: embeddings/custom_embedding_function.md
|
||||
- "Example: Multi-lingual semantic search": notebooks/multi_lingual_example.ipynb
|
||||
- "Example: MultiModal CLIP Embeddings": notebooks/DisappearingEmbeddingFunction.ipynb
|
||||
@@ -150,10 +188,8 @@ nav:
|
||||
- Chatbot: examples/python_examples/chatbot.md
|
||||
- Evaluation: examples/python_examples/evaluations.md
|
||||
- AI Agent: examples/python_examples/aiagent.md
|
||||
- Recommender System: examples/python_examples/recommendersystem.md
|
||||
- Miscellaneous:
|
||||
- YouTube Transcript Search: notebooks/youtube_transcript_search.ipynb
|
||||
- Documentation QA Bot using LangChain: notebooks/code_qa_bot.ipynb
|
||||
- Multimodal search using CLIP: notebooks/multimodal_search.ipynb
|
||||
- Serverless QA Bot with S3 and Lambda: examples/serverless_lancedb_with_s3_and_lambda.md
|
||||
- Serverless QA Bot with Modal: examples/serverless_qa_bot_with_modal_and_langchain.md
|
||||
- 👾 JavaScript:
|
||||
@@ -163,6 +199,8 @@ nav:
|
||||
- TransformersJS Embedding Search: examples/transformerjs_embedding_search_nodejs.md
|
||||
- 🦀 Rust:
|
||||
- Overview: examples/examples_rust.md
|
||||
- Studies:
|
||||
- ↗Improve retrievers with hybrid search and reranking: https://blog.lancedb.com/hybrid-search-and-reranking-report/
|
||||
- 💭 FAQs: faq.md
|
||||
- ⚙️ API reference:
|
||||
- 🐍 Python: python/python.md
|
||||
@@ -179,7 +217,9 @@ nav:
|
||||
- Quick start: basic.md
|
||||
- Concepts:
|
||||
- Vector search: concepts/vector_search.md
|
||||
- Indexing: concepts/index_ivfpq.md
|
||||
- Indexing:
|
||||
- IVFPQ: concepts/index_ivfpq.md
|
||||
- HNSW: concepts/index_hnsw.md
|
||||
- Storage: concepts/storage.md
|
||||
- Data management: concepts/data_management.md
|
||||
- Guides:
|
||||
@@ -192,6 +232,17 @@ nav:
|
||||
- Overview: hybrid_search/hybrid_search.md
|
||||
- Comparing Rerankers: hybrid_search/eval.md
|
||||
- Airbnb financial data example: notebooks/hybrid_search.ipynb
|
||||
- RAG:
|
||||
- Vanilla RAG: rag/vanilla_rag.md
|
||||
- Multi-head RAG: rag/multi_head_rag.md
|
||||
- Corrective RAG: rag/corrective_rag.md
|
||||
- Agentic RAG: rag/agentic_rag.md
|
||||
- Graph RAG: rag/graph_rag.md
|
||||
- Self RAG: rag/self_rag.md
|
||||
- Adaptive RAG: rag/adaptive_rag.md
|
||||
- Advanced Techniques:
|
||||
- HyDE: rag/advanced_techniques/hyde.md
|
||||
- FLARE: rag/advanced_techniques/flare.md
|
||||
- Reranking:
|
||||
- Quickstart: reranking/index.md
|
||||
- Cohere Reranker: reranking/cohere.md
|
||||
@@ -201,6 +252,7 @@ nav:
|
||||
- ColBERT Reranker: reranking/colbert.md
|
||||
- Jina Reranker: reranking/jina.md
|
||||
- OpenAI Reranker: reranking/openai.md
|
||||
- AnswerDotAi Rerankers: reranking/answerdotai.md
|
||||
- Building Custom Rerankers: reranking/custom_reranker.md
|
||||
- Example: notebooks/lancedb_reranking.ipynb
|
||||
- Filtering: sql.md
|
||||
@@ -212,9 +264,26 @@ nav:
|
||||
- Reranking: guides/tuning_retrievers/2_reranking.md
|
||||
- Embedding fine-tuning: guides/tuning_retrievers/3_embed_tuning.md
|
||||
- Managing Embeddings:
|
||||
- Overview: embeddings/index.md
|
||||
- Understand Embeddings: embeddings/understanding_embeddings.md
|
||||
- Get Started: embeddings/index.md
|
||||
- Embedding functions: embeddings/embedding_functions.md
|
||||
- Available models: embeddings/default_embedding_functions.md
|
||||
- Available models:
|
||||
- Overview: embeddings/default_embedding_functions.md
|
||||
- Text Embedding Functions:
|
||||
- Sentence Transformers: embeddings/available_embedding_models/text_embedding_functions/sentence_transformers.md
|
||||
- Huggingface Embedding Models: embeddings/available_embedding_models/text_embedding_functions/huggingface_embedding.md
|
||||
- Ollama Embeddings: embeddings/available_embedding_models/text_embedding_functions/ollama_embedding.md
|
||||
- OpenAI Embeddings: embeddings/available_embedding_models/text_embedding_functions/openai_embedding.md
|
||||
- Instructor Embeddings: embeddings/available_embedding_models/text_embedding_functions/instructor_embedding.md
|
||||
- Gemini Embeddings: embeddings/available_embedding_models/text_embedding_functions/gemini_embedding.md
|
||||
- Cohere Embeddings: embeddings/available_embedding_models/text_embedding_functions/cohere_embedding.md
|
||||
- Jina Embeddings: embeddings/available_embedding_models/text_embedding_functions/jina_embedding.md
|
||||
- AWS Bedrock Text Embedding Functions: embeddings/available_embedding_models/text_embedding_functions/aws_bedrock_embedding.md
|
||||
- IBM watsonx.ai Embeddings: embeddings/available_embedding_models/text_embedding_functions/ibm_watsonx_ai_embedding.md
|
||||
- Multimodal Embedding Functions:
|
||||
- OpenClip embeddings: embeddings/available_embedding_models/multimodal_embedding_functions/openclip_embedding.md
|
||||
- Imagebind embeddings: embeddings/available_embedding_models/multimodal_embedding_functions/imagebind_embedding.md
|
||||
- Jina Embeddings: embeddings/available_embedding_models/multimodal_embedding_functions/jina_multimodal_embedding.md
|
||||
- User-defined embedding functions: embeddings/custom_embedding_function.md
|
||||
- "Example: Multi-lingual semantic search": notebooks/multi_lingual_example.ipynb
|
||||
- "Example: MultiModal CLIP Embeddings": notebooks/DisappearingEmbeddingFunction.ipynb
|
||||
@@ -241,10 +310,8 @@ nav:
|
||||
- Chatbot: examples/python_examples/chatbot.md
|
||||
- Evaluation: examples/python_examples/evaluations.md
|
||||
- AI Agent: examples/python_examples/aiagent.md
|
||||
- Recommender System: examples/python_examples/recommendersystem.md
|
||||
- Miscellaneous:
|
||||
- YouTube Transcript Search: notebooks/youtube_transcript_search.ipynb
|
||||
- Documentation QA Bot using LangChain: notebooks/code_qa_bot.ipynb
|
||||
- Multimodal search using CLIP: notebooks/multimodal_search.ipynb
|
||||
- Serverless QA Bot with S3 and Lambda: examples/serverless_lancedb_with_s3_and_lambda.md
|
||||
- Serverless QA Bot with Modal: examples/serverless_qa_bot_with_modal_and_langchain.md
|
||||
- 👾 JavaScript:
|
||||
@@ -254,6 +321,9 @@ nav:
|
||||
- TransformersJS Embedding Search: examples/transformerjs_embedding_search_nodejs.md
|
||||
- 🦀 Rust:
|
||||
- Overview: examples/examples_rust.md
|
||||
- Studies:
|
||||
- studies/overview.md
|
||||
- ↗Improve retrievers with hybrid search and reranking: https://blog.lancedb.com/hybrid-search-and-reranking-report/
|
||||
- API reference:
|
||||
- Overview: api_reference.md
|
||||
- Python: python/python.md
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -572,7 +572,7 @@ You can use the embedding API when working with embedding models. It automatical
|
||||
--8<-- "rust/lancedb/examples/openai.rs:openai_embeddings"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Learn about using the existing integrations and creating custom embedding functions in the [embedding API guide](./embeddings/).
|
||||
Learn about using the existing integrations and creating custom embedding functions in the [embedding API guide](./embeddings/index.md).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## What's next
|
||||
|
||||
92
docs/src/concepts/index_hnsw.md
Normal file
92
docs/src/concepts/index_hnsw.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,92 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# Understanding HNSW index
|
||||
|
||||
Approximate Nearest Neighbor (ANN) search is a method for finding data points near a given point in a dataset, though not always the exact nearest one. HNSW is one of the most accurate and fastest Approximate Nearest Neighbour search algorithms, It’s beneficial in high-dimensional spaces where finding the same nearest neighbor would be too slow and costly
|
||||
|
||||
[Jump to usage](#usage)
|
||||
There are three main types of ANN search algorithms:
|
||||
|
||||
* **Tree-based search algorithms**: Use a tree structure to organize and store data points.
|
||||
* * **Hash-based search algorithms**: Use a specialized geometric hash table to store and manage data points. These algorithms typically focus on theoretical guarantees, and don't usually perform as well as the other approaches in practice.
|
||||
* **Graph-based search algorithms**: Use a graph structure to store data points, which can be a bit complex.
|
||||
|
||||
HNSW is a graph-based algorithm. All graph-based search algorithms rely on the idea of a k-nearest neighbor (or k-approximate nearest neighbor) graph, which we outline below.
|
||||
HNSW also combines this with the ideas behind a classic 1-dimensional search data structure: the skip list.
|
||||
|
||||
## k-Nearest Neighbor Graphs and k-approximate Nearest neighbor Graphs
|
||||
The k-nearest neighbor graph actually predates its use for ANN search. Its construction is quite simple:
|
||||
|
||||
* Each vector in the dataset is given an associated vertex.
|
||||
* Each vertex has outgoing edges to its k nearest neighbors. That is, the k closest other vertices by Euclidean distance between the two corresponding vectors. This can be thought of as a "friend list" for the vertex.
|
||||
* For some applications (including nearest-neighbor search), the incoming edges are also added.
|
||||
|
||||
Eventually, it was realized that the following greedy search method over such a graph typically results in good approximate nearest neighbors:
|
||||
|
||||
* Given a query vector, start at some fixed "entry point" vertex (e.g. the approximate center node).
|
||||
* Look at that vertex's neighbors. If any of them are closer to the query vector than the current vertex, then move to that vertex.
|
||||
* Repeat until a local optimum is found.
|
||||
|
||||
The above algorithm also generalizes to e.g. top 10 approximate nearest neighbors.
|
||||
|
||||
Computing a k-nearest neighbor graph is actually quite slow, taking quadratic time in the dataset size. It was quickly realized that near-identical performance can be achieved using a k-approximate nearest neighbor graph. That is, instead of obtaining the k-nearest neighbors for each vertex, an approximate nearest neighbor search data structure is used to build much faster.
|
||||
In fact, another data structure is not needed: This can be done "incrementally".
|
||||
That is, if you start with a k-ANN graph for n-1 vertices, you can extend it to a k-ANN graph for n vertices as well by using the graph to obtain the k-ANN for the new vertex.
|
||||
|
||||
One downside of k-NN and k-ANN graphs alone is that one must typically build them with a large value of k to get decent results, resulting in a large index.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## HNSW: Hierarchical Navigable Small Worlds
|
||||
|
||||
HNSW builds on k-ANN in two main ways:
|
||||
|
||||
* Instead of getting the k-approximate nearest neighbors for a large value of k, it sparsifies the k-ANN graph using a carefully chosen "edge pruning" heuristic, allowing for the number of edges per vertex to be limited to a relatively small constant.
|
||||
* The "entry point" vertex is chosen dynamically using a recursively constructed data structure on a subset of the data, similarly to a skip list.
|
||||
|
||||
This recursive structure can be thought of as separating into layers:
|
||||
|
||||
* At the bottom-most layer, an k-ANN graph on the whole dataset is present.
|
||||
* At the second layer, a k-ANN graph on a fraction of the dataset (e.g. 10%) is present.
|
||||
* At the Lth layer, a k-ANN graph is present. It is over a (constant) fraction (e.g. 10%) of the vectors/vertices present in the L-1th layer.
|
||||
|
||||
Then the greedy search routine operates as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
* At the top layer (using an arbitrary vertex as an entry point), use the greedy local search routine on the k-ANN graph to get an approximate nearest neighbor at that layer.
|
||||
* Using the approximate nearest neighbor found in the previous layer as an entry point, find an approximate nearest neighbor in the next layer with the same method.
|
||||
* Repeat until the bottom-most layer is reached. Then use the entry point to find multiple nearest neighbors (e.g. top 10).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage
|
||||
|
||||
We can combine the above concepts to understand how to build and query an HNSW index in LanceDB.
|
||||
|
||||
### Construct index
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
uri = "/tmp/lancedb"
|
||||
db = lancedb.connect(uri)
|
||||
|
||||
# Create 10,000 sample vectors
|
||||
data = [
|
||||
{"vector": row, "item": f"item {i}"}
|
||||
for i, row in enumerate(np.random.random((10_000, 1536)).astype('float32'))
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
# Add the vectors to a table
|
||||
tbl = db.create_table("my_vectors", data=data)
|
||||
|
||||
# Create and train the HNSW index for a 1536-dimensional vector
|
||||
# Make sure you have enough data in the table for an effective training step
|
||||
tbl.create_index(index_type=IVF_HNSW_SQ)
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Query the index
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# Search using a random 1536-dimensional embedding
|
||||
tbl.search(np.random.random((1536))) \
|
||||
.limit(2) \
|
||||
.to_pandas()
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,67 @@
|
||||
# Imagebind embeddings
|
||||
We have support for [imagebind](https://github.com/facebookresearch/ImageBind) model embeddings. You can download our version of the packaged model via - `pip install imagebind-packaged==0.1.2`.
|
||||
|
||||
This function is registered as `imagebind` and supports Audio, Video and Text modalities(extending to Thermal,Depth,IMU data):
|
||||
|
||||
| Parameter | Type | Default Value | Description |
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|
|
||||
| `name` | `str` | `"imagebind_huge"` | Name of the model. |
|
||||
| `device` | `str` | `"cpu"` | The device to run the model on. Can be `"cpu"` or `"gpu"`. |
|
||||
| `normalize` | `bool` | `False` | set to `True` to normalize your inputs before model ingestion. |
|
||||
|
||||
Below is an example demonstrating how the API works:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
from lancedb.pydantic import LanceModel, Vector
|
||||
from lancedb.embeddings import get_registry
|
||||
|
||||
db = lancedb.connect(tmp_path)
|
||||
func = get_registry().get("imagebind").create()
|
||||
|
||||
class ImageBindModel(LanceModel):
|
||||
text: str
|
||||
image_uri: str = func.SourceField()
|
||||
audio_path: str
|
||||
vector: Vector(func.ndims()) = func.VectorField()
|
||||
|
||||
# add locally accessible image paths
|
||||
text_list=["A dog.", "A car", "A bird"]
|
||||
image_paths=[".assets/dog_image.jpg", ".assets/car_image.jpg", ".assets/bird_image.jpg"]
|
||||
audio_paths=[".assets/dog_audio.wav", ".assets/car_audio.wav", ".assets/bird_audio.wav"]
|
||||
|
||||
# Load data
|
||||
inputs = [
|
||||
{"text": a, "audio_path": b, "image_uri": c}
|
||||
for a, b, c in zip(text_list, audio_paths, image_paths)
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
#create table and add data
|
||||
table = db.create_table("img_bind", schema=ImageBindModel)
|
||||
table.add(inputs)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now, we can search using any modality:
|
||||
|
||||
#### image search
|
||||
```python
|
||||
query_image = "./assets/dog_image2.jpg" #download an image and enter that path here
|
||||
actual = table.search(query_image).limit(1).to_pydantic(ImageBindModel)[0]
|
||||
print(actual.text == "dog")
|
||||
```
|
||||
#### audio search
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
query_audio = "./assets/car_audio2.wav" #download an audio clip and enter path here
|
||||
actual = table.search(query_audio).limit(1).to_pydantic(ImageBindModel)[0]
|
||||
print(actual.text == "car")
|
||||
```
|
||||
#### Text search
|
||||
You can add any input query and fetch the result as follows:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
query = "an animal which flies and tweets"
|
||||
actual = table.search(query).limit(1).to_pydantic(ImageBindModel)[0]
|
||||
print(actual.text == "bird")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you have any questions about the embeddings API, supported models, or see a relevant model missing, please raise an issue [on GitHub](https://github.com/lancedb/lancedb/issues).
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,51 @@
|
||||
# Jina Embeddings : Multimodal
|
||||
|
||||
Jina embeddings can also be used to embed both text and image data, only some of the models support image data and you can check the list
|
||||
under [https://jina.ai/embeddings/](https://jina.ai/embeddings/)
|
||||
|
||||
Supported parameters (to be passed in `create` method) are:
|
||||
|
||||
| Parameter | Type | Default Value | Description |
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|
|
||||
| `name` | `str` | `"jina-clip-v1"` | The model ID of the jina model to use |
|
||||
|
||||
Usage Example:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import requests
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
from lancedb.pydantic import LanceModel, Vector
|
||||
from lancedb.embeddings import get_registry
|
||||
import pandas as pd
|
||||
|
||||
os.environ['JINA_API_KEY'] = 'jina_*'
|
||||
|
||||
db = lancedb.connect("~/.lancedb")
|
||||
func = get_registry().get("jina").create()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Images(LanceModel):
|
||||
label: str
|
||||
image_uri: str = func.SourceField() # image uri as the source
|
||||
image_bytes: bytes = func.SourceField() # image bytes as the source
|
||||
vector: Vector(func.ndims()) = func.VectorField() # vector column
|
||||
vec_from_bytes: Vector(func.ndims()) = func.VectorField() # Another vector column
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
table = db.create_table("images", schema=Images)
|
||||
labels = ["cat", "cat", "dog", "dog", "horse", "horse"]
|
||||
uris = [
|
||||
"http://farm1.staticflickr.com/53/167798175_7c7845bbbd_z.jpg",
|
||||
"http://farm1.staticflickr.com/134/332220238_da527d8140_z.jpg",
|
||||
"http://farm9.staticflickr.com/8387/8602747737_2e5c2a45d4_z.jpg",
|
||||
"http://farm5.staticflickr.com/4092/5017326486_1f46057f5f_z.jpg",
|
||||
"http://farm9.staticflickr.com/8216/8434969557_d37882c42d_z.jpg",
|
||||
"http://farm6.staticflickr.com/5142/5835678453_4f3a4edb45_z.jpg",
|
||||
]
|
||||
# get each uri as bytes
|
||||
image_bytes = [requests.get(uri).content for uri in uris]
|
||||
table.add(
|
||||
pd.DataFrame({"label": labels, "image_uri": uris, "image_bytes": image_bytes})
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,82 @@
|
||||
# OpenClip embeddings
|
||||
We support CLIP model embeddings using the open source alternative, [open-clip](https://github.com/mlfoundations/open_clip) which supports various customizations. It is registered as `open-clip` and supports the following customizations:
|
||||
|
||||
| Parameter | Type | Default Value | Description |
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|
|
||||
| `name` | `str` | `"ViT-B-32"` | The name of the model. |
|
||||
| `pretrained` | `str` | `"laion2b_s34b_b79k"` | The name of the pretrained model to load. |
|
||||
| `device` | `str` | `"cpu"` | The device to run the model on. Can be `"cpu"` or `"gpu"`. |
|
||||
| `batch_size` | `int` | `64` | The number of images to process in a batch. |
|
||||
| `normalize` | `bool` | `True` | Whether to normalize the input images before feeding them to the model. |
|
||||
|
||||
This embedding function supports ingesting images as both bytes and urls. You can query them using both test and other images.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! info
|
||||
LanceDB supports ingesting images directly from accessible links.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
from lancedb.pydantic import LanceModel, Vector
|
||||
from lancedb.embeddings import get_registry
|
||||
|
||||
db = lancedb.connect(tmp_path)
|
||||
func = get_registry().get("open-clip").create()
|
||||
|
||||
class Images(LanceModel):
|
||||
label: str
|
||||
image_uri: str = func.SourceField() # image uri as the source
|
||||
image_bytes: bytes = func.SourceField() # image bytes as the source
|
||||
vector: Vector(func.ndims()) = func.VectorField() # vector column
|
||||
vec_from_bytes: Vector(func.ndims()) = func.VectorField() # Another vector column
|
||||
|
||||
table = db.create_table("images", schema=Images)
|
||||
labels = ["cat", "cat", "dog", "dog", "horse", "horse"]
|
||||
uris = [
|
||||
"http://farm1.staticflickr.com/53/167798175_7c7845bbbd_z.jpg",
|
||||
"http://farm1.staticflickr.com/134/332220238_da527d8140_z.jpg",
|
||||
"http://farm9.staticflickr.com/8387/8602747737_2e5c2a45d4_z.jpg",
|
||||
"http://farm5.staticflickr.com/4092/5017326486_1f46057f5f_z.jpg",
|
||||
"http://farm9.staticflickr.com/8216/8434969557_d37882c42d_z.jpg",
|
||||
"http://farm6.staticflickr.com/5142/5835678453_4f3a4edb45_z.jpg",
|
||||
]
|
||||
# get each uri as bytes
|
||||
image_bytes = [requests.get(uri).content for uri in uris]
|
||||
table.add(
|
||||
pd.DataFrame({"label": labels, "image_uri": uris, "image_bytes": image_bytes})
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
Now we can search using text from both the default vector column and the custom vector column
|
||||
```python
|
||||
|
||||
# text search
|
||||
actual = table.search("man's best friend").limit(1).to_pydantic(Images)[0]
|
||||
print(actual.label) # prints "dog"
|
||||
|
||||
frombytes = (
|
||||
table.search("man's best friend", vector_column_name="vec_from_bytes")
|
||||
.limit(1)
|
||||
.to_pydantic(Images)[0]
|
||||
)
|
||||
print(frombytes.label)
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Because we're using a multi-modal embedding function, we can also search using images
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# image search
|
||||
query_image_uri = "http://farm1.staticflickr.com/200/467715466_ed4a31801f_z.jpg"
|
||||
image_bytes = requests.get(query_image_uri).content
|
||||
query_image = Image.open(io.BytesIO(image_bytes))
|
||||
actual = table.search(query_image).limit(1).to_pydantic(Images)[0]
|
||||
print(actual.label == "dog")
|
||||
|
||||
# image search using a custom vector column
|
||||
other = (
|
||||
table.search(query_image, vector_column_name="vec_from_bytes")
|
||||
.limit(1)
|
||||
.to_pydantic(Images)[0]
|
||||
)
|
||||
print(actual.label)
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,51 @@
|
||||
# AWS Bedrock Text Embedding Functions
|
||||
|
||||
AWS Bedrock supports multiple base models for generating text embeddings. You need to setup the AWS credentials to use this embedding function.
|
||||
You can do so by using `awscli` and also add your session_token:
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
aws configure
|
||||
aws configure set aws_session_token "<your_session_token>"
|
||||
```
|
||||
to ensure that the credentials are set up correctly, you can run the following command:
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
aws sts get-caller-identity
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Supported Embedding modelIDs are:
|
||||
* `amazon.titan-embed-text-v1`
|
||||
* `cohere.embed-english-v3`
|
||||
* `cohere.embed-multilingual-v3`
|
||||
|
||||
Supported parameters (to be passed in `create` method) are:
|
||||
|
||||
| Parameter | Type | Default Value | Description |
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|
|
||||
| **name** | str | "amazon.titan-embed-text-v1" | The model ID of the bedrock model to use. Supported base models for Text Embeddings: amazon.titan-embed-text-v1, cohere.embed-english-v3, cohere.embed-multilingual-v3 |
|
||||
| **region** | str | "us-east-1" | Optional name of the AWS Region in which the service should be called (e.g., "us-east-1"). |
|
||||
| **profile_name** | str | None | Optional name of the AWS profile to use for calling the Bedrock service. If not specified, the default profile will be used. |
|
||||
| **assumed_role** | str | None | Optional ARN of an AWS IAM role to assume for calling the Bedrock service. If not specified, the current active credentials will be used. |
|
||||
| **role_session_name** | str | "lancedb-embeddings" | Optional name of the AWS IAM role session to use for calling the Bedrock service. If not specified, a "lancedb-embeddings" name will be used. |
|
||||
| **runtime** | bool | True | Optional choice of getting different client to perform operations with the Amazon Bedrock service. |
|
||||
| **max_retries** | int | 7 | Optional number of retries to perform when a request fails. |
|
||||
|
||||
Usage Example:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
from lancedb.pydantic import LanceModel, Vector
|
||||
from lancedb.embeddings import get_registry
|
||||
import pandas as pd
|
||||
|
||||
model = get_registry().get("bedrock-text").create()
|
||||
|
||||
class TextModel(LanceModel):
|
||||
text: str = model.SourceField()
|
||||
vector: Vector(model.ndims()) = model.VectorField()
|
||||
|
||||
df = pd.DataFrame({"text": ["hello world", "goodbye world"]})
|
||||
db = lancedb.connect("tmp_path")
|
||||
tbl = db.create_table("test", schema=TextModel, mode="overwrite")
|
||||
|
||||
tbl.add(df)
|
||||
rs = tbl.search("hello").limit(1).to_pandas()
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,63 @@
|
||||
# Cohere Embeddings
|
||||
|
||||
Using cohere API requires cohere package, which can be installed using `pip install cohere`. Cohere embeddings are used to generate embeddings for text data. The embeddings can be used for various tasks like semantic search, clustering, and classification.
|
||||
You also need to set the `COHERE_API_KEY` environment variable to use the Cohere API.
|
||||
|
||||
Supported models are:
|
||||
|
||||
- embed-english-v3.0
|
||||
- embed-multilingual-v3.0
|
||||
- embed-english-light-v3.0
|
||||
- embed-multilingual-light-v3.0
|
||||
- embed-english-v2.0
|
||||
- embed-english-light-v2.0
|
||||
- embed-multilingual-v2.0
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Supported parameters (to be passed in `create` method) are:
|
||||
|
||||
| Parameter | Type | Default Value | Description |
|
||||
|---|---|--------|---------|
|
||||
| `name` | `str` | `"embed-english-v2.0"` | The model ID of the cohere model to use. Supported base models for Text Embeddings: embed-english-v3.0, embed-multilingual-v3.0, embed-english-light-v3.0, embed-multilingual-light-v3.0, embed-english-v2.0, embed-english-light-v2.0, embed-multilingual-v2.0 |
|
||||
| `source_input_type` | `str` | `"search_document"` | The type of input data to be used for the source column. |
|
||||
| `query_input_type` | `str` | `"search_query"` | The type of input data to be used for the query. |
|
||||
|
||||
Cohere supports following input types:
|
||||
|
||||
| Input Type | Description |
|
||||
|-------------------------|---------------------------------------|
|
||||
| "`search_document`" | Used for embeddings stored in a vector|
|
||||
| | database for search use-cases. |
|
||||
| "`search_query`" | Used for embeddings of search queries |
|
||||
| | run against a vector DB |
|
||||
| "`semantic_similarity`" | Specifies the given text will be used |
|
||||
| | for Semantic Textual Similarity (STS) |
|
||||
| "`classification`" | Used for embeddings passed through a |
|
||||
| | text classifier. |
|
||||
| "`clustering`" | Used for the embeddings run through a |
|
||||
| | clustering algorithm |
|
||||
|
||||
Usage Example:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
from lancedb.pydantic import LanceModel, Vector
|
||||
from lancedb.embeddings import EmbeddingFunctionRegistry
|
||||
|
||||
cohere = EmbeddingFunctionRegistry
|
||||
.get_instance()
|
||||
.get("cohere")
|
||||
.create(name="embed-multilingual-v2.0")
|
||||
|
||||
class TextModel(LanceModel):
|
||||
text: str = cohere.SourceField()
|
||||
vector: Vector(cohere.ndims()) = cohere.VectorField()
|
||||
|
||||
data = [ { "text": "hello world" },
|
||||
{ "text": "goodbye world" }]
|
||||
|
||||
db = lancedb.connect("~/.lancedb")
|
||||
tbl = db.create_table("test", schema=TextModel, mode="overwrite")
|
||||
|
||||
tbl.add(data)
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
|
||||
# Gemini Embeddings
|
||||
With Google's Gemini, you can represent text (words, sentences, and blocks of text) in a vectorized form, making it easier to compare and contrast embeddings. For example, two texts that share a similar subject matter or sentiment should have similar embeddings, which can be identified through mathematical comparison techniques such as cosine similarity. For more on how and why you should use embeddings, refer to the Embeddings guide.
|
||||
The Gemini Embedding Model API supports various task types:
|
||||
|
||||
| Task Type | Description |
|
||||
|-------------------------|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| "`retrieval_query`" | Specifies the given text is a query in a search/retrieval setting. |
|
||||
| "`retrieval_document`" | Specifies the given text is a document in a search/retrieval setting. Using this task type requires a title but is automatically proided by Embeddings API |
|
||||
| "`semantic_similarity`" | Specifies the given text will be used for Semantic Textual Similarity (STS). |
|
||||
| "`classification`" | Specifies that the embeddings will be used for classification. |
|
||||
| "`clusering`" | Specifies that the embeddings will be used for clustering. |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Usage Example:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
import pandas as pd
|
||||
from lancedb.pydantic import LanceModel, Vector
|
||||
from lancedb.embeddings import get_registry
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
model = get_registry().get("gemini-text").create()
|
||||
|
||||
class TextModel(LanceModel):
|
||||
text: str = model.SourceField()
|
||||
vector: Vector(model.ndims()) = model.VectorField()
|
||||
|
||||
df = pd.DataFrame({"text": ["hello world", "goodbye world"]})
|
||||
db = lancedb.connect("~/.lancedb")
|
||||
tbl = db.create_table("test", schema=TextModel, mode="overwrite")
|
||||
|
||||
tbl.add(df)
|
||||
rs = tbl.search("hello").limit(1).to_pandas()
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,24 @@
|
||||
# Huggingface embedding models
|
||||
We offer support for all huggingface models (which can be loaded via [transformers](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/en/index) library). The default model is `colbert-ir/colbertv2.0` which also has its own special callout - `registry.get("colbert")`
|
||||
|
||||
Example usage -
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
import pandas as pd
|
||||
|
||||
from lancedb.embeddings import get_registry
|
||||
from lancedb.pydantic import LanceModel, Vector
|
||||
|
||||
model = get_registry().get("huggingface").create(name='facebook/bart-base')
|
||||
|
||||
class Words(LanceModel):
|
||||
text: str = model.SourceField()
|
||||
vector: Vector(model.ndims()) = model.VectorField()
|
||||
|
||||
df = pd.DataFrame({"text": ["hi hello sayonara", "goodbye world"]})
|
||||
table = db.create_table("greets", schema=Words)
|
||||
table.add(df)
|
||||
query = "old greeting"
|
||||
actual = table.search(query).limit(1).to_pydantic(Words)[0]
|
||||
print(actual.text)
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,75 @@
|
||||
# IBM watsonx.ai Embeddings
|
||||
|
||||
Generate text embeddings using IBM's watsonx.ai platform.
|
||||
|
||||
## Supported Models
|
||||
|
||||
You can find a list of supported models at [IBM watsonx.ai Documentation](https://dataplatform.cloud.ibm.com/docs/content/wsj/analyze-data/fm-models-embed.html?context=wx). The currently supported model names are:
|
||||
|
||||
- `ibm/slate-125m-english-rtrvr`
|
||||
- `ibm/slate-30m-english-rtrvr`
|
||||
- `sentence-transformers/all-minilm-l12-v2`
|
||||
- `intfloat/multilingual-e5-large`
|
||||
|
||||
## Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
The following parameters can be passed to the `create` method:
|
||||
|
||||
| Parameter | Type | Default Value | Description |
|
||||
|------------|----------|----------------------------------|-----------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| name | str | "ibm/slate-125m-english-rtrvr" | The model ID of the watsonx.ai model to use |
|
||||
| api_key | str | None | Optional IBM Cloud API key (or set `WATSONX_API_KEY`) |
|
||||
| project_id | str | None | Optional watsonx project ID (or set `WATSONX_PROJECT_ID`) |
|
||||
| url | str | None | Optional custom URL for the watsonx.ai instance |
|
||||
| params | dict | None | Optional additional parameters for the embedding model |
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage Example
|
||||
|
||||
First, the watsonx.ai library is an optional dependency, so must be installed seperately:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
pip install ibm-watsonx-ai
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Optionally set environment variables (if not passing credentials to `create` directly):
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
export WATSONX_API_KEY="YOUR_WATSONX_API_KEY"
|
||||
export WATSONX_PROJECT_ID="YOUR_WATSONX_PROJECT_ID"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
from lancedb.pydantic import LanceModel, Vector
|
||||
from lancedb.embeddings import EmbeddingFunctionRegistry
|
||||
|
||||
watsonx_embed = EmbeddingFunctionRegistry
|
||||
.get_instance()
|
||||
.get("watsonx")
|
||||
.create(
|
||||
name="ibm/slate-125m-english-rtrvr",
|
||||
# Uncomment and set these if not using environment variables
|
||||
# api_key="your_api_key_here",
|
||||
# project_id="your_project_id_here",
|
||||
# url="your_watsonx_url_here",
|
||||
# params={...},
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
class TextModel(LanceModel):
|
||||
text: str = watsonx_embed.SourceField()
|
||||
vector: Vector(watsonx_embed.ndims()) = watsonx_embed.VectorField()
|
||||
|
||||
data = [
|
||||
{"text": "hello world"},
|
||||
{"text": "goodbye world"},
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
db = lancedb.connect("~/.lancedb")
|
||||
tbl = db.create_table("watsonx_test", schema=TextModel, mode="overwrite")
|
||||
|
||||
tbl.add(data)
|
||||
|
||||
rs = tbl.search("hello").limit(1).to_pandas()
|
||||
print(rs)
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,50 @@
|
||||
# Instructor Embeddings
|
||||
[Instructor](https://instructor-embedding.github.io/) is an instruction-finetuned text embedding model that can generate text embeddings tailored to any task (e.g. classification, retrieval, clustering, text evaluation, etc.) and domains (e.g. science, finance, etc.) by simply providing the task instruction, without any finetuning.
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to calculate customized embeddings for specific sentences, you can follow the unified template to write instructions.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! info
|
||||
Represent the `domain` `text_type` for `task_objective`:
|
||||
|
||||
* `domain` is optional, and it specifies the domain of the text, e.g. science, finance, medicine, etc.
|
||||
* `text_type` is required, and it specifies the encoding unit, e.g. sentence, document, paragraph, etc.
|
||||
* `task_objective` is optional, and it specifies the objective of embedding, e.g. retrieve a document, classify the sentence, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
More information about the model can be found at the [source URL](https://github.com/xlang-ai/instructor-embedding).
|
||||
|
||||
| Argument | Type | Default | Description |
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|
|
||||
| `name` | `str` | "hkunlp/instructor-base" | The name of the model to use |
|
||||
| `batch_size` | `int` | `32` | The batch size to use when generating embeddings |
|
||||
| `device` | `str` | `"cpu"` | The device to use when generating embeddings |
|
||||
| `show_progress_bar` | `bool` | `True` | Whether to show a progress bar when generating embeddings |
|
||||
| `normalize_embeddings` | `bool` | `True` | Whether to normalize the embeddings |
|
||||
| `quantize` | `bool` | `False` | Whether to quantize the model |
|
||||
| `source_instruction` | `str` | `"represent the docuement for retreival"` | The instruction for the source column |
|
||||
| `query_instruction` | `str` | `"represent the document for retreiving the most similar documents"` | The instruction for the query |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
from lancedb.pydantic import LanceModel, Vector
|
||||
from lancedb.embeddings import get_registry, InstuctorEmbeddingFunction
|
||||
|
||||
instructor = get_registry().get("instructor").create(
|
||||
source_instruction="represent the docuement for retreival",
|
||||
query_instruction="represent the document for retreiving the most similar documents"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
class Schema(LanceModel):
|
||||
vector: Vector(instructor.ndims()) = instructor.VectorField()
|
||||
text: str = instructor.SourceField()
|
||||
|
||||
db = lancedb.connect("~/.lancedb")
|
||||
tbl = db.create_table("test", schema=Schema, mode="overwrite")
|
||||
|
||||
texts = [{"text": "Capitalism has been dominant in the Western world since the end of feudalism, but most feel[who?] that..."},
|
||||
{"text": "The disparate impact theory is especially controversial under the Fair Housing Act because the Act..."},
|
||||
{"text": "Disparate impact in United States labor law refers to practices in employment, housing, and other areas that.."}]
|
||||
|
||||
tbl.add(texts)
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
|
||||
# Jina Embeddings
|
||||
|
||||
Jina embeddings are used to generate embeddings for text and image data.
|
||||
You also need to set the `JINA_API_KEY` environment variable to use the Jina API.
|
||||
|
||||
You can find a list of supported models under [https://jina.ai/embeddings/](https://jina.ai/embeddings/)
|
||||
|
||||
Supported parameters (to be passed in `create` method) are:
|
||||
|
||||
| Parameter | Type | Default Value | Description |
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|
|
||||
| `name` | `str` | `"jina-clip-v1"` | The model ID of the jina model to use |
|
||||
|
||||
Usage Example:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
from lancedb.pydantic import LanceModel, Vector
|
||||
from lancedb.embeddings import EmbeddingFunctionRegistry
|
||||
|
||||
os.environ['JINA_API_KEY'] = 'jina_*'
|
||||
|
||||
jina_embed = EmbeddingFunctionRegistry.get_instance().get("jina").create(name="jina-embeddings-v2-base-en")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class TextModel(LanceModel):
|
||||
text: str = jina_embed.SourceField()
|
||||
vector: Vector(jina_embed.ndims()) = jina_embed.VectorField()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
data = [{"text": "hello world"},
|
||||
{"text": "goodbye world"}]
|
||||
|
||||
db = lancedb.connect("~/.lancedb-2")
|
||||
tbl = db.create_table("test", schema=TextModel, mode="overwrite")
|
||||
|
||||
tbl.add(data)
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
|
||||
# Ollama embeddings
|
||||
|
||||
Generate embeddings via the [ollama](https://github.com/ollama/ollama-python) python library. More details:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Ollama docs on embeddings](https://github.com/ollama/ollama/blob/main/docs/api.md#generate-embeddings)
|
||||
- [Ollama blog on embeddings](https://ollama.com/blog/embedding-models)
|
||||
|
||||
| Parameter | Type | Default Value | Description |
|
||||
|------------------------|----------------------------|--------------------------|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| `name` | `str` | `nomic-embed-text` | The name of the model. |
|
||||
| `host` | `str` | `http://localhost:11434` | The Ollama host to connect to. |
|
||||
| `options` | `ollama.Options` or `dict` | `None` | Additional model parameters listed in the documentation for the Modelfile such as `temperature`. |
|
||||
| `keep_alive` | `float` or `str` | `"5m"` | Controls how long the model will stay loaded into memory following the request. |
|
||||
| `ollama_client_kwargs` | `dict` | `{}` | kwargs that can be past to the `ollama.Client`. |
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
from lancedb.pydantic import LanceModel, Vector
|
||||
from lancedb.embeddings import get_registry
|
||||
|
||||
db = lancedb.connect("/tmp/db")
|
||||
func = get_registry().get("ollama").create(name="nomic-embed-text")
|
||||
|
||||
class Words(LanceModel):
|
||||
text: str = func.SourceField()
|
||||
vector: Vector(func.ndims()) = func.VectorField()
|
||||
|
||||
table = db.create_table("words", schema=Words, mode="overwrite")
|
||||
table.add([
|
||||
{"text": "hello world"},
|
||||
{"text": "goodbye world"}
|
||||
])
|
||||
|
||||
query = "greetings"
|
||||
actual = table.search(query).limit(1).to_pydantic(Words)[0]
|
||||
print(actual.text)
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,34 @@
|
||||
# OpenAI embeddings
|
||||
|
||||
LanceDB registers the OpenAI embeddings function in the registry by default, as `openai`. Below are the parameters that you can customize when creating the instances:
|
||||
|
||||
| Parameter | Type | Default Value | Description |
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|
|
||||
| `name` | `str` | `"text-embedding-ada-002"` | The name of the model. |
|
||||
| `dim` | `int` | Model default | For OpenAI's newer text-embedding-3 model, we can specify a dimensionality that is smaller than the 1536 size. This feature supports it |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
from lancedb.pydantic import LanceModel, Vector
|
||||
from lancedb.embeddings import get_registry
|
||||
|
||||
db = lancedb.connect("/tmp/db")
|
||||
func = get_registry().get("openai").create(name="text-embedding-ada-002")
|
||||
|
||||
class Words(LanceModel):
|
||||
text: str = func.SourceField()
|
||||
vector: Vector(func.ndims()) = func.VectorField()
|
||||
|
||||
table = db.create_table("words", schema=Words, mode="overwrite")
|
||||
table.add(
|
||||
[
|
||||
{"text": "hello world"},
|
||||
{"text": "goodbye world"}
|
||||
]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
query = "greetings"
|
||||
actual = table.search(query).limit(1).to_pydantic(Words)[0]
|
||||
print(actual.text)
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,174 @@
|
||||
# Sentence transformers
|
||||
Allows you to set parameters when registering a `sentence-transformers` object.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! info
|
||||
Sentence transformer embeddings are normalized by default. It is recommended to use normalized embeddings for similarity search.
|
||||
|
||||
| Parameter | Type | Default Value | Description |
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|
|
||||
| `name` | `str` | `all-MiniLM-L6-v2` | The name of the model |
|
||||
| `device` | `str` | `cpu` | The device to run the model on (can be `cpu` or `gpu`) |
|
||||
| `normalize` | `bool` | `True` | Whether to normalize the input text before feeding it to the model |
|
||||
| `trust_remote_code` | `bool` | `False` | Whether to trust and execute remote code from the model's Huggingface repository |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
??? "Check out available sentence-transformer models here!"
|
||||
```markdown
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L12-v2
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/paraphrase-mpnet-base-v2
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/gtr-t5-base
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/LaBSE
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/bert-base-nli-max-tokens
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/bert-base-nli-mean-tokens
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/bert-base-nli-stsb-mean-tokens
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/bert-base-wikipedia-sections-mean-tokens
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/bert-large-nli-cls-token
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/bert-large-nli-max-tokens
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/bert-large-nli-mean-tokens
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/bert-large-nli-stsb-mean-tokens
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/distilbert-base-nli-max-tokens
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/distilbert-base-nli-mean-tokens
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/distilbert-base-nli-stsb-mean-tokens
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/distilroberta-base-msmarco-v1
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/distilroberta-base-msmarco-v2
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/nli-bert-base-cls-pooling
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/nli-bert-base-max-pooling
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/nli-bert-base
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/nli-bert-large-cls-pooling
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/nli-bert-large-max-pooling
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/nli-bert-large
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/nli-distilbert-base-max-pooling
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/nli-distilbert-base
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/nli-roberta-base
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/nli-roberta-large
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/roberta-base-nli-mean-tokens
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/roberta-base-nli-stsb-mean-tokens
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/roberta-large-nli-mean-tokens
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/roberta-large-nli-stsb-mean-tokens
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/stsb-bert-base
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/stsb-bert-large
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/stsb-distilbert-base
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/stsb-roberta-base
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/stsb-roberta-large
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/xlm-r-100langs-bert-base-nli-mean-tokens
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/xlm-r-100langs-bert-base-nli-stsb-mean-tokens
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/xlm-r-base-en-ko-nli-ststb
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/xlm-r-bert-base-nli-mean-tokens
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/xlm-r-bert-base-nli-stsb-mean-tokens
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/xlm-r-large-en-ko-nli-ststb
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/bert-base-nli-cls-token
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/all-distilroberta-v1
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/multi-qa-MiniLM-L6-dot-v1
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/multi-qa-distilbert-cos-v1
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/multi-qa-distilbert-dot-v1
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/multi-qa-mpnet-base-cos-v1
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/multi-qa-mpnet-base-dot-v1
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/nli-distilroberta-base-v2
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v1
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/all-mpnet-base-v1
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/all-mpnet-base-v2
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/all-roberta-large-v1
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/allenai-specter
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/average_word_embeddings_glove.6B.300d
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/average_word_embeddings_glove.840B.300d
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/average_word_embeddings_komninos
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/average_word_embeddings_levy_dependency
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/clip-ViT-B-32-multilingual-v1
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/clip-ViT-B-32
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/distilbert-base-nli-stsb-quora-ranking
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/distilbert-multilingual-nli-stsb-quora-ranking
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/distilroberta-base-paraphrase-v1
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/distiluse-base-multilingual-cased-v1
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/distiluse-base-multilingual-cased-v2
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/distiluse-base-multilingual-cased
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/facebook-dpr-ctx_encoder-multiset-base
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/facebook-dpr-ctx_encoder-single-nq-base
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/facebook-dpr-question_encoder-multiset-base
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/facebook-dpr-question_encoder-single-nq-base
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/gtr-t5-large
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/gtr-t5-xl
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/gtr-t5-xxl
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/msmarco-MiniLM-L-12-v3
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/msmarco-MiniLM-L-6-v3
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/msmarco-MiniLM-L12-cos-v5
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/msmarco-MiniLM-L6-cos-v5
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/msmarco-bert-base-dot-v5
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/msmarco-bert-co-condensor
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/msmarco-distilbert-base-dot-prod-v3
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/msmarco-distilbert-base-tas-b
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/msmarco-distilbert-base-v2
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/msmarco-distilbert-base-v3
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/msmarco-distilbert-base-v4
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/msmarco-distilbert-cos-v5
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/msmarco-distilbert-dot-v5
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/msmarco-distilbert-multilingual-en-de-v2-tmp-lng-aligned
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/msmarco-distilbert-multilingual-en-de-v2-tmp-trained-scratch
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/msmarco-distilroberta-base-v2
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/msmarco-roberta-base-ance-firstp
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/msmarco-roberta-base-v2
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/msmarco-roberta-base-v3
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/multi-qa-MiniLM-L6-cos-v1
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/nli-mpnet-base-v2
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/nli-roberta-base-v2
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/nq-distilbert-base-v1
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/paraphrase-MiniLM-L12-v2
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/paraphrase-MiniLM-L3-v2
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/paraphrase-MiniLM-L6-v2
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/paraphrase-TinyBERT-L6-v2
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/paraphrase-albert-base-v2
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/paraphrase-albert-small-v2
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/paraphrase-distilroberta-base-v1
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/paraphrase-distilroberta-base-v2
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/paraphrase-multilingual-MiniLM-L12-v2
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/paraphrase-multilingual-mpnet-base-v2
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/paraphrase-xlm-r-multilingual-v1
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/quora-distilbert-base
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/quora-distilbert-multilingual
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/sentence-t5-base
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/sentence-t5-large
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/sentence-t5-xxl
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/sentence-t5-xl
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/stsb-distilroberta-base-v2
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/stsb-mpnet-base-v2
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/stsb-roberta-base-v2
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/stsb-xlm-r-multilingual
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/xlm-r-distilroberta-base-paraphrase-v1
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/clip-ViT-L-14
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/clip-ViT-B-16
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/use-cmlm-multilingual
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L12-v1
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! info
|
||||
You can also load many other model architectures from the library. For example models from sources such as BAAI, nomic, salesforce research, etc.
|
||||
See this HF hub page for all [supported models](https://huggingface.co/models?library=sentence-transformers).
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note "BAAI Embeddings example"
|
||||
Here is an example that uses BAAI embedding model from the HuggingFace Hub [supported models](https://huggingface.co/models?library=sentence-transformers)
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
from lancedb.pydantic import LanceModel, Vector
|
||||
from lancedb.embeddings import get_registry
|
||||
|
||||
db = lancedb.connect("/tmp/db")
|
||||
model = get_registry().get("sentence-transformers").create(name="BAAI/bge-small-en-v1.5", device="cpu")
|
||||
|
||||
class Words(LanceModel):
|
||||
text: str = model.SourceField()
|
||||
vector: Vector(model.ndims()) = model.VectorField()
|
||||
|
||||
table = db.create_table("words", schema=Words)
|
||||
table.add(
|
||||
[
|
||||
{"text": "hello world"},
|
||||
{"text": "goodbye world"}
|
||||
]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
query = "greetings"
|
||||
actual = table.search(query).limit(1).to_pydantic(Words)[0]
|
||||
print(actual.text)
|
||||
```
|
||||
Visit sentence-transformers [HuggingFace HUB](https://huggingface.co/sentence-transformers) page for more information on the available models.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,800 +1,84 @@
|
||||
There are various embedding functions available out of the box with LanceDB to manage your embeddings implicitly. We're actively working on adding other popular embedding APIs and models.
|
||||
# 📚 Available Embedding Models
|
||||
|
||||
## Text embedding functions
|
||||
Contains the text embedding functions registered by default.
|
||||
There are various embedding functions available out of the box with LanceDB to manage your embeddings implicitly. We're actively working on adding other popular embedding APIs and models. 🚀
|
||||
|
||||
* Embedding functions have an inbuilt rate limit handler wrapper for source and query embedding function calls that retry with exponential backoff.
|
||||
* Each `EmbeddingFunction` implementation automatically takes `max_retries` as an argument which has the default value of 7.
|
||||
Before jumping on the list of available models, let's understand how to get an embedding model initialized and configured to use in our code:
|
||||
|
||||
### Sentence transformers
|
||||
Allows you to set parameters when registering a `sentence-transformers` object.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! info
|
||||
Sentence transformer embeddings are normalized by default. It is recommended to use normalized embeddings for similarity search.
|
||||
|
||||
| Parameter | Type | Default Value | Description |
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|
|
||||
| `name` | `str` | `all-MiniLM-L6-v2` | The name of the model |
|
||||
| `device` | `str` | `cpu` | The device to run the model on (can be `cpu` or `gpu`) |
|
||||
| `normalize` | `bool` | `True` | Whether to normalize the input text before feeding it to the model |
|
||||
| `trust_remote_code` | `bool` | `False` | Whether to trust and execute remote code from the model's Huggingface repository |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
??? "Check out available sentence-transformer models here!"
|
||||
```markdown
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L12-v2
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/paraphrase-mpnet-base-v2
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/gtr-t5-base
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/LaBSE
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/bert-base-nli-max-tokens
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/bert-base-nli-mean-tokens
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/bert-base-nli-stsb-mean-tokens
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/bert-base-wikipedia-sections-mean-tokens
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/bert-large-nli-cls-token
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/bert-large-nli-max-tokens
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/bert-large-nli-mean-tokens
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/bert-large-nli-stsb-mean-tokens
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/distilbert-base-nli-max-tokens
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/distilbert-base-nli-mean-tokens
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/distilbert-base-nli-stsb-mean-tokens
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/distilroberta-base-msmarco-v1
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/distilroberta-base-msmarco-v2
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/nli-bert-base-cls-pooling
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/nli-bert-base-max-pooling
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/nli-bert-base
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/nli-bert-large-cls-pooling
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/nli-bert-large-max-pooling
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/nli-bert-large
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/nli-distilbert-base-max-pooling
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/nli-distilbert-base
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/nli-roberta-base
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/nli-roberta-large
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/roberta-base-nli-mean-tokens
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/roberta-base-nli-stsb-mean-tokens
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/roberta-large-nli-mean-tokens
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/roberta-large-nli-stsb-mean-tokens
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/stsb-bert-base
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/stsb-bert-large
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/stsb-distilbert-base
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/stsb-roberta-base
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/stsb-roberta-large
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/xlm-r-100langs-bert-base-nli-mean-tokens
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/xlm-r-100langs-bert-base-nli-stsb-mean-tokens
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/xlm-r-base-en-ko-nli-ststb
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/xlm-r-bert-base-nli-mean-tokens
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/xlm-r-bert-base-nli-stsb-mean-tokens
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/xlm-r-large-en-ko-nli-ststb
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/bert-base-nli-cls-token
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/all-distilroberta-v1
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/multi-qa-MiniLM-L6-dot-v1
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/multi-qa-distilbert-cos-v1
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/multi-qa-distilbert-dot-v1
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/multi-qa-mpnet-base-cos-v1
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/multi-qa-mpnet-base-dot-v1
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/nli-distilroberta-base-v2
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v1
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/all-mpnet-base-v1
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/all-mpnet-base-v2
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/all-roberta-large-v1
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/allenai-specter
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/average_word_embeddings_glove.6B.300d
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/average_word_embeddings_glove.840B.300d
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/average_word_embeddings_komninos
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/average_word_embeddings_levy_dependency
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/clip-ViT-B-32-multilingual-v1
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/clip-ViT-B-32
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/distilbert-base-nli-stsb-quora-ranking
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/distilbert-multilingual-nli-stsb-quora-ranking
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/distilroberta-base-paraphrase-v1
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/distiluse-base-multilingual-cased-v1
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/distiluse-base-multilingual-cased-v2
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/distiluse-base-multilingual-cased
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/facebook-dpr-ctx_encoder-multiset-base
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/facebook-dpr-ctx_encoder-single-nq-base
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/facebook-dpr-question_encoder-multiset-base
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/facebook-dpr-question_encoder-single-nq-base
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/gtr-t5-large
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/gtr-t5-xl
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/gtr-t5-xxl
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/msmarco-MiniLM-L-12-v3
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/msmarco-MiniLM-L-6-v3
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/msmarco-MiniLM-L12-cos-v5
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/msmarco-MiniLM-L6-cos-v5
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/msmarco-bert-base-dot-v5
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/msmarco-bert-co-condensor
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/msmarco-distilbert-base-dot-prod-v3
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/msmarco-distilbert-base-tas-b
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/msmarco-distilbert-base-v2
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/msmarco-distilbert-base-v3
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/msmarco-distilbert-base-v4
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/msmarco-distilbert-cos-v5
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/msmarco-distilbert-dot-v5
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/msmarco-distilbert-multilingual-en-de-v2-tmp-lng-aligned
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/msmarco-distilbert-multilingual-en-de-v2-tmp-trained-scratch
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/msmarco-distilroberta-base-v2
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/msmarco-roberta-base-ance-firstp
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/msmarco-roberta-base-v2
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/msmarco-roberta-base-v3
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/multi-qa-MiniLM-L6-cos-v1
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/nli-mpnet-base-v2
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/nli-roberta-base-v2
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/nq-distilbert-base-v1
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/paraphrase-MiniLM-L12-v2
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/paraphrase-MiniLM-L3-v2
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/paraphrase-MiniLM-L6-v2
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/paraphrase-TinyBERT-L6-v2
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/paraphrase-albert-base-v2
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/paraphrase-albert-small-v2
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/paraphrase-distilroberta-base-v1
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/paraphrase-distilroberta-base-v2
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/paraphrase-multilingual-MiniLM-L12-v2
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/paraphrase-multilingual-mpnet-base-v2
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/paraphrase-xlm-r-multilingual-v1
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/quora-distilbert-base
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/quora-distilbert-multilingual
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/sentence-t5-base
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/sentence-t5-large
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/sentence-t5-xxl
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/sentence-t5-xl
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/stsb-distilroberta-base-v2
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/stsb-mpnet-base-v2
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/stsb-roberta-base-v2
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/stsb-xlm-r-multilingual
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/xlm-r-distilroberta-base-paraphrase-v1
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/clip-ViT-L-14
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/clip-ViT-B-16
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/use-cmlm-multilingual
|
||||
- sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L12-v1
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! info
|
||||
You can also load many other model architectures from the library. For example models from sources such as BAAI, nomic, salesforce research, etc.
|
||||
See this HF hub page for all [supported models](https://huggingface.co/models?library=sentence-transformers).
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note "BAAI Embeddings example"
|
||||
Here is an example that uses BAAI embedding model from the HuggingFace Hub [supported models](https://huggingface.co/models?library=sentence-transformers)
|
||||
!!! example "Example usage"
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
from lancedb.pydantic import LanceModel, Vector
|
||||
from lancedb.embeddings import get_registry
|
||||
|
||||
db = lancedb.connect("/tmp/db")
|
||||
model = get_registry().get("sentence-transformers").create(name="BAAI/bge-small-en-v1.5", device="cpu")
|
||||
|
||||
class Words(LanceModel):
|
||||
text: str = model.SourceField()
|
||||
vector: Vector(model.ndims()) = model.VectorField()
|
||||
|
||||
table = db.create_table("words", schema=Words)
|
||||
table.add(
|
||||
[
|
||||
{"text": "hello world"},
|
||||
{"text": "goodbye world"}
|
||||
]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
query = "greetings"
|
||||
actual = table.search(query).limit(1).to_pydantic(Words)[0]
|
||||
print(actual.text)
|
||||
```
|
||||
Visit sentence-transformers [HuggingFace HUB](https://huggingface.co/sentence-transformers) page for more information on the available models.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Huggingface embedding models
|
||||
We offer support for all huggingface models (which can be loaded via [transformers](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/en/index) library). The default model is `colbert-ir/colbertv2.0` which also has its own special callout - `registry.get("colbert")`
|
||||
|
||||
Example usage -
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
import pandas as pd
|
||||
|
||||
from lancedb.embeddings import get_registry
|
||||
from lancedb.pydantic import LanceModel, Vector
|
||||
|
||||
model = get_registry().get("huggingface").create(name='facebook/bart-base')
|
||||
|
||||
class Words(LanceModel):
|
||||
text: str = model.SourceField()
|
||||
vector: Vector(model.ndims()) = model.VectorField()
|
||||
|
||||
df = pd.DataFrame({"text": ["hi hello sayonara", "goodbye world"]})
|
||||
table = db.create_table("greets", schema=Words)
|
||||
table.add(df)
|
||||
query = "old greeting"
|
||||
actual = table.search(query).limit(1).to_pydantic(Words)[0]
|
||||
print(actual.text)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Ollama embeddings
|
||||
Generate embeddings via the [ollama](https://github.com/ollama/ollama-python) python library. More details:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Ollama docs on embeddings](https://github.com/ollama/ollama/blob/main/docs/api.md#generate-embeddings)
|
||||
- [Ollama blog on embeddings](https://ollama.com/blog/embedding-models)
|
||||
|
||||
| Parameter | Type | Default Value | Description |
|
||||
|------------------------|----------------------------|--------------------------|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| `name` | `str` | `nomic-embed-text` | The name of the model. |
|
||||
| `host` | `str` | `http://localhost:11434` | The Ollama host to connect to. |
|
||||
| `options` | `ollama.Options` or `dict` | `None` | Additional model parameters listed in the documentation for the Modelfile such as `temperature`. |
|
||||
| `keep_alive` | `float` or `str` | `"5m"` | Controls how long the model will stay loaded into memory following the request. |
|
||||
| `ollama_client_kwargs` | `dict` | `{}` | kwargs that can be past to the `ollama.Client`. |
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
from lancedb.pydantic import LanceModel, Vector
|
||||
from lancedb.embeddings import get_registry
|
||||
|
||||
db = lancedb.connect("/tmp/db")
|
||||
func = get_registry().get("ollama").create(name="nomic-embed-text")
|
||||
|
||||
class Words(LanceModel):
|
||||
text: str = func.SourceField()
|
||||
vector: Vector(func.ndims()) = func.VectorField()
|
||||
|
||||
table = db.create_table("words", schema=Words, mode="overwrite")
|
||||
table.add([
|
||||
{"text": "hello world"},
|
||||
{"text": "goodbye world"}
|
||||
])
|
||||
|
||||
query = "greetings"
|
||||
actual = table.search(query).limit(1).to_pydantic(Words)[0]
|
||||
print(actual.text)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### OpenAI embeddings
|
||||
LanceDB registers the OpenAI embeddings function in the registry by default, as `openai`. Below are the parameters that you can customize when creating the instances:
|
||||
|
||||
| Parameter | Type | Default Value | Description |
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|
|
||||
| `name` | `str` | `"text-embedding-ada-002"` | The name of the model. |
|
||||
| `dim` | `int` | Model default | For OpenAI's newer text-embedding-3 model, we can specify a dimensionality that is smaller than the 1536 size. This feature supports it |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
from lancedb.pydantic import LanceModel, Vector
|
||||
from lancedb.embeddings import get_registry
|
||||
|
||||
db = lancedb.connect("/tmp/db")
|
||||
func = get_registry().get("openai").create(name="text-embedding-ada-002")
|
||||
|
||||
class Words(LanceModel):
|
||||
text: str = func.SourceField()
|
||||
vector: Vector(func.ndims()) = func.VectorField()
|
||||
|
||||
table = db.create_table("words", schema=Words, mode="overwrite")
|
||||
table.add(
|
||||
[
|
||||
{"text": "hello world"},
|
||||
{"text": "goodbye world"}
|
||||
]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
query = "greetings"
|
||||
actual = table.search(query).limit(1).to_pydantic(Words)[0]
|
||||
print(actual.text)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Instructor Embeddings
|
||||
[Instructor](https://instructor-embedding.github.io/) is an instruction-finetuned text embedding model that can generate text embeddings tailored to any task (e.g. classification, retrieval, clustering, text evaluation, etc.) and domains (e.g. science, finance, etc.) by simply providing the task instruction, without any finetuning.
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to calculate customized embeddings for specific sentences, you can follow the unified template to write instructions.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! info
|
||||
Represent the `domain` `text_type` for `task_objective`:
|
||||
|
||||
* `domain` is optional, and it specifies the domain of the text, e.g. science, finance, medicine, etc.
|
||||
* `text_type` is required, and it specifies the encoding unit, e.g. sentence, document, paragraph, etc.
|
||||
* `task_objective` is optional, and it specifies the objective of embedding, e.g. retrieve a document, classify the sentence, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
More information about the model can be found at the [source URL](https://github.com/xlang-ai/instructor-embedding).
|
||||
|
||||
| Argument | Type | Default | Description |
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|
|
||||
| `name` | `str` | "hkunlp/instructor-base" | The name of the model to use |
|
||||
| `batch_size` | `int` | `32` | The batch size to use when generating embeddings |
|
||||
| `device` | `str` | `"cpu"` | The device to use when generating embeddings |
|
||||
| `show_progress_bar` | `bool` | `True` | Whether to show a progress bar when generating embeddings |
|
||||
| `normalize_embeddings` | `bool` | `True` | Whether to normalize the embeddings |
|
||||
| `quantize` | `bool` | `False` | Whether to quantize the model |
|
||||
| `source_instruction` | `str` | `"represent the docuement for retreival"` | The instruction for the source column |
|
||||
| `query_instruction` | `str` | `"represent the document for retreiving the most similar documents"` | The instruction for the query |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
from lancedb.pydantic import LanceModel, Vector
|
||||
from lancedb.embeddings import get_registry, InstuctorEmbeddingFunction
|
||||
|
||||
instructor = get_registry().get("instructor").create(
|
||||
source_instruction="represent the docuement for retreival",
|
||||
query_instruction="represent the document for retreiving the most similar documents"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
class Schema(LanceModel):
|
||||
vector: Vector(instructor.ndims()) = instructor.VectorField()
|
||||
text: str = instructor.SourceField()
|
||||
|
||||
db = lancedb.connect("~/.lancedb")
|
||||
tbl = db.create_table("test", schema=Schema, mode="overwrite")
|
||||
|
||||
texts = [{"text": "Capitalism has been dominant in the Western world since the end of feudalism, but most feel[who?] that..."},
|
||||
{"text": "The disparate impact theory is especially controversial under the Fair Housing Act because the Act..."},
|
||||
{"text": "Disparate impact in United States labor law refers to practices in employment, housing, and other areas that.."}]
|
||||
|
||||
tbl.add(texts)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Gemini Embeddings
|
||||
With Google's Gemini, you can represent text (words, sentences, and blocks of text) in a vectorized form, making it easier to compare and contrast embeddings. For example, two texts that share a similar subject matter or sentiment should have similar embeddings, which can be identified through mathematical comparison techniques such as cosine similarity. For more on how and why you should use embeddings, refer to the Embeddings guide.
|
||||
The Gemini Embedding Model API supports various task types:
|
||||
|
||||
| Task Type | Description |
|
||||
|-------------------------|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| "`retrieval_query`" | Specifies the given text is a query in a search/retrieval setting. |
|
||||
| "`retrieval_document`" | Specifies the given text is a document in a search/retrieval setting. Using this task type requires a title but is automatically proided by Embeddings API |
|
||||
| "`semantic_similarity`" | Specifies the given text will be used for Semantic Textual Similarity (STS). |
|
||||
| "`classification`" | Specifies that the embeddings will be used for classification. |
|
||||
| "`clusering`" | Specifies that the embeddings will be used for clustering. |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Usage Example:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
import pandas as pd
|
||||
from lancedb.pydantic import LanceModel, Vector
|
||||
from lancedb.embeddings import get_registry
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
model = get_registry().get("gemini-text").create()
|
||||
|
||||
class TextModel(LanceModel):
|
||||
text: str = model.SourceField()
|
||||
vector: Vector(model.ndims()) = model.VectorField()
|
||||
|
||||
df = pd.DataFrame({"text": ["hello world", "goodbye world"]})
|
||||
db = lancedb.connect("~/.lancedb")
|
||||
tbl = db.create_table("test", schema=TextModel, mode="overwrite")
|
||||
|
||||
tbl.add(df)
|
||||
rs = tbl.search("hello").limit(1).to_pandas()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Cohere Embeddings
|
||||
Using cohere API requires cohere package, which can be installed using `pip install cohere`. Cohere embeddings are used to generate embeddings for text data. The embeddings can be used for various tasks like semantic search, clustering, and classification.
|
||||
You also need to set the `COHERE_API_KEY` environment variable to use the Cohere API.
|
||||
|
||||
Supported models are:
|
||||
```
|
||||
* embed-english-v3.0
|
||||
* embed-multilingual-v3.0
|
||||
* embed-english-light-v3.0
|
||||
* embed-multilingual-light-v3.0
|
||||
* embed-english-v2.0
|
||||
* embed-english-light-v2.0
|
||||
* embed-multilingual-v2.0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Supported parameters (to be passed in `create` method) are:
|
||||
|
||||
| Parameter | Type | Default Value | Description |
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|
|
||||
| `name` | `str` | `"embed-english-v2.0"` | The model ID of the cohere model to use. Supported base models for Text Embeddings: embed-english-v3.0, embed-multilingual-v3.0, embed-english-light-v3.0, embed-multilingual-light-v3.0, embed-english-v2.0, embed-english-light-v2.0, embed-multilingual-v2.0 |
|
||||
| `source_input_type` | `str` | `"search_document"` | The type of input data to be used for the source column. |
|
||||
| `query_input_type` | `str` | `"search_query"` | The type of input data to be used for the query. |
|
||||
|
||||
Cohere supports following input types:
|
||||
|
||||
| Input Type | Description |
|
||||
|-------------------------|---------------------------------------|
|
||||
| "`search_document`" | Used for embeddings stored in a vector|
|
||||
| | database for search use-cases. |
|
||||
| "`search_query`" | Used for embeddings of search queries |
|
||||
| | run against a vector DB |
|
||||
| "`semantic_similarity`" | Specifies the given text will be used |
|
||||
| | for Semantic Textual Similarity (STS) |
|
||||
| "`classification`" | Used for embeddings passed through a |
|
||||
| | text classifier. |
|
||||
| "`clustering`" | Used for the embeddings run through a |
|
||||
| | clustering algorithm |
|
||||
|
||||
Usage Example:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
from lancedb.pydantic import LanceModel, Vector
|
||||
from lancedb.embeddings import EmbeddingFunctionRegistry
|
||||
|
||||
cohere = EmbeddingFunctionRegistry
|
||||
.get_instance()
|
||||
.get("cohere")
|
||||
.create(name="embed-multilingual-v2.0")
|
||||
|
||||
class TextModel(LanceModel):
|
||||
text: str = cohere.SourceField()
|
||||
vector: Vector(cohere.ndims()) = cohere.VectorField()
|
||||
|
||||
data = [ { "text": "hello world" },
|
||||
{ "text": "goodbye world" }]
|
||||
|
||||
db = lancedb.connect("~/.lancedb")
|
||||
tbl = db.create_table("test", schema=TextModel, mode="overwrite")
|
||||
|
||||
tbl.add(data)
|
||||
model = get_registry()
|
||||
.get("openai")
|
||||
.create(name="text-embedding-ada-002")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Jina Embeddings
|
||||
Jina embeddings are used to generate embeddings for text and image data.
|
||||
You also need to set the `JINA_API_KEY` environment variable to use the Jina API.
|
||||
|
||||
You can find a list of supported models under [https://jina.ai/embeddings/](https://jina.ai/embeddings/)
|
||||
|
||||
Supported parameters (to be passed in `create` method) are:
|
||||
|
||||
| Parameter | Type | Default Value | Description |
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|
|
||||
| `name` | `str` | `"jina-clip-v1"` | The model ID of the jina model to use |
|
||||
|
||||
Usage Example:
|
||||
|
||||
Now let's understand the above syntax:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
from lancedb.pydantic import LanceModel, Vector
|
||||
from lancedb.embeddings import EmbeddingFunctionRegistry
|
||||
|
||||
os.environ['JINA_API_KEY'] = 'jina_*'
|
||||
|
||||
jina_embed = EmbeddingFunctionRegistry.get_instance().get("jina").create(name="jina-embeddings-v2-base-en")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class TextModel(LanceModel):
|
||||
text: str = jina_embed.SourceField()
|
||||
vector: Vector(jina_embed.ndims()) = jina_embed.VectorField()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
data = [{"text": "hello world"},
|
||||
{"text": "goodbye world"}]
|
||||
|
||||
db = lancedb.connect("~/.lancedb-2")
|
||||
tbl = db.create_table("test", schema=TextModel, mode="overwrite")
|
||||
|
||||
tbl.add(data)
|
||||
model = get_registry().get("model_id").create(...params)
|
||||
```
|
||||
**This👆 line effectively creates a configured instance of an `embedding function` with `model` of choice that is ready for use.**
|
||||
|
||||
### AWS Bedrock Text Embedding Functions
|
||||
AWS Bedrock supports multiple base models for generating text embeddings. You need to setup the AWS credentials to use this embedding function.
|
||||
You can do so by using `awscli` and also add your session_token:
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
aws configure
|
||||
aws configure set aws_session_token "<your_session_token>"
|
||||
```
|
||||
to ensure that the credentials are set up correctly, you can run the following command:
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
aws sts get-caller-identity
|
||||
```
|
||||
- `get_registry()` : This function call returns an instance of a `EmbeddingFunctionRegistry` object. This registry manages the registration and retrieval of embedding functions.
|
||||
|
||||
Supported Embedding modelIDs are:
|
||||
* `amazon.titan-embed-text-v1`
|
||||
* `cohere.embed-english-v3`
|
||||
* `cohere.embed-multilingual-v3`
|
||||
- `.get("model_id")` : This method call on the registry object and retrieves the **embedding models functions** associated with the `"model_id"` (1) .
|
||||
{ .annotate }
|
||||
|
||||
Supported parameters (to be passed in `create` method) are:
|
||||
1. Hover over the names in table below to find out the `model_id` of different embedding functions.
|
||||
|
||||
| Parameter | Type | Default Value | Description |
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|
|
||||
| **name** | str | "amazon.titan-embed-text-v1" | The model ID of the bedrock model to use. Supported base models for Text Embeddings: amazon.titan-embed-text-v1, cohere.embed-english-v3, cohere.embed-multilingual-v3 |
|
||||
| **region** | str | "us-east-1" | Optional name of the AWS Region in which the service should be called (e.g., "us-east-1"). |
|
||||
| **profile_name** | str | None | Optional name of the AWS profile to use for calling the Bedrock service. If not specified, the default profile will be used. |
|
||||
| **assumed_role** | str | None | Optional ARN of an AWS IAM role to assume for calling the Bedrock service. If not specified, the current active credentials will be used. |
|
||||
| **role_session_name** | str | "lancedb-embeddings" | Optional name of the AWS IAM role session to use for calling the Bedrock service. If not specified, a "lancedb-embeddings" name will be used. |
|
||||
| **runtime** | bool | True | Optional choice of getting different client to perform operations with the Amazon Bedrock service. |
|
||||
| **max_retries** | int | 7 | Optional number of retries to perform when a request fails. |
|
||||
- `.create(...params)` : This method call is on the object returned by the `get` method. It instantiates an embedding model function using the **specified parameters**.
|
||||
|
||||
Usage Example:
|
||||
??? question "What parameters does the `.create(...params)` method accepts?"
|
||||
**Checkout the documentation of specific embedding models (links in the table below👇) to know what parameters it takes**.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
from lancedb.pydantic import LanceModel, Vector
|
||||
from lancedb.embeddings import get_registry
|
||||
!!! tip "Moving on"
|
||||
Now that we know how to get the **desired embedding model** and use it in our code, let's explore the comprehensive **list** of embedding models **supported by LanceDB**, in the tables below.
|
||||
|
||||
model = get_registry().get("bedrock-text").create()
|
||||
## Text Embedding Functions 📝
|
||||
These functions are registered by default to handle text embeddings.
|
||||
|
||||
class TextModel(LanceModel):
|
||||
text: str = model.SourceField()
|
||||
vector: Vector(model.ndims()) = model.VectorField()
|
||||
- 🔄 **Embedding functions** have an inbuilt rate limit handler wrapper for source and query embedding function calls that retry with **exponential backoff**.
|
||||
|
||||
df = pd.DataFrame({"text": ["hello world", "goodbye world"]})
|
||||
db = lancedb.connect("tmp_path")
|
||||
tbl = db.create_table("test", schema=TextModel, mode="overwrite")
|
||||
- 🌕 Each `EmbeddingFunction` implementation automatically takes `max_retries` as an argument which has the default value of 7.
|
||||
|
||||
tbl.add(df)
|
||||
rs = tbl.search("hello").limit(1).to_pandas()
|
||||
```
|
||||
🌟 **Available Text Embeddings**
|
||||
|
||||
# IBM watsonx.ai Embeddings
|
||||
| **Embedding** :material-information-outline:{ title="Hover over the name to find out the model_id" } | **Description** | **Documentation** |
|
||||
|-----------|-------------|---------------|
|
||||
| [**Sentence Transformers**](available_embedding_models/text_embedding_functions/sentence_transformers.md "sentence-transformers") | 🧠 **SentenceTransformers** is a Python framework for state-of-the-art sentence, text, and image embeddings. | [<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lancedb/assets/main/docs/assets/logos/sbert_2.png" alt="Sentence Transformers Icon" width="90" height="35">](available_embedding_models/text_embedding_functions/sentence_transformers.md)|
|
||||
| [**Huggingface Models**](available_embedding_models/text_embedding_functions/huggingface_embedding.md "huggingface") |🤗 We offer support for all **Huggingface** models. The default model is `colbert-ir/colbertv2.0`. | [<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lancedb/assets/main/docs/assets/logos/hugging_face.png" alt="Huggingface Icon" width="130" height="35">](available_embedding_models/text_embedding_functions/huggingface_embedding.md) |
|
||||
| [**Ollama Embeddings**](available_embedding_models/text_embedding_functions/ollama_embedding.md "ollama") | 🔍 Generate embeddings via the **Ollama** python library. Ollama supports embedding models, making it possible to build RAG apps. | [<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lancedb/assets/main/docs/assets/logos/Ollama.png" alt="Ollama Icon" width="110" height="35">](available_embedding_models/text_embedding_functions/ollama_embedding.md)|
|
||||
| [**OpenAI Embeddings**](available_embedding_models/text_embedding_functions/openai_embedding.md "openai")| 🔑 **OpenAI’s** text embeddings measure the relatedness of text strings. **LanceDB** supports state-of-the-art embeddings from OpenAI. | [<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lancedb/assets/main/docs/assets/logos/openai.png" alt="OpenAI Icon" width="100" height="35">](available_embedding_models/text_embedding_functions/openai_embedding.md)|
|
||||
| [**Instructor Embeddings**](available_embedding_models/text_embedding_functions/instructor_embedding.md "instructor") | 📚 **Instructor**: An instruction-finetuned text embedding model that can generate text embeddings tailored to any task and domains by simply providing the task instruction, without any finetuning. | [<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lancedb/assets/main/docs/assets/logos/instructor_embedding.png" alt="Instructor Embedding Icon" width="140" height="35">](available_embedding_models/text_embedding_functions/instructor_embedding.md) |
|
||||
| [**Gemini Embeddings**](available_embedding_models/text_embedding_functions/gemini_embedding.md "gemini-text") | 🌌 Google’s Gemini API generates state-of-the-art embeddings for words, phrases, and sentences. | [<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lancedb/assets/main/docs/assets/logos/gemini.png" alt="Gemini Icon" width="95" height="35">](available_embedding_models/text_embedding_functions/gemini_embedding.md) |
|
||||
| [**Cohere Embeddings**](available_embedding_models/text_embedding_functions/cohere_embedding.md "cohere") | 💬 This will help you get started with **Cohere** embedding models using LanceDB. Using cohere API requires cohere package. Install it via `pip`. | [<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lancedb/assets/main/docs/assets/logos/cohere.png" alt="Cohere Icon" width="140" height="35">](available_embedding_models/text_embedding_functions/cohere_embedding.md) |
|
||||
| [**Jina Embeddings**](available_embedding_models/text_embedding_functions/jina_embedding.md "jina") | 🔗 World-class embedding models to improve your search and RAG systems. You will need **jina api key**. | [<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lancedb/assets/main/docs/assets/logos/jina.png" alt="Jina Icon" width="90" height="35">](available_embedding_models/text_embedding_functions/jina_embedding.md) |
|
||||
| [ **AWS Bedrock Functions**](available_embedding_models/text_embedding_functions/aws_bedrock_embedding.md "bedrock-text") | ☁️ AWS Bedrock supports multiple base models for generating text embeddings. You need to setup the AWS credentials to use this embedding function. | [<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lancedb/assets/main/docs/assets/logos/aws_bedrock.png" alt="AWS Bedrock Icon" width="120" height="35">](available_embedding_models/text_embedding_functions/aws_bedrock_embedding.md) |
|
||||
| [**IBM Watsonx.ai**](available_embedding_models/text_embedding_functions/ibm_watsonx_ai_embedding.md "watsonx") | 💡 Generate text embeddings using IBM's watsonx.ai platform. **Note**: watsonx.ai library is an optional dependency. | [<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lancedb/assets/main/docs/assets/logos/watsonx.png" alt="Watsonx Icon" width="140" height="35">](available_embedding_models/text_embedding_functions/ibm_watsonx_ai_embedding.md) |
|
||||
|
||||
Generate text embeddings using IBM's watsonx.ai platform.
|
||||
|
||||
## Supported Models
|
||||
|
||||
You can find a list of supported models at [IBM watsonx.ai Documentation](https://dataplatform.cloud.ibm.com/docs/content/wsj/analyze-data/fm-models-embed.html?context=wx). The currently supported model names are:
|
||||
[st-key]: "sentence-transformers"
|
||||
[hf-key]: "huggingface"
|
||||
[ollama-key]: "ollama"
|
||||
[openai-key]: "openai"
|
||||
[instructor-key]: "instructor"
|
||||
[gemini-key]: "gemini-text"
|
||||
[cohere-key]: "cohere"
|
||||
[jina-key]: "jina"
|
||||
[aws-key]: "bedrock-text"
|
||||
[watsonx-key]: "watsonx"
|
||||
|
||||
- `ibm/slate-125m-english-rtrvr`
|
||||
- `ibm/slate-30m-english-rtrvr`
|
||||
- `sentence-transformers/all-minilm-l12-v2`
|
||||
- `intfloat/multilingual-e5-large`
|
||||
|
||||
## Parameters
|
||||
## Multi-modal Embedding Functions🖼️
|
||||
|
||||
The following parameters can be passed to the `create` method:
|
||||
Multi-modal embedding functions allow you to query your table using both images and text. 💬🖼️
|
||||
|
||||
| Parameter | Type | Default Value | Description |
|
||||
|------------|----------|----------------------------------|-----------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| name | str | "ibm/slate-125m-english-rtrvr" | The model ID of the watsonx.ai model to use |
|
||||
| api_key | str | None | Optional IBM Cloud API key (or set `WATSONX_API_KEY`) |
|
||||
| project_id | str | None | Optional watsonx project ID (or set `WATSONX_PROJECT_ID`) |
|
||||
| url | str | None | Optional custom URL for the watsonx.ai instance |
|
||||
| params | dict | None | Optional additional parameters for the embedding model |
|
||||
🌐 **Available Multi-modal Embeddings**
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage Example
|
||||
| Embedding :material-information-outline:{ title="Hover over the name to find out the model_id" } | Description | Documentation |
|
||||
|-----------|-------------|---------------|
|
||||
| [**OpenClip Embeddings**](available_embedding_models/multimodal_embedding_functions/openclip_embedding.md "open-clip") | 🎨 We support CLIP model embeddings using the open source alternative, **open-clip** which supports various customizations. | [<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lancedb/assets/main/docs/assets/logos/openclip_github.png" alt="openclip Icon" width="150" height="35">](available_embedding_models/multimodal_embedding_functions/openclip_embedding.md) |
|
||||
| [**Imagebind Embeddings**](available_embedding_models/multimodal_embedding_functions/imagebind_embedding.md "imageind") | 🌌 We have support for **imagebind model embeddings**. You can download our version of the packaged model via - `pip install imagebind-packaged==0.1.2`. | [<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lancedb/assets/main/docs/assets/logos/imagebind_meta.png" alt="imagebind Icon" width="150" height="35">](available_embedding_models/multimodal_embedding_functions/imagebind_embedding.md)|
|
||||
| [**Jina Multi-modal Embeddings**](available_embedding_models/multimodal_embedding_functions/jina_multimodal_embedding.md "jina") | 🔗 **Jina embeddings** can also be used to embed both **text** and **image** data, only some of the models support image data and you can check the detailed documentation. 👉 | [<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lancedb/assets/main/docs/assets/logos/jina.png" alt="jina Icon" width="90" height="35">](available_embedding_models/multimodal_embedding_functions/jina_multimodal_embedding.md) |
|
||||
|
||||
First, the watsonx.ai library is an optional dependency, so must be installed seperately:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
pip install ibm-watsonx-ai
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Optionally set environment variables (if not passing credentials to `create` directly):
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
export WATSONX_API_KEY="YOUR_WATSONX_API_KEY"
|
||||
export WATSONX_PROJECT_ID="YOUR_WATSONX_PROJECT_ID"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
from lancedb.pydantic import LanceModel, Vector
|
||||
from lancedb.embeddings import EmbeddingFunctionRegistry
|
||||
|
||||
watsonx_embed = EmbeddingFunctionRegistry
|
||||
.get_instance()
|
||||
.get("watsonx")
|
||||
.create(
|
||||
name="ibm/slate-125m-english-rtrvr",
|
||||
# Uncomment and set these if not using environment variables
|
||||
# api_key="your_api_key_here",
|
||||
# project_id="your_project_id_here",
|
||||
# url="your_watsonx_url_here",
|
||||
# params={...},
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
class TextModel(LanceModel):
|
||||
text: str = watsonx_embed.SourceField()
|
||||
vector: Vector(watsonx_embed.ndims()) = watsonx_embed.VectorField()
|
||||
|
||||
data = [
|
||||
{"text": "hello world"},
|
||||
{"text": "goodbye world"},
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
db = lancedb.connect("~/.lancedb")
|
||||
tbl = db.create_table("watsonx_test", schema=TextModel, mode="overwrite")
|
||||
|
||||
tbl.add(data)
|
||||
|
||||
rs = tbl.search("hello").limit(1).to_pandas()
|
||||
print(rs)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Multi-modal embedding functions
|
||||
Multi-modal embedding functions allow you to query your table using both images and text.
|
||||
|
||||
### OpenClip embeddings
|
||||
We support CLIP model embeddings using the open source alternative, [open-clip](https://github.com/mlfoundations/open_clip) which supports various customizations. It is registered as `open-clip` and supports the following customizations:
|
||||
|
||||
| Parameter | Type | Default Value | Description |
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|
|
||||
| `name` | `str` | `"ViT-B-32"` | The name of the model. |
|
||||
| `pretrained` | `str` | `"laion2b_s34b_b79k"` | The name of the pretrained model to load. |
|
||||
| `device` | `str` | `"cpu"` | The device to run the model on. Can be `"cpu"` or `"gpu"`. |
|
||||
| `batch_size` | `int` | `64` | The number of images to process in a batch. |
|
||||
| `normalize` | `bool` | `True` | Whether to normalize the input images before feeding them to the model. |
|
||||
|
||||
This embedding function supports ingesting images as both bytes and urls. You can query them using both test and other images.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! info
|
||||
LanceDB supports ingesting images directly from accessible links.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
from lancedb.pydantic import LanceModel, Vector
|
||||
from lancedb.embeddings import get_registry
|
||||
|
||||
db = lancedb.connect(tmp_path)
|
||||
func = get_registry.get("open-clip").create()
|
||||
|
||||
class Images(LanceModel):
|
||||
label: str
|
||||
image_uri: str = func.SourceField() # image uri as the source
|
||||
image_bytes: bytes = func.SourceField() # image bytes as the source
|
||||
vector: Vector(func.ndims()) = func.VectorField() # vector column
|
||||
vec_from_bytes: Vector(func.ndims()) = func.VectorField() # Another vector column
|
||||
|
||||
table = db.create_table("images", schema=Images)
|
||||
labels = ["cat", "cat", "dog", "dog", "horse", "horse"]
|
||||
uris = [
|
||||
"http://farm1.staticflickr.com/53/167798175_7c7845bbbd_z.jpg",
|
||||
"http://farm1.staticflickr.com/134/332220238_da527d8140_z.jpg",
|
||||
"http://farm9.staticflickr.com/8387/8602747737_2e5c2a45d4_z.jpg",
|
||||
"http://farm5.staticflickr.com/4092/5017326486_1f46057f5f_z.jpg",
|
||||
"http://farm9.staticflickr.com/8216/8434969557_d37882c42d_z.jpg",
|
||||
"http://farm6.staticflickr.com/5142/5835678453_4f3a4edb45_z.jpg",
|
||||
]
|
||||
# get each uri as bytes
|
||||
image_bytes = [requests.get(uri).content for uri in uris]
|
||||
table.add(
|
||||
pd.DataFrame({"label": labels, "image_uri": uris, "image_bytes": image_bytes})
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
Now we can search using text from both the default vector column and the custom vector column
|
||||
```python
|
||||
|
||||
# text search
|
||||
actual = table.search("man's best friend").limit(1).to_pydantic(Images)[0]
|
||||
print(actual.label) # prints "dog"
|
||||
|
||||
frombytes = (
|
||||
table.search("man's best friend", vector_column_name="vec_from_bytes")
|
||||
.limit(1)
|
||||
.to_pydantic(Images)[0]
|
||||
)
|
||||
print(frombytes.label)
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Because we're using a multi-modal embedding function, we can also search using images
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# image search
|
||||
query_image_uri = "http://farm1.staticflickr.com/200/467715466_ed4a31801f_z.jpg"
|
||||
image_bytes = requests.get(query_image_uri).content
|
||||
query_image = Image.open(io.BytesIO(image_bytes))
|
||||
actual = table.search(query_image).limit(1).to_pydantic(Images)[0]
|
||||
print(actual.label == "dog")
|
||||
|
||||
# image search using a custom vector column
|
||||
other = (
|
||||
table.search(query_image, vector_column_name="vec_from_bytes")
|
||||
.limit(1)
|
||||
.to_pydantic(Images)[0]
|
||||
)
|
||||
print(actual.label)
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Imagebind embeddings
|
||||
We have support for [imagebind](https://github.com/facebookresearch/ImageBind) model embeddings. You can download our version of the packaged model via - `pip install imagebind-packaged==0.1.2`.
|
||||
|
||||
This function is registered as `imagebind` and supports Audio, Video and Text modalities(extending to Thermal,Depth,IMU data):
|
||||
|
||||
| Parameter | Type | Default Value | Description |
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|
|
||||
| `name` | `str` | `"imagebind_huge"` | Name of the model. |
|
||||
| `device` | `str` | `"cpu"` | The device to run the model on. Can be `"cpu"` or `"gpu"`. |
|
||||
| `normalize` | `bool` | `False` | set to `True` to normalize your inputs before model ingestion. |
|
||||
|
||||
Below is an example demonstrating how the API works:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
from lancedb.pydantic import LanceModel, Vector
|
||||
from lancedb.embeddings import get_registry
|
||||
|
||||
db = lancedb.connect(tmp_path)
|
||||
func = get_registry.get("imagebind").create()
|
||||
|
||||
class ImageBindModel(LanceModel):
|
||||
text: str
|
||||
image_uri: str = func.SourceField()
|
||||
audio_path: str
|
||||
vector: Vector(func.ndims()) = func.VectorField()
|
||||
|
||||
# add locally accessible image paths
|
||||
text_list=["A dog.", "A car", "A bird"]
|
||||
image_paths=[".assets/dog_image.jpg", ".assets/car_image.jpg", ".assets/bird_image.jpg"]
|
||||
audio_paths=[".assets/dog_audio.wav", ".assets/car_audio.wav", ".assets/bird_audio.wav"]
|
||||
|
||||
# Load data
|
||||
inputs = [
|
||||
{"text": a, "audio_path": b, "image_uri": c}
|
||||
for a, b, c in zip(text_list, audio_paths, image_paths)
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
#create table and add data
|
||||
table = db.create_table("img_bind", schema=ImageBindModel)
|
||||
table.add(inputs)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now, we can search using any modality:
|
||||
|
||||
#### image search
|
||||
```python
|
||||
query_image = "./assets/dog_image2.jpg" #download an image and enter that path here
|
||||
actual = table.search(query_image).limit(1).to_pydantic(ImageBindModel)[0]
|
||||
print(actual.text == "dog")
|
||||
```
|
||||
#### audio search
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
query_audio = "./assets/car_audio2.wav" #download an audio clip and enter path here
|
||||
actual = table.search(query_audio).limit(1).to_pydantic(ImageBindModel)[0]
|
||||
print(actual.text == "car")
|
||||
```
|
||||
#### Text search
|
||||
You can add any input query and fetch the result as follows:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
query = "an animal which flies and tweets"
|
||||
actual = table.search(query).limit(1).to_pydantic(ImageBindModel)[0]
|
||||
print(actual.text == "bird")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you have any questions about the embeddings API, supported models, or see a relevant model missing, please raise an issue [on GitHub](https://github.com/lancedb/lancedb/issues).
|
||||
|
||||
### Jina Embeddings
|
||||
Jina embeddings can also be used to embed both text and image data, only some of the models support image data and you can check the list
|
||||
under [https://jina.ai/embeddings/](https://jina.ai/embeddings/)
|
||||
|
||||
Supported parameters (to be passed in `create` method) are:
|
||||
|
||||
| Parameter | Type | Default Value | Description |
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|
|
||||
| `name` | `str` | `"jina-clip-v1"` | The model ID of the jina model to use |
|
||||
|
||||
Usage Example:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import requests
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
from lancedb.pydantic import LanceModel, Vector
|
||||
from lancedb.embeddings import get_registry
|
||||
import pandas as pd
|
||||
|
||||
os.environ['JINA_API_KEY'] = 'jina_*'
|
||||
|
||||
db = lancedb.connect("~/.lancedb")
|
||||
func = get_registry().get("jina").create()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Images(LanceModel):
|
||||
label: str
|
||||
image_uri: str = func.SourceField() # image uri as the source
|
||||
image_bytes: bytes = func.SourceField() # image bytes as the source
|
||||
vector: Vector(func.ndims()) = func.VectorField() # vector column
|
||||
vec_from_bytes: Vector(func.ndims()) = func.VectorField() # Another vector column
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
table = db.create_table("images", schema=Images)
|
||||
labels = ["cat", "cat", "dog", "dog", "horse", "horse"]
|
||||
uris = [
|
||||
"http://farm1.staticflickr.com/53/167798175_7c7845bbbd_z.jpg",
|
||||
"http://farm1.staticflickr.com/134/332220238_da527d8140_z.jpg",
|
||||
"http://farm9.staticflickr.com/8387/8602747737_2e5c2a45d4_z.jpg",
|
||||
"http://farm5.staticflickr.com/4092/5017326486_1f46057f5f_z.jpg",
|
||||
"http://farm9.staticflickr.com/8216/8434969557_d37882c42d_z.jpg",
|
||||
"http://farm6.staticflickr.com/5142/5835678453_4f3a4edb45_z.jpg",
|
||||
]
|
||||
# get each uri as bytes
|
||||
image_bytes = [requests.get(uri).content for uri in uris]
|
||||
table.add(
|
||||
pd.DataFrame({"label": labels, "image_uri": uris, "image_bytes": image_bytes})
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
!!! note
|
||||
If you'd like to request support for additional **embedding functions**, please feel free to open an issue on our LanceDB [GitHub issue page](https://github.com/lancedb/lancedb/issues).
|
||||
133
docs/src/embeddings/understanding_embeddings.md
Normal file
133
docs/src/embeddings/understanding_embeddings.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,133 @@
|
||||
# Understand Embeddings
|
||||
|
||||
The term **dimension** is a synonym for the number of elements in a feature vector. Each feature can be thought of as a different axis in a geometric space.
|
||||
|
||||
High-dimensional data means there are many features(or attributes) in the data.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! example
|
||||
1. An image is a data point and it might have thousands of dimensions because each pixel could be considered as a feature.
|
||||
|
||||
2. Text data, when represented by each word or character, can also lead to high dimensions, especially when considering all possible words in a language.
|
||||
|
||||
Embedding captures **meaning and relationships** within data by mapping high-dimensional data into a lower-dimensional space. It captures it by placing inputs that are more **similar in meaning** closer together in the **embedding space**.
|
||||
|
||||
## What are Vector Embeddings?
|
||||
|
||||
Vector embeddings is a way to convert complex data, like text, images, or audio into numerical coordinates (called vectors) that can be plotted in an n-dimensional space(embedding space).
|
||||
|
||||
The closer these data points are related in the real world, the closer their corresponding numerical coordinates (vectors) will be to each other in the embedding space. This proximity in the embedding space reflects their semantic similarities, allowing machines to intuitively understand and process the data in a way that mirrors human perception of relationships and meaning.
|
||||
|
||||
In a way, it captures the most important aspects of the data while ignoring the less important ones. As a result, tasks like searching for related content or identifying patterns become more efficient and accurate, as the embeddings make it possible to quantify how **closely related** different **data points** are and **reduce** the **computational complexity**.
|
||||
|
||||
??? question "Are vectors and embeddings the same thing?"
|
||||
|
||||
When we say “vectors” we mean - **list of numbers** that **represents the data**.
|
||||
When we say “embeddings” we mean - **list of numbers** that **capture important details and relationships**.
|
||||
|
||||
Although the terms are often used interchangeably, “embeddings” highlight how the data is represented with meaning and structure, while “vector” simply refers to the numerical form of that representation.
|
||||
|
||||
## Embedding vs Indexing
|
||||
|
||||
We already saw that creating **embeddings** on data is a method of creating **vectors** for a **n-dimensional embedding space** that captures the meaning and relationships inherent in the data.
|
||||
|
||||
Once we have these **vectors**, indexing comes into play. Indexing is a method of organizing these vector embeddings, that allows us to quickly and efficiently locate and retrieve them from the entire dataset of vector embeddings.
|
||||
|
||||
## What types of data/objects can be embedded?
|
||||
|
||||
The following are common types of data that can be embedded:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Text**: Text data includes sentences, paragraphs, documents, or any written content.
|
||||
2. **Images**: Image data encompasses photographs, illustrations, or any visual content.
|
||||
3. **Audio**: Audio data includes sounds, music, speech, or any auditory content.
|
||||
4. **Video**: Video data consists of moving images and sound, which can convey complex information.
|
||||
|
||||
Large datasets of multi-modal data (text, audio, images, etc.) can be converted into embeddings with the appropriate model.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip "LanceDB vs Other traditional Vector DBs"
|
||||
While many vector databases primarily focus on the storage and retrieval of vector embeddings, **LanceDB** uses **Lance file format** (operates on a disk-based architecture), which allows for the storage and management of not just embeddings but also **raw file data (bytes)**. This capability means that users can integrate various types of data, including images and text, alongside their vector embeddings in a unified system.
|
||||
|
||||
With the ability to store both vectors and associated file data, LanceDB enhances the querying process. Users can perform semantic searches that not only retrieve similar embeddings but also access related files and metadata, thus streamlining the workflow.
|
||||
|
||||
## How does embedding works?
|
||||
|
||||
As mentioned, after creating embedding, each data point is represented as a vector in a n-dimensional space (embedding space). The dimensionality of this space can vary depending on the complexity of the data and the specific embedding technique used.
|
||||
|
||||
Points that are close to each other in vector space are considered similar (or appear in similar contexts), and points that are far away are considered dissimilar. To quantify this closeness, we use distance as a metric which can be measured in the following way -
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Euclidean Distance (L2)**: It calculates the straight-line distance between two points (vectors) in a multidimensional space.
|
||||
2. **Cosine Similarity**: It measures the cosine of the angle between two vectors, providing a normalized measure of similarity based on their direction.
|
||||
3. **Dot product**: It is calculated as the sum of the products of their corresponding components. To measure relatedness it considers both the magnitude and direction of the vectors.
|
||||
|
||||
## How do you create and store vector embeddings for your data?
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Creating embeddings**: Choose an embedding model, it can be a pre-trained model (open-source or commercial) or you can train a custom embedding model for your scenario. Then feed your preprocessed data into the chosen model to obtain embeddings.
|
||||
|
||||
??? question "Popular choices for embedding models"
|
||||
For text data, popular choices are OpenAI’s text-embedding models, Google Gemini text-embedding models, Cohere’s Embed models, and SentenceTransformers, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
For image data, popular choices are CLIP (Contrastive Language–Image Pretraining), Imagebind embeddings by meta (supports audio, video, and image), and Jina multi-modal embeddings, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
2. **Storing vector embeddings**: This effectively requires **specialized databases** that can handle the complexity of vector data, as traditional databases often struggle with this task. Vector databases are designed specifically for storing and querying vector embeddings. They optimize for efficient nearest-neighbor searches and provide built-in indexing mechanisms.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip "Why LanceDB"
|
||||
LanceDB **automates** the entire process of creating and storing embeddings for your data. LanceDB allows you to define and use **embedding functions**, which can be **pre-trained models** or **custom models**.
|
||||
|
||||
This enables you to **generate** embeddings tailored to the nature of your data (e.g., text, images) and **store** both the **original data** and **embeddings** in a **structured schema** thus providing efficient querying capabilities for similarity searches.
|
||||
|
||||
Let's quickly [get started](./index.md) and learn how to manage embeddings in LanceDB.
|
||||
|
||||
## Bonus: As a developer, what you can create using embeddings?
|
||||
|
||||
As a developer, you can create a variety of innovative applications using vector embeddings. Check out the following -
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="grid cards" markdown>
|
||||
|
||||
- __Chatbots__
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Develop chatbots that utilize embeddings to retrieve relevant context and generate coherent, contextually aware responses to user queries.
|
||||
|
||||
[:octicons-arrow-right-24: Check out examples](../examples/python_examples/chatbot.md)
|
||||
|
||||
- __Recommendation Systems__
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Develop systems that recommend content (such as articles, movies, or products) based on the similarity of keywords and descriptions, enhancing user experience.
|
||||
|
||||
[:octicons-arrow-right-24: Check out examples](../examples/python_examples/recommendersystem.md)
|
||||
|
||||
- __Vector Search__
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Build powerful applications that harness the full potential of semantic search, enabling them to retrieve relevant data quickly and effectively.
|
||||
|
||||
[:octicons-arrow-right-24: Check out examples](../examples/python_examples/vector_search.md)
|
||||
|
||||
- __RAG Applications__
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Combine the strengths of large language models (LLMs) with retrieval-based approaches to create more useful applications.
|
||||
|
||||
[:octicons-arrow-right-24: Check out examples](../examples/python_examples/rag.md)
|
||||
|
||||
- __Many more examples__
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Explore applied examples available as Colab notebooks or Python scripts to integrate into your applications.
|
||||
|
||||
[:octicons-arrow-right-24: More](../examples/examples_python.md)
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,17 +1,22 @@
|
||||
# Examples: Python
|
||||
# Overview : Python Examples
|
||||
|
||||
To help you get started, we provide some examples, projects and applications that use the LanceDB Python API. You can always find the latest examples in our [VectorDB Recipes](https://github.com/lancedb/vectordb-recipes) repository.
|
||||
To help you get started, we provide some examples, projects, and applications that use the LanceDB Python API. These examples are designed to get you right into the code with minimal introduction, enabling you to move from an idea to a proof of concept in minutes.
|
||||
|
||||
| Example | Interactive Envs | Scripts |
|
||||
|-------- | ---------------- | ------ |
|
||||
| | | |
|
||||
| [Youtube transcript search bot](https://github.com/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/tree/main/examples/youtube_bot/) | <a href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/examples/youtube_bot/main.ipynb"><img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" alt="Open In Colab"></a>| [](https://github.com/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/tree/main/examples/youtube_bot/main.py)|
|
||||
| [Langchain: Code Docs QA bot](https://github.com/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/tree/main/examples/Code-Documentation-QA-Bot/) | <a href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/examples/Code-Documentation-QA-Bot/main.ipynb"><img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" alt="Open In Colab"></a>| [](https://github.com/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/tree/main/examples/Code-Documentation-QA-Bot/main.py) |
|
||||
| [AI Agents: Reducing Hallucination](https://github.com/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/tree/main/examples/reducing_hallucinations_ai_agents/) | <a href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/examples/reducing_hallucinations_ai_agents/main.ipynb"><img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" alt="Open In Colab"></a>| [](https://github.com/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/tree/main/examples/reducing_hallucinations_ai_agents/main.py)|
|
||||
| [Multimodal CLIP: DiffusionDB](https://github.com/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/tree/main/examples/multimodal_clip/) | <a href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/examples/multimodal_clip/main.ipynb"><img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" alt="Open In Colab"></a>| [](https://github.com/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/tree/main/examples/multimodal_clip/main.py) |
|
||||
| [Multimodal CLIP: Youtube videos](https://github.com/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/tree/main/examples/multimodal_video_search/) | <a href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/examples/multimodal_video_search/main.ipynb"><img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" alt="Open In Colab"></a>| [](https://github.com/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/tree/main/examples/multimodal_video_search/main.py) |
|
||||
| [Movie Recommender](https://github.com/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/tree/main/examples/movie-recommender/) | <a href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/examples/movie-recommender/main.ipynb"><img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" alt="Open In Colab"></a> | [](https://github.com/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/tree/main/examples/movie-recommender/main.py) |
|
||||
| [Audio Search](https://github.com/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/tree/main/examples/audio_search/) | <a href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/examples/audio_search/main.ipynb"><img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" alt="Open In Colab"></a> | [](https://github.com/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/tree/main/examples/audio_search/main.py) |
|
||||
| [Multimodal Image + Text Search](https://github.com/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/tree/main/examples/multimodal_search/) | <a href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/examples/multimodal_search/main.ipynb"><img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" alt="Open In Colab"></a> | [](https://github.com/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/tree/main/examples/multimodal_search/main.py) |
|
||||
| [Evaluating Prompts with Prompttools](https://github.com/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/tree/main/examples/prompttools-eval-prompts/) | <a href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/examples/prompttools-eval-prompts/main.ipynb"><img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" alt="Open In Colab"></a> | |
|
||||
You can find the latest examples in our [VectorDB Recipes](https://github.com/lancedb/vectordb-recipes) repository.
|
||||
|
||||
**Introduction**
|
||||
|
||||
Explore applied examples available as Colab notebooks or Python scripts to integrate into your applications. You can also checkout our blog posts related to the particular example for deeper understanding.
|
||||
|
||||
| Explore | Description |
|
||||
|----------------------------------------------------|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| [**Build from Scratch with LanceDB** 🛠️🚀](python_examples/build_from_scratch.md) | Start building your **GenAI applications** from the **ground up** using **LanceDB's** efficient vector-based document retrieval capabilities! Get started quickly with a solid foundation. |
|
||||
| [**Multimodal Search with LanceDB** 🤹♂️🔍](python_examples/multimodal.md) | Combine **text** and **image queries** to find the most relevant results using **LanceDB’s multimodal** capabilities. Leverage the efficient vector-based similarity search. |
|
||||
| [**RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) with LanceDB** 🔓🧐](python_examples/rag.md) | Build RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) with **LanceDB** for efficient **vector-based information retrieval** and more accurate responses from AI. |
|
||||
| [**Vector Search: Efficient Retrieval** 🔓👀](python_examples/vector_search.md) | Use **LanceDB's** vector search capabilities to perform efficient and accurate **similarity searches**, enabling rapid discovery and retrieval of relevant documents in Large datasets. |
|
||||
| [**Chatbot applications with LanceDB** 🤖](python_examples/chatbot.md) | Create **chatbots** that retrieves relevant context for **coherent and context-aware replies**, enhancing user experience through advanced conversational AI. |
|
||||
| [**Evaluation: Assessing Text Performance with Precision** 📊💡](python_examples/evaluations.md) | Develop **evaluation** applications that allows you to input reference and candidate texts to **measure** their performance across various metrics. |
|
||||
| [**AI Agents: Intelligent Collaboration** 🤖](python_examples/aiagent.md) | Enable **AI agents** to communicate and collaborate efficiently through dense vector representations, achieving shared goals seamlessly. |
|
||||
| [**Recommender Systems: Personalized Discovery** 🍿📺](python_examples/recommendersystem.md) | Deliver **personalized experiences** by efficiently storing and querying item embeddings with **LanceDB's** powerful vector database capabilities. |
|
||||
| **Miscellaneous Examples🌟** | Find other **unique examples** and **creative solutions** using **LanceDB**, showcasing the flexibility and broad applicability of the platform. |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,15 +1,15 @@
|
||||
# AI Agents: Intelligent Collaboration🤖
|
||||
|
||||
Think of a platform💻 where AI Agents🤖 can seamlessly exchange information, coordinate over tasks, and achieve shared targets with great efficiency📈🚀.
|
||||
Think of a platform where AI Agents can seamlessly exchange information, coordinate over tasks, and achieve shared targets with great efficiency💻📈.
|
||||
|
||||
## Vector-Based Coordination: The Technical Advantage
|
||||
Leveraging LanceDB's vector-based capabilities, our coordination application enables AI agents to communicate and collaborate through dense vector representations 🤖. AI agents can exchange information, coordinate on a task or work towards a common goal, just by giving queries📝.
|
||||
Leveraging LanceDB's vector-based capabilities, we can enable **AI agents 🤖** to communicate and collaborate through dense vector representations. AI agents can exchange information, coordinate on a task or work towards a common goal, just by giving queries📝.
|
||||
|
||||
| **AI Agents** | **Description** | **Links** |
|
||||
|:--------------|:----------------|:----------|
|
||||
| **AI Agents: Reducing Hallucinationt📊** | 🤖💡 Reduce AI hallucinations using Critique-Based Contexting! Learn by Simplifying and Automating tedious workflows by going through fitness trainer agent example.💪 | [][hullucination_github] <br>[][hullucination_colab] <br>[][hullucination_python] <br>[][hullucination_ghost] |
|
||||
| **AI Trends Searcher: CrewAI🔍️** | 🔍️ Learn about CrewAI Agents ! Utilize the features of CrewAI - Role-based Agents, Task Management, and Inter-agent Delegation ! Make AI agents work together to do tricky stuff 😺| [][trend_github] <br>[][trend_colab] <br>[][trend_ghost] |
|
||||
| **SuperAgent Autogen🤖** | 💻 AI interactions with the Super Agent! Integrating Autogen, LanceDB, LangChain, LiteLLM, and Ollama to create AI agent that excels in understanding and processing complex queries.🤖 | [][superagent_github] <br>[][superagent_colab] |
|
||||
| **AI Agents: Reducing Hallucinationt📊** | 🤖💡 **Reduce AI hallucinations** using Critique-Based Contexting! Learn by Simplifying and Automating tedious workflows by going through fitness trainer agent example.💪 | [][hullucination_github] <br>[][hullucination_colab] <br>[][hullucination_python] <br>[][hullucination_ghost] |
|
||||
| **AI Trends Searcher: CrewAI🔍️** | 🔍️ Learn about **CrewAI Agents** ! Utilize the features of CrewAI - Role-based Agents, Task Management, and Inter-agent Delegation ! Make AI agents work together to do tricky stuff 😺| [][trend_github] <br>[][trend_colab] <br>[][trend_ghost] |
|
||||
| **SuperAgent Autogen🤖** | 💻 AI interactions with the Super Agent! Integrating **Autogen**, **LanceDB**, **LangChain**, **LiteLLM**, and **Ollama** to create AI agent that excels in understanding and processing complex queries.🤖 | [][superagent_github] <br>[][superagent_colab] |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
[hullucination_github]: https://github.com/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/examples/reducing_hallucinations_ai_agents
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,10 +1,10 @@
|
||||
# **Build from Scratch with LanceDB 🛠️🚀**
|
||||
|
||||
Start building your GenAI applications from the ground up using LanceDB's efficient vector-based document retrieval capabilities! 📑
|
||||
Start building your GenAI applications from the ground up using **LanceDB's** efficient vector-based document retrieval capabilities! 📑
|
||||
|
||||
**Get Started in Minutes ⏱️**
|
||||
|
||||
These examples provide a solid foundation for building your own GenAI applications using LanceDB. Jump from idea to proof of concept quickly with applied examples. Get started and see what you can create! 💻
|
||||
These examples provide a solid foundation for building your own GenAI applications using LanceDB. Jump from idea to **proof of concept** quickly with applied examples. Get started and see what you can create! 💻
|
||||
|
||||
| **Build From Scratch** | **Description** | **Links** |
|
||||
|:-------------------------------------------|:-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|:-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
**Chatbot Application with LanceDB 🤖**
|
||||
**Chatbot applications with LanceDB 🤖**
|
||||
====================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
Create an innovative chatbot application that utilizes LanceDB for efficient vector-based response generation! 🌐✨
|
||||
Create innovative chatbot applications that utilizes LanceDB for efficient vector-based response generation! 🌐✨
|
||||
|
||||
**Introduction 👋✨**
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -10,12 +10,12 @@
|
||||
|
||||
| **Chatbot** | **Description** | **Links** |
|
||||
|:----------------|:-----------------|:-----------|
|
||||
| **Databricks DBRX Website Bot ⚡️** | Unlock magical conversations with the Hogwarts chatbot, powered by Open-source RAG, DBRX, LanceDB, LLama-index, and Hugging Face Embeddings, delivering enchanting user experiences and spellbinding interactions ✨ | [][databricks_github] <br>[][databricks_python] |
|
||||
| **CLI SDK Manual Chatbot Locally 💻** | CLI chatbot for SDK/hardware documents, powered by Local RAG, LLama3, Ollama, LanceDB, and Openhermes Embeddings, built with Phidata Assistant and Knowledge Base for instant technical support 🤖 | [][clisdk_github] <br>[][clisdk_python] |
|
||||
| **Youtube Transcript Search QA Bot 📹** | Unlock the power of YouTube transcripts with a Q&A bot, leveraging natural language search and LanceDB for effortless data management and instant answers 💬 | [][youtube_github] <br>[][youtube_colab] <br>[][youtube_python] |
|
||||
| **Code Documentation Q&A Bot with LangChain 🤖** | Revolutionize code documentation with a Q&A bot, powered by LangChain and LanceDB, allowing effortless querying of documentation using natural language, demonstrated with Numpy 1.26 docs 📚 | [][docs_github] <br>[][docs_colab] <br>[][docs_python] |
|
||||
| **Context-aware Chatbot using Llama 2 & LanceDB 🤖** | Experience the future of conversational AI with a context-aware chatbot, powered by Llama 2, LanceDB, and LangChain, enabling intuitive and meaningful conversations with your data 📚💬 | [][aware_github] <br>[][aware_colab] <br>[][aware_ghost] |
|
||||
| **Chat with csv using Hybrid Search 📊** | Revolutionize data interaction with a chat application that harnesses LanceDB's hybrid search capabilities to converse with CSV and Excel files, enabling efficient and scalable data exploration and analysis 🚀 | [][csv_github] <br>[][csv_colab] <br>[][csv_ghost] |
|
||||
| **Databricks DBRX Website Bot ⚡️** | Engage with the **Hogwarts chatbot**, that uses Open-source RAG with **DBRX**, **LanceDB** and **LLama-index with Hugging Face Embeddings**, to provide interactive and engaging user experiences. ✨ | [][databricks_github] <br>[][databricks_python] |
|
||||
| **CLI SDK Manual Chatbot Locally 💻** | CLI chatbot for SDK/hardware documents using **Local RAG** with **LLama3**, **Ollama**, **LanceDB**, and **Openhermes Embeddings**, built with **Phidata** Assistant and Knowledge Base 🤖 | [][clisdk_github] <br>[][clisdk_python] |
|
||||
| **Youtube Transcript Search QA Bot 📹** | Search through **youtube transcripts** using natural language with a Q&A bot, leveraging **LanceDB** for effortless data storage and management 💬 | [][youtube_github] <br>[][youtube_colab] <br>[][youtube_python] |
|
||||
| **Code Documentation Q&A Bot with LangChain 🤖** | Query your own documentation easily using questions in natural language with a Q&A bot, powered by **LangChain** and **LanceDB**, demonstrated with **Numpy 1.26 docs** 📚 | [][docs_github] <br>[][docs_colab] <br>[][docs_python] |
|
||||
| **Context-aware Chatbot using Llama 2 & LanceDB 🤖** | Build **conversational AI** with a **context-aware chatbot**, powered by **Llama 2**, **LanceDB**, and **LangChain**, that enables intuitive and meaningful conversations with your data 📚💬 | [][aware_github] <br>[][aware_colab] <br>[][aware_ghost] |
|
||||
| **Chat with csv using Hybrid Search 📊** | **Chat** application that interacts with **CSV** and **Excel files** using **LanceDB’s** hybrid search capabilities, performing direct operations on large-scale columnar data efficiently 🚀 | [][csv_github] <br>[][csv_colab] <br>[][csv_ghost] |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
[databricks_github]: https://github.com/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/examples/databricks_DBRX_website_bot
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,18 +1,16 @@
|
||||
**Evaluation: Assessing Text Performance with Precision 📊💡**
|
||||
====================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
**Evaluation Fundamentals 📊**
|
||||
|
||||
Evaluation is a comprehensive tool designed to measure the performance of text-based inputs, enabling data-driven optimization and improvement 📈.
|
||||
|
||||
**Text Evaluation 101 📚**
|
||||
|
||||
By leveraging cutting-edge technologies, this provides a robust framework for evaluating reference and candidate texts across various metrics 📊, ensuring high-quality text outputs that meet specific requirements and standards 📝.
|
||||
Using robust framework for assessing reference and candidate texts across various metrics📊, ensure that the text outputs are high-quality and meet specific requirements and standards📝.
|
||||
|
||||
| **Evaluation** | **Description** | **Links** |
|
||||
| -------------- | --------------- | --------- |
|
||||
| **Evaluating Prompts with Prompttools 🤖** | Compare, visualize & evaluate embedding functions (incl. OpenAI) across metrics like latency & custom evaluation 📈📊 | [][prompttools_github] <br>[][prompttools_colab] |
|
||||
| **Evaluating RAG with RAGAs and GPT-4o 📊** | Evaluate RAG pipelines with cutting-edge metrics and tools, integrate with CI/CD for continuous performance checks, and generate responses with GPT-4o 🤖📈 | [][RAGAs_github] <br>[][RAGAs_colab] |
|
||||
| **Evaluating Prompts with Prompttools 🤖** | Compare, visualize & evaluate **embedding functions** (incl. OpenAI) across metrics like latency & custom evaluation 📈📊 | [][prompttools_github] <br>[][prompttools_colab] |
|
||||
| **Evaluating RAG with RAGAs and GPT-4o 📊** | Evaluate **RAG pipelines** with cutting-edge metrics and tools, integrate with CI/CD for continuous performance checks, and generate responses with GPT-4o 🤖📈 | [][RAGAs_github] <br>[][RAGAs_colab] |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
|
||||
# **Multimodal Search with LanceDB 🤹♂️🔍**
|
||||
|
||||
Experience the future of search with LanceDB's multimodal capabilities. Combine text and image queries to find the most relevant results in your corpus ! 🔓💡
|
||||
Using LanceDB's multimodal capabilities, combine text and image queries to find the most relevant results in your corpus ! 🔓💡
|
||||
|
||||
**Explore the Future of Search 🚀**
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -10,10 +10,10 @@ LanceDB supports multimodal search by indexing and querying vector representatio
|
||||
|
||||
| **Multimodal** | **Description** | **Links** |
|
||||
|:----------------|:-----------------|:-----------|
|
||||
| **Multimodal CLIP: DiffusionDB 🌐💥** | Revolutionize search with Multimodal CLIP and DiffusionDB, combining text and image understanding for a new dimension of discovery! 🔓 | [][Clip_diffusionDB_github] <br>[][Clip_diffusionDB_colab] <br>[][Clip_diffusionDB_python] <br>[][Clip_diffusionDB_ghost] |
|
||||
| **Multimodal CLIP: Youtube Videos 📹👀** | Search Youtube videos using Multimodal CLIP, finding relevant content with ease and accuracy! 🎯 | [][Clip_youtube_github] <br>[][Clip_youtube_colab] <br> [][Clip_youtube_python] <br>[][Clip_youtube_python] |
|
||||
| **Multimodal Image + Text Search 📸🔍** | Discover relevant documents and images with a single query, using LanceDB's multimodal search capabilities to bridge the gap between text and visuals! 🌉 | [](https://github.com/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/examples/multimodal_search) <br>[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/examples/multimodal_search/main.ipynb) <br> [](https://github.com/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/examples/multimodal_search/main.py)<br> [](https://blog.lancedb.com/multi-modal-ai-made-easy-with-lancedb-clip-5aaf8801c939/) |
|
||||
| **Cambrian-1: Vision-Centric Image Exploration 🔍👀** | Dive into vision-centric exploration of images with Cambrian-1, powered by LanceDB's multimodal search to uncover new insights! 🔎 | [](https://www.kaggle.com/code/prasantdixit/cambrian-1-vision-centric-exploration-of-images/)<br> [](https://blog.lancedb.com/cambrian-1-vision-centric-exploration/) |
|
||||
| **Multimodal CLIP: DiffusionDB 🌐💥** | Multi-Modal Search with **CLIP** and **LanceDB** Using **DiffusionDB** Data for Combined Text and Image Understanding ! 🔓 | [][Clip_diffusionDB_github] <br>[][Clip_diffusionDB_colab] <br>[][Clip_diffusionDB_python] <br>[][Clip_diffusionDB_ghost] |
|
||||
| **Multimodal CLIP: Youtube Videos 📹👀** | Search **Youtube videos** using Multimodal CLIP, finding relevant content with ease and accuracy! 🎯 | [][Clip_youtube_github] <br>[][Clip_youtube_colab] <br> [][Clip_youtube_python] <br>[][Clip_youtube_python] |
|
||||
| **Multimodal Image + Text Search 📸🔍** | Find **relevant documents** and **images** with a single query using **LanceDB's** multimodal search capabilities, to seamlessly integrate text and visuals ! 🌉 | [](https://github.com/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/examples/multimodal_search) <br>[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/examples/multimodal_search/main.ipynb) <br> [](https://github.com/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/examples/multimodal_search/main.py)<br> [](https://blog.lancedb.com/multi-modal-ai-made-easy-with-lancedb-clip-5aaf8801c939/) |
|
||||
| **Cambrian-1: Vision-Centric Image Exploration 🔍👀** | Learn how **Cambrian-1** works, using an example of **Vision-Centric** exploration on images found through vector search ! Work on **Flickr-8k** dataset 🔎 | [](https://www.kaggle.com/code/prasantdixit/cambrian-1-vision-centric-exploration-of-images/)<br> [](https://blog.lancedb.com/cambrian-1-vision-centric-exploration/) |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
[Clip_diffusionDB_github]: https://github.com/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/examples/multimodal_clip_diffusiondb
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,12 +1,11 @@
|
||||
|
||||
**RAG: Revolutionize Information Retrieval with LanceDB 🔓🧐**
|
||||
**RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) with LanceDB 🔓🧐**
|
||||
====================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
Unlock the full potential of Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) with LanceDB, a solution for efficient vector-based information retrieval 📊.
|
||||
Build RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) with LanceDB, a powerful solution for efficient vector-based information retrieval 📊.
|
||||
|
||||
**Experience the Future of Search 🔄**
|
||||
|
||||
RAG integrates large language models (LLMs) with scalable knowledge bases, enabling efficient information retrieval and answer generation 🤖. By applying RAG to industry-specific use cases, developers can optimize query processing 📊, reduce response latency ⏱️, and improve resource utilization 💻. LanceDB provides a robust framework for integrating LLMs with external knowledge sources, facilitating accurate and informative responses 📝.
|
||||
🤖 RAG enables AI to **retrieve** relevant information from external sources and use it to **generate** more accurate and context-specific responses. 💻 LanceDB provides a robust framework for integrating LLMs with external knowledge sources 📝.
|
||||
|
||||
| **RAG** | **Description** | **Links** |
|
||||
|----------------------------------------------|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|----------------------------|
|
||||
@@ -18,10 +17,10 @@ RAG integrates large language models (LLMs) with scalable knowledge bases, enabl
|
||||
| **Advanced RAG: Parent Document Retriever** 📑🔗 | Use **Parent Document & Bigger Chunk Retriever** to maintain context and relevance when generating related content. 🎵📄 | [][parent_doc_retriever_github] <br>[][parent_doc_retriever_colab] <br>[][parent_doc_retriever_ghost] |
|
||||
| **Corrective RAG with Langgraph** 🔧📊 | Enhance RAG reliability with **Corrective RAG (CRAG)** by self-reflecting and fact-checking for accurate and trustworthy results. ✅🔍 |[][corrective_rag_github] <br>[][corrective_rag_colab] <br>[][corrective_rag_ghost] |
|
||||
| **Contextual Compression with RAG** 🗜️🧠 | Apply **contextual compression techniques** to condense large documents while retaining essential information. 📄🗜️ | [][compression_rag_github] <br>[][compression_rag_colab] <br>[][compression_rag_ghost] |
|
||||
| **Improve RAG with FLARE** 🔥| Enable users to ask questions directly to academic papers, focusing on ArXiv papers, with Forward-Looking Active REtrieval augmented generation.🚀🌟 | [][flare_github] <br>[][flare_colab] <br>[][flare_ghost] |
|
||||
| **Query Expansion and Reranker** 🔍🔄 | Enhance RAG with query expansion using Large Language Models and advanced **reranking methods** like Cross Encoders, ColBERT v2, and FlashRank for improved document retrieval precision and recall 🔍📈 | [][query_github] <br>[][query_colab] |
|
||||
| **RAG Fusion** ⚡🌐 | Revolutionize search with RAG Fusion, utilizing the **RRF algorithm** to rerank documents based on user queries, and leveraging LanceDB and OPENAI Embeddings for efficient information retrieval ⚡🌐 | [][fusion_github] <br>[][fusion_colab] |
|
||||
| **Agentic RAG** 🤖📚 | Unlock autonomous information retrieval with **Agentic RAG**, a framework of **intelligent agents** that collaborate to synthesize, summarize, and compare data across sources, enabling proactive and informed decision-making 🤖📚 | [][agentic_github] <br>[][agentic_colab] |
|
||||
| **Improve RAG with FLARE** 🔥| Enable users to ask questions directly to **academic papers**, focusing on **ArXiv papers**, with **F**orward-**L**ooking **A**ctive **RE**trieval augmented generation.🚀🌟 | [][flare_github] <br>[][flare_colab] <br>[][flare_ghost] |
|
||||
| **Query Expansion and Reranker** 🔍🔄 | Enhance RAG with query expansion using Large Language Models and advanced **reranking methods** like **Cross Encoders**, **ColBERT v2**, and **FlashRank** for improved document retrieval precision and recall 🔍📈 | [][query_github] <br>[][query_colab] |
|
||||
| **RAG Fusion** ⚡🌐 | Build RAG Fusion, utilize the **RRF algorithm** to rerank documents based on user queries ! Use **LanceDB** as vector database to store and retrieve documents related to queries via **OPENAI Embeddings**⚡🌐 | [][fusion_github] <br>[][fusion_colab] |
|
||||
| **Agentic RAG** 🤖📚 | Build autonomous information retrieval with **Agentic RAG**, a framework of **intelligent agents** that collaborate to synthesize, summarize, and compare data across sources, that enables proactive and informed decision-making 🤖📚 | [][agentic_github] <br>[][agentic_colab] |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
37
docs/src/examples/python_examples/recommendersystem.md
Normal file
37
docs/src/examples/python_examples/recommendersystem.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
|
||||
**Recommender Systems: Personalized Discovery🍿📺**
|
||||
==============================================================
|
||||
Deliver personalized experiences with Recommender Systems. 🎁
|
||||
|
||||
**Technical Overview📜**
|
||||
|
||||
🔍️ LanceDB's powerful vector database capabilities can efficiently store and query item embeddings. Recommender Systems can utilize it and provide personalized recommendations based on user preferences 🤝 and item features 📊 and therefore enhance the user experience.🗂️
|
||||
|
||||
| **Recommender System** | **Description** | **Links** |
|
||||
| ---------------------- | --------------- | --------- |
|
||||
| **Movie Recommender System🎬** | 🤝 Use **collaborative filtering** to predict user preferences, assuming similar users will like similar movies, and leverage **Singular Value Decomposition** (SVD) from Numpy for precise matrix factorization and accurate recommendations📊 | [][movie_github] <br>[][movie_colab] <br>[][movie_python] |
|
||||
| **🎥 Movie Recommendation with Genres** | 🔍 Creates movie embeddings using **Doc2Vec**, capturing genre and characteristic nuances, and leverages VectorDB for efficient storage and querying, enabling accurate genre classification and personalized movie recommendations through **similarity searches**🎥 | [][genre_github] <br>[][genre_colab] <br>[][genre_ghost] |
|
||||
| **🛍️ Product Recommender using Collaborative Filtering and LanceDB** | 📈 Using **Collaborative Filtering** and **LanceDB** to analyze your past purchases, recommends products based on user's past purchases. Demonstrated with the Instacart dataset in our example🛒 | [][product_github] <br>[][product_colab] <br>[][product_python] |
|
||||
| **🔍 Arxiv Search with OpenCLIP and LanceDB** | 💡 Build a semantic search engine for **Arxiv papers** using **LanceDB**, and benchmarks its performance against traditional keyword-based search on **Nomic's Atlas**, to demonstrate the power of semantic search in finding relevant research papers📚 | [][arxiv_github] <br>[][arxiv_colab] <br>[][arxiv_python] |
|
||||
| **Food Recommendation System🍴** | 🍔 Build a food recommendation system with **LanceDB**, featuring vector-based recommendations, full-text search, hybrid search, and reranking model integration for personalized and accurate food suggestions👌 | [][food_github] <br>[][food_colab] |
|
||||
|
||||
[movie_github]: https://github.com/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/examples/movie-recommender
|
||||
[movie_colab]: https://colab.research.google.com/github/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/examples/movie-recommender/main.ipynb
|
||||
[movie_python]: https://github.com/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/examples/movie-recommender/main.py
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
[genre_github]: https://github.com/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/examples/movie-recommendation-with-genres
|
||||
[genre_colab]: https://colab.research.google.com/github/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/examples/movie-recommendation-with-genres/movie_recommendation_with_doc2vec_and_lancedb.ipynb
|
||||
[genre_ghost]: https://blog.lancedb.com/movie-recommendation-system-using-lancedb-and-doc2vec/
|
||||
|
||||
[product_github]: https://github.com/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/examples/product-recommender
|
||||
[product_colab]: https://colab.research.google.com/github/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/examples/product-recommender/main.ipynb
|
||||
[product_python]: https://github.com/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/examples/product-recommender/main.py
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
[arxiv_github]: https://github.com/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/examples/arxiv-recommender
|
||||
[arxiv_colab]: https://colab.research.google.com/github/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/examples/arxiv-recommender/main.ipynb
|
||||
[arxiv_python]: https://github.com/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/examples/arxiv-recommender/main.py
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
[food_github]: https://github.com/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/examples/Food_recommendation
|
||||
[food_colab]: https://colab.research.google.com/github/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/examples/Food_recommendation/main.ipynb
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
**Vector Search: Unlock Efficient Document Retrieval 🔓👀**
|
||||
**Vector Search: Efficient Retrieval 🔓👀**
|
||||
====================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
Unlock the power of vector search with LanceDB, a cutting-edge solution for efficient vector-based document retrieval 📊.
|
||||
Vector search with LanceDB, is a solution for efficient and accurate similarity searches in large datasets 📊.
|
||||
|
||||
**Vector Search Capabilities in LanceDB🔝**
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -9,19 +9,19 @@ LanceDB implements vector search algorithms for efficient document retrieval and
|
||||
|
||||
| **Vector Search** | **Description** | **Links** |
|
||||
|:-----------------|:---------------|:---------|
|
||||
| **Inbuilt Hybrid Search 🔄** | Combine the power of traditional search algorithms with LanceDB's vector-based search for a robust and efficient search experience 📊 | [][inbuilt_hybrid_search_github] <br>[][inbuilt_hybrid_search_colab] |
|
||||
| **Hybrid Search with BM25 and LanceDB 💡** | Synergizes BM25's keyword-focused precision (term frequency, document length normalization, bias-free retrieval) with LanceDB's semantic understanding (contextual analysis, query intent alignment) for nuanced search results in complex datasets 📈 | [][BM25_github] <br>[][BM25_colab] <br>[][BM25_ghost] |
|
||||
| **NER-powered Semantic Search 🔎** | Unlock contextual understanding with Named Entity Recognition (NER) methods: Dictionary-Based, Rule-Based, and Deep Learning-Based, to accurately identify and extract entities, enabling precise semantic search results 🗂️ | [][NER_github] <br>[][NER_colab] <br>[][NER_ghost]|
|
||||
| **Audio Similarity Search using Vector Embeddings 🎵** | Create vector embeddings of audio files to find similar audio content, enabling efficient audio similarity search and retrieval in LanceDB's vector store 📻 |[][audio_search_github] <br>[][audio_search_colab] <br>[][audio_search_python]|
|
||||
| **LanceDB Embeddings API: Multi-lingual Semantic Search 🌎** | Build a universal semantic search table with LanceDB's Embeddings API, supporting multiple languages (e.g., English, French) using cohere's multi-lingual model, for accurate cross-lingual search results 📄 | [][mls_github] <br>[][mls_colab] <br>[][mls_python] |
|
||||
| **Facial Recognition: Face Embeddings 🤖** | Detect, crop, and embed faces using Facenet, then store and query face embeddings in LanceDB for efficient facial recognition and top-K matching results 👥 | [][fr_github] <br>[][fr_colab] |
|
||||
| **Sentiment Analysis: Hotel Reviews 🏨** | Analyze customer sentiments towards the hotel industry using BERT models, storing sentiment labels, scores, and embeddings in LanceDB, enabling queries on customer opinions and potential areas for improvement 💬 | [][sentiment_analysis_github] <br>[][sentiment_analysis_colab] <br>[][sentiment_analysis_ghost] |
|
||||
| **Vector Arithmetic with LanceDB ⚖️** | Unlock powerful semantic search capabilities by performing vector arithmetic on embeddings, enabling complex relationships and nuances in data to be captured, and simplifying the process of retrieving semantically similar results 📊 | [][arithmetic_github] <br>[][arithmetic_colab] <br>[][arithmetic_ghost] |
|
||||
| **Imagebind Demo 🖼️** | Explore the multi-modal capabilities of Imagebind through a Gradio app, leveraging LanceDB API for seamless image search and retrieval experiences 📸 | [][imagebind_github] <br> [][imagebind_huggingface] |
|
||||
| **Search Engine using SAM & CLIP 🔍** | Build a search engine within an image using SAM and CLIP models, enabling object-level search and retrieval, with LanceDB indexing and search capabilities to find the closest match between image embeddings and user queries 📸 | [][swi_github] <br>[][swi_colab] <br>[][swi_ghost] |
|
||||
| **Zero Shot Object Localization and Detection with CLIP 🔎** | Perform object detection on images using OpenAI's CLIP, enabling zero-shot localization and detection of objects, with capabilities to split images into patches, parse with CLIP, and plot bounding boxes 📊 | [][zsod_github] <br>[][zsod_colab] |
|
||||
| **Accelerate Vector Search with OpenVINO 🚀** | Boost vector search applications using OpenVINO, achieving significant speedups with CLIP for text-to-image and image-to-image searching, through PyTorch model optimization, FP16 and INT8 format conversion, and quantization with OpenVINO NNCF 📈 | [][openvino_github] <br>[][openvino_colab] <br>[][openvino_ghost] |
|
||||
| **Zero-Shot Image Classification with CLIP and LanceDB 📸** | Achieve zero-shot image classification using CLIP and LanceDB, enabling models to classify images without prior training on specific use cases, unlocking flexible and adaptable image classification capabilities 🔓 | [][zsic_github] <br>[][zsic_colab] <br>[][zsic_ghost] |
|
||||
| **Inbuilt Hybrid Search 🔄** | Perform hybrid search in **LanceDB** by combining the results of semantic and full-text search via a reranking algorithm of your choice 📊 | [][inbuilt_hybrid_search_github] <br>[][inbuilt_hybrid_search_colab] |
|
||||
| **Hybrid Search with BM25 and LanceDB 💡** | Use **Synergizes BM25's** keyword-focused precision (term frequency, document length normalization, bias-free retrieval) with **LanceDB's** semantic understanding (contextual analysis, query intent alignment) for nuanced search results in complex datasets 📈 | [][BM25_github] <br>[][BM25_colab] <br>[][BM25_ghost] |
|
||||
| **NER-powered Semantic Search 🔎** | Extract and identify essential information from text with Named Entity Recognition **(NER)** methods: Dictionary-Based, Rule-Based, and Deep Learning-Based, to accurately extract and categorize entities, enabling precise semantic search results 🗂️ | [][NER_github] <br>[][NER_colab] <br>[][NER_ghost]|
|
||||
| **Audio Similarity Search using Vector Embeddings 🎵** | Create vector **embeddings of audio files** to find similar audio content, enabling efficient audio similarity search and retrieval in **LanceDB's** vector store 📻 |[][audio_search_github] <br>[][audio_search_colab] <br>[][audio_search_python]|
|
||||
| **LanceDB Embeddings API: Multi-lingual Semantic Search 🌎** | Build a universal semantic search table with **LanceDB's Embeddings API**, supporting multiple languages (e.g., English, French) using **cohere's** multi-lingual model, for accurate cross-lingual search results 📄 | [][mls_github] <br>[][mls_colab] <br>[][mls_python] |
|
||||
| **Facial Recognition: Face Embeddings 🤖** | Detect, crop, and embed faces using Facenet, then store and query face embeddings in **LanceDB** for efficient facial recognition and top-K matching results 👥 | [][fr_github] <br>[][fr_colab] |
|
||||
| **Sentiment Analysis: Hotel Reviews 🏨** | Analyze customer sentiments towards the hotel industry using **BERT models**, storing sentiment labels, scores, and embeddings in **LanceDB**, enabling queries on customer opinions and potential areas for improvement 💬 | [][sentiment_analysis_github] <br>[][sentiment_analysis_colab] <br>[][sentiment_analysis_ghost] |
|
||||
| **Vector Arithmetic with LanceDB ⚖️** | Perform **vector arithmetic** on embeddings, enabling complex relationships and nuances in data to be captured, and simplifying the process of retrieving semantically similar results 📊 | [][arithmetic_github] <br>[][arithmetic_colab] <br>[][arithmetic_ghost] |
|
||||
| **Imagebind Demo 🖼️** | Explore the multi-modal capabilities of **Imagebind** through a Gradio app, use **LanceDB API** for seamless image search and retrieval experiences 📸 | [][imagebind_github] <br> [][imagebind_huggingface] |
|
||||
| **Search Engine using SAM & CLIP 🔍** | Build a search engine within an image using **SAM** and **CLIP** models, enabling object-level search and retrieval, with LanceDB indexing and search capabilities to find the closest match between image embeddings and user queries 📸 | [][swi_github] <br>[][swi_colab] <br>[][swi_ghost] |
|
||||
| **Zero Shot Object Localization and Detection with CLIP 🔎** | Perform object detection on images using **OpenAI's CLIP**, enabling zero-shot localization and detection of objects, with capabilities to split images into patches, parse with CLIP, and plot bounding boxes 📊 | [][zsod_github] <br>[][zsod_colab] |
|
||||
| **Accelerate Vector Search with OpenVINO 🚀** | Boost vector search applications using **OpenVINO**, achieving significant speedups with **CLIP** for text-to-image and image-to-image searching, through PyTorch model optimization, FP16 and INT8 format conversion, and quantization with **OpenVINO NNCF** 📈 | [][openvino_github] <br>[][openvino_colab] <br>[][openvino_ghost] |
|
||||
| **Zero-Shot Image Classification with CLIP and LanceDB 📸** | Achieve zero-shot image classification using **CLIP** and **LanceDB**, enabling models to classify images without prior training on specific use cases, unlocking flexible and adaptable image classification capabilities 🔓 | [][zsic_github] <br>[][zsic_colab] <br>[][zsic_ghost] |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -25,8 +25,8 @@ s3://eto-public/datasets/sift/vec_data.lance
|
||||
Then, we can write a quick Python script to populate our LanceDB Table:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import pylance
|
||||
sift_dataset = pylance.dataset("/path/to/local/vec_data.lance")
|
||||
import lance
|
||||
sift_dataset = lance.dataset("/path/to/local/vec_data.lance")
|
||||
df = sift_dataset.to_table().to_pandas()
|
||||
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -2,7 +2,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
LanceDB provides support for full-text search via Lance (before via [Tantivy](https://github.com/quickwit-oss/tantivy) (Python only)), allowing you to incorporate keyword-based search (based on BM25) in your retrieval solutions.
|
||||
|
||||
Currently, the Lance full text search is missing some features that are in the Tantivy full text search. This includes phrase queries, re-ranking, and customizing the tokenizer. Thus, in Python, Tantivy is still the default way to do full text search and many of the instructions below apply just to Tantivy-based indices.
|
||||
Currently, the Lance full text search is missing some features that are in the Tantivy full text search. This includes query parser and customizing the tokenizer. Thus, in Python, Tantivy is still the default way to do full text search and many of the instructions below apply just to Tantivy-based indices.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Installation (Only for Tantivy-based FTS)
|
||||
@@ -62,7 +62,7 @@ Consider that we have a LanceDB table named `my_table`, whose string column `tex
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
await tbl
|
||||
.search("puppy")
|
||||
.search("puppy", queryType="fts")
|
||||
.select(["text"])
|
||||
.limit(10)
|
||||
.toArray();
|
||||
@@ -205,7 +205,7 @@ table.create_fts_index(["text_field"], use_tantivy=True, ordering_field_names=["
|
||||
## Phrase queries vs. terms queries
|
||||
|
||||
!!! warning "Warn"
|
||||
Phrase queries are available for only Tantivy-based FTS
|
||||
Lance-based FTS doesn't support queries using boolean operators `OR`, `AND`.
|
||||
|
||||
For full-text search you can specify either a **phrase** query like `"the old man and the sea"`,
|
||||
or a **terms** search query like `"(Old AND Man) AND Sea"`. For more details on the terms
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -416,7 +416,6 @@ You can create an empty table for scenarios where you want to add data to the ta
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Python"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
|
||||
An empty table can be initialized via a PyArrow schema.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -43,200 +43,32 @@ table.create_fts_index("text")
|
||||
# hybrid search with default re-ranker
|
||||
results = table.search("flower moon", query_type="hybrid").to_pandas()
|
||||
```
|
||||
!!! Note
|
||||
You can also pass the vector and text query manually. This is useful if you're not using the embedding API or if you're using a separate embedder service.
|
||||
### Explicitly passing the vector and text query
|
||||
```python
|
||||
vector_query = [0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5]
|
||||
text_query = "flower moon"
|
||||
results = table.search(query_type="hybrid")
|
||||
.vector(vector_query)
|
||||
.text(text_query)
|
||||
.limit(5)
|
||||
.to_pandas()
|
||||
|
||||
By default, LanceDB uses `LinearCombinationReranker(weight=0.7)` to combine and rerank the results of semantic and full-text search. You can customize the hyperparameters as needed or write your own custom reranker. Here's how you can use any of the available rerankers:
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
By default, LanceDB uses `RRFReranker()`, which uses reciprocal rank fusion score, to combine and rerank the results of semantic and full-text search. You can customize the hyperparameters as needed or write your own custom reranker. Here's how you can use any of the available rerankers:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### `rerank()` arguments
|
||||
* `normalize`: `str`, default `"score"`:
|
||||
The method to normalize the scores. Can be "rank" or "score". If "rank", the scores are converted to ranks and then normalized. If "score", the scores are normalized directly.
|
||||
* `reranker`: `Reranker`, default `LinearCombinationReranker(weight=0.7)`.
|
||||
* `reranker`: `Reranker`, default `RRF()`.
|
||||
The reranker to use. If not specified, the default reranker is used.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Available Rerankers
|
||||
LanceDB provides a number of re-rankers out of the box. You can use any of these re-rankers by passing them to the `rerank()` method. Here's a list of available re-rankers:
|
||||
|
||||
### Linear Combination Reranker
|
||||
This is the default re-ranker used by LanceDB. It combines the results of semantic and full-text search using a linear combination of the scores. The weights for the linear combination can be specified. It defaults to 0.7, i.e, 70% weight for semantic search and 30% weight for full-text search.
|
||||
LanceDB provides a number of re-rankers out of the box. You can use any of these re-rankers by passing them to the `rerank()` method.
|
||||
Go to [Rerankers](../reranking/index.md) to learn more about using the available rerankers and implementing custom rerankers.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from lancedb.rerankers import LinearCombinationReranker
|
||||
|
||||
reranker = LinearCombinationReranker(weight=0.3) # Use 0.3 as the weight for vector search
|
||||
|
||||
results = table.search("rebel", query_type="hybrid").rerank(reranker=reranker).to_pandas()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Arguments
|
||||
----------------
|
||||
* `weight`: `float`, default `0.7`:
|
||||
The weight to use for the semantic search score. The weight for the full-text search score is `1 - weights`.
|
||||
* `fill`: `float`, default `1.0`:
|
||||
The score to give to results that are only in one of the two result sets.This is treated as penalty, so a higher value means a lower score.
|
||||
TODO: We should just hardcode this-- its pretty confusing as we invert scores to calculate final score
|
||||
* `return_score` : str, default `"relevance"`
|
||||
options are "relevance" or "all"
|
||||
The type of score to return. If "relevance", will return only the `_relevance_score. If "all", will return all scores from the vector and FTS search along with the relevance score.
|
||||
|
||||
### Cohere Reranker
|
||||
This re-ranker uses the [Cohere](https://cohere.ai/) API to combine the results of semantic and full-text search. You can use this re-ranker by passing `CohereReranker()` to the `rerank()` method. Note that you'll need to set the `COHERE_API_KEY` environment variable to use this re-ranker.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from lancedb.rerankers import CohereReranker
|
||||
|
||||
reranker = CohereReranker()
|
||||
|
||||
results = table.search("vampire weekend", query_type="hybrid").rerank(reranker=reranker).to_pandas()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Arguments
|
||||
----------------
|
||||
* `model_name` : str, default `"rerank-english-v2.0"`
|
||||
The name of the cross encoder model to use. Available cohere models are:
|
||||
- rerank-english-v2.0
|
||||
- rerank-multilingual-v2.0
|
||||
* `column` : str, default `"text"`
|
||||
The name of the column to use as input to the cross encoder model.
|
||||
* `top_n` : str, default `None`
|
||||
The number of results to return. If None, will return all results.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! Note
|
||||
Only returns `_relevance_score`. Does not support `return_score = "all"`.
|
||||
|
||||
### Cross Encoder Reranker
|
||||
This reranker uses the [Sentence Transformers](https://www.sbert.net/) library to combine the results of semantic and full-text search. You can use it by passing `CrossEncoderReranker()` to the `rerank()` method.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from lancedb.rerankers import CrossEncoderReranker
|
||||
|
||||
reranker = CrossEncoderReranker()
|
||||
|
||||
results = table.search("harmony hall", query_type="hybrid").rerank(reranker=reranker).to_pandas()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Arguments
|
||||
----------------
|
||||
* `model` : str, default `"cross-encoder/ms-marco-TinyBERT-L-6"`
|
||||
The name of the cross encoder model to use. Available cross encoder models can be found [here](https://www.sbert.net/docs/pretrained_cross-encoders.html)
|
||||
* `column` : str, default `"text"`
|
||||
The name of the column to use as input to the cross encoder model.
|
||||
* `device` : str, default `None`
|
||||
The device to use for the cross encoder model. If None, will use "cuda" if available, otherwise "cpu".
|
||||
|
||||
!!! Note
|
||||
Only returns `_relevance_score`. Does not support `return_score = "all"`.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### ColBERT Reranker
|
||||
This reranker uses the ColBERT model to combine the results of semantic and full-text search. You can use it by passing `ColbertrReranker()` to the `rerank()` method.
|
||||
|
||||
ColBERT reranker model calculates relevance of given docs against the query and don't take existing fts and vector search scores into account, so it currently only supports `return_score="relevance"`. By default, it looks for `text` column to rerank the results. But you can specify the column name to use as input to the cross encoder model as described below.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from lancedb.rerankers import ColbertReranker
|
||||
|
||||
reranker = ColbertReranker()
|
||||
|
||||
results = table.search("harmony hall", query_type="hybrid").rerank(reranker=reranker).to_pandas()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Arguments
|
||||
----------------
|
||||
* `model_name` : `str`, default `"colbert-ir/colbertv2.0"`
|
||||
The name of the cross encoder model to use.
|
||||
* `column` : `str`, default `"text"`
|
||||
The name of the column to use as input to the cross encoder model.
|
||||
* `return_score` : `str`, default `"relevance"`
|
||||
options are `"relevance"` or `"all"`. Only `"relevance"` is supported for now.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! Note
|
||||
Only returns `_relevance_score`. Does not support `return_score = "all"`.
|
||||
|
||||
### OpenAI Reranker
|
||||
This reranker uses the OpenAI API to combine the results of semantic and full-text search. You can use it by passing `OpenaiReranker()` to the `rerank()` method.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! Note
|
||||
This prompts chat model to rerank results which is not a dedicated reranker model. This should be treated as experimental.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! Tip
|
||||
- You might run out of token limit so set the search `limits` based on your token limit.
|
||||
- It is recommended to use gpt-4-turbo-preview, the default model, older models might lead to undesired behaviour
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from lancedb.rerankers import OpenaiReranker
|
||||
|
||||
reranker = OpenaiReranker()
|
||||
|
||||
results = table.search("harmony hall", query_type="hybrid").rerank(reranker=reranker).to_pandas()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Arguments
|
||||
----------------
|
||||
* `model_name` : `str`, default `"gpt-4-turbo-preview"`
|
||||
The name of the cross encoder model to use.
|
||||
* `column` : `str`, default `"text"`
|
||||
The name of the column to use as input to the cross encoder model.
|
||||
* `return_score` : `str`, default `"relevance"`
|
||||
options are "relevance" or "all". Only "relevance" is supported for now.
|
||||
* `api_key` : `str`, default `None`
|
||||
The API key to use. If None, will use the OPENAI_API_KEY environment variable.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Building Custom Rerankers
|
||||
You can build your own custom reranker by subclassing the `Reranker` class and implementing the `rerank_hybrid()` method. Here's an example of a custom reranker that combines the results of semantic and full-text search using a linear combination of the scores.
|
||||
|
||||
The `Reranker` base interface comes with a `merge_results()` method that can be used to combine the results of semantic and full-text search. This is a vanilla merging algorithm that simply concatenates the results and removes the duplicates without taking the scores into consideration. It only keeps the first copy of the row encountered. This works well in cases that don't require the scores of semantic and full-text search to combine the results. If you want to use the scores or want to support `return_score="all"`, you'll need to implement your own merging algorithm.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
|
||||
from lancedb.rerankers import Reranker
|
||||
import pyarrow as pa
|
||||
|
||||
class MyReranker(Reranker):
|
||||
def __init__(self, param1, param2, ..., return_score="relevance"):
|
||||
super().__init__(return_score)
|
||||
self.param1 = param1
|
||||
self.param2 = param2
|
||||
|
||||
def rerank_hybrid(self, query: str, vector_results: pa.Table, fts_results: pa.Table):
|
||||
# Use the built-in merging function
|
||||
combined_result = self.merge_results(vector_results, fts_results)
|
||||
|
||||
# Do something with the combined results
|
||||
# ...
|
||||
|
||||
# Return the combined results
|
||||
return combined_result
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Example of a Custom Reranker
|
||||
For the sake of simplicity let's build custom reranker that just enchances the Cohere Reranker by accepting a filter query, and accept other CohereReranker params as kwags.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
|
||||
from typing import List, Union
|
||||
import pandas as pd
|
||||
from lancedb.rerankers import CohereReranker
|
||||
|
||||
class MofidifiedCohereReranker(CohereReranker):
|
||||
def __init__(self, filters: Union[str, List[str]], **kwargs):
|
||||
super().__init__(**kwargs)
|
||||
filters = filters if isinstance(filters, list) else [filters]
|
||||
self.filters = filters
|
||||
|
||||
def rerank_hybrid(self, query: str, vector_results: pa.Table, fts_results: pa.Table)-> pa.Table:
|
||||
combined_result = super().rerank_hybrid(query, vector_results, fts_results)
|
||||
df = combined_result.to_pandas()
|
||||
for filter in self.filters:
|
||||
df = df.query("not text.str.contains(@filter)")
|
||||
|
||||
return pa.Table.from_pandas(df)
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
The `vector_results` and `fts_results` are pyarrow tables. You can convert them to pandas dataframes using `to_pandas()` method and perform any operations you want. After you are done, you can convert the dataframe back to pyarrow table using `pa.Table.from_pandas()` method and return it.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -68,3 +68,25 @@ currently is also a memory intensive operation.
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
[`Index`](Index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
### fts()
|
||||
|
||||
> `static` **fts**(`options`?): [`Index`](Index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Create a full text search index
|
||||
|
||||
This index is used to search for text data. The index is created by tokenizing the text
|
||||
into words and then storing occurrences of these words in a data structure called inverted index
|
||||
that allows for fast search.
|
||||
|
||||
During a search the query is tokenized and the inverted index is used to find the rows that
|
||||
contain the query words. The rows are then scored based on BM25 and the top scoring rows are
|
||||
sorted and returned.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
• **options?**: `Partial`<[`FtsOptions`](../interfaces/FtsOptions.md)>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
[`Index`](Index.md)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -501,16 +501,28 @@ Get the schema of the table.
|
||||
|
||||
#### search(query)
|
||||
|
||||
> `abstract` **search**(`query`): [`VectorQuery`](VectorQuery.md)
|
||||
> `abstract` **search**(`query`, `queryType`, `ftsColumns`): [`VectorQuery`](VectorQuery.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Create a search query to find the nearest neighbors
|
||||
of the given query vector
|
||||
of the given query vector, or the documents
|
||||
with the highest relevance to the query string.
|
||||
|
||||
##### Parameters
|
||||
|
||||
• **query**: `string`
|
||||
|
||||
the query. This will be converted to a vector using the table's provided embedding function
|
||||
the query. This will be converted to a vector using the table's provided embedding function,
|
||||
or the query string for full-text search if `queryType` is "fts".
|
||||
|
||||
• **queryType**: `string` = `"auto"` \| `"fts"`
|
||||
|
||||
the type of query to run. If "auto", the query type will be determined based on the query.
|
||||
|
||||
• **ftsColumns**: `string[] | str` = undefined
|
||||
|
||||
the columns to search in. If not provided, all indexed columns will be searched.
|
||||
|
||||
For now, this can support to search only one column.
|
||||
|
||||
##### Returns
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -37,6 +37,7 @@
|
||||
- [IndexOptions](interfaces/IndexOptions.md)
|
||||
- [IndexStatistics](interfaces/IndexStatistics.md)
|
||||
- [IvfPqOptions](interfaces/IvfPqOptions.md)
|
||||
- [FtsOptions](interfaces/FtsOptions.md)
|
||||
- [TableNamesOptions](interfaces/TableNamesOptions.md)
|
||||
- [UpdateOptions](interfaces/UpdateOptions.md)
|
||||
- [WriteOptions](interfaces/WriteOptions.md)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,378 +0,0 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cells": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"attachments": {},
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"id": "13cb272e",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Code documentation Q&A bot example with LangChain\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"This Q&A bot will allow you to query your own documentation easily using questions. We'll also demonstrate the use of LangChain and LanceDB using the OpenAI API. \n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"In this example we'll use Pandas 2.0 documentation, but, this could be replaced for your own docs as well\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"<a href=\"https://colab.research.google.com/github/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/examples/Code-Documentation-QA-Bot/main.ipynb\"><img src=\"https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg\" alt=\"Open In Colab\"></a>\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Scripts - [](./examples/Code-Documentation-QA-Bot/main.py) [](./examples/Code-Documentation-QA-Bot/index.js)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 40,
|
||||
"id": "66638d6c",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"!pip install --quiet openai langchain\n",
|
||||
"!pip install --quiet -U lancedb"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"attachments": {},
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"id": "d1cdcac3",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"First, let's get some setup out of the way. As we're using the OpenAI API, ensure that you've set your key (and organization if needed):"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 42,
|
||||
"id": "58ee1868",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from openai import OpenAI\n",
|
||||
"import os\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# Configuring the environment variable OPENAI_API_KEY\n",
|
||||
"if \"OPENAI_API_KEY\" not in os.environ:\n",
|
||||
" os.environ[\"OPENAI_API_KEY\"] = \"sk-...\"\n",
|
||||
"client = OpenAI()\n",
|
||||
"assert len(client.models.list().data) > 0"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"attachments": {},
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"id": "34f524d3",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Loading in our code documentation, generating embeddings and storing our documents in LanceDB\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"We're going to use the power of LangChain to help us create our Q&A bot. It comes with several APIs that can make our development much easier as well as a LanceDB integration for vectorstore."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 43,
|
||||
"id": "b55d22f1",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"import lancedb\n",
|
||||
"import re\n",
|
||||
"import pickle\n",
|
||||
"import requests\n",
|
||||
"import zipfile\n",
|
||||
"from pathlib import Path\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"from langchain.document_loaders import UnstructuredHTMLLoader\n",
|
||||
"from langchain.embeddings import OpenAIEmbeddings\n",
|
||||
"from langchain.text_splitter import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter\n",
|
||||
"from langchain.vectorstores import LanceDB\n",
|
||||
"from langchain.llms import OpenAI\n",
|
||||
"from langchain.chains import RetrievalQA"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"attachments": {},
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"id": "56cc6d50",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"To make this easier, we've downloaded Pandas documentation and stored the raw HTML files for you to download. We'll download them and then use LangChain's HTML document readers to parse them and store them in LanceDB as a vector store, along with relevant metadata."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"id": "7da77e75",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"pandas_docs = requests.get(\"https://eto-public.s3.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/datasets/pandas_docs/pandas.documentation.zip\")\n",
|
||||
"with open('/tmp/pandas.documentation.zip', 'wb') as f:\n",
|
||||
" f.write(pandas_docs.content)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"file = zipfile.ZipFile(\"/tmp/pandas.documentation.zip\")\n",
|
||||
"file.extractall(path=\"/tmp/pandas_docs\")"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"attachments": {},
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"id": "ae42496c",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"We'll create a simple helper function that can help to extract metadata, so we can use this downstream when we're wanting to query with filters. In this case, we want to keep the lineage of the uri or path for each document that we process:"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 44,
|
||||
"id": "d171d062",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"def get_document_title(document):\n",
|
||||
" m = str(document.metadata[\"source\"])\n",
|
||||
" title = re.findall(\"pandas.documentation(.*).html\", m)\n",
|
||||
" if title[0] is not None:\n",
|
||||
" return(title[0])\n",
|
||||
" return ''"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"attachments": {},
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"id": "130162ad",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Pre-processing and loading the documentation\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Next, let's pre-process and load the documentation. To make sure we don't need to do this repeatedly if we were updating code, we're caching it using pickle so we can retrieve it again (this could take a few minutes to run the first time you do it). We'll also add some more metadata to the docs here such as the title and version of the code:"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 45,
|
||||
"id": "33bfe7d8",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"docs_path = Path(\"docs.pkl\")\n",
|
||||
"docs = []\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"if not docs_path.exists():\n",
|
||||
" for p in Path(\"/tmp/pandas_docs/pandas.documentation\").rglob(\"*.html\"):\n",
|
||||
" print(p)\n",
|
||||
" if p.is_dir():\n",
|
||||
" continue\n",
|
||||
" loader = UnstructuredHTMLLoader(p)\n",
|
||||
" raw_document = loader.load()\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" m = {}\n",
|
||||
" m[\"title\"] = get_document_title(raw_document[0])\n",
|
||||
" m[\"version\"] = \"2.0rc0\"\n",
|
||||
" raw_document[0].metadata = raw_document[0].metadata | m\n",
|
||||
" raw_document[0].metadata[\"source\"] = str(raw_document[0].metadata[\"source\"])\n",
|
||||
" docs = docs + raw_document\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" with docs_path.open(\"wb\") as fh:\n",
|
||||
" pickle.dump(docs, fh)\n",
|
||||
"else:\n",
|
||||
" with docs_path.open(\"rb\") as fh:\n",
|
||||
" docs = pickle.load(fh)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"attachments": {},
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"id": "c3852dd3",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Generating embeddings from our docs\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Now that we have our raw documents loaded, we need to pre-process them to generate embeddings:"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 47,
|
||||
"id": "82230563",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(\n",
|
||||
" chunk_size=1000,\n",
|
||||
" chunk_overlap=200,\n",
|
||||
")\n",
|
||||
"documents = text_splitter.split_documents(docs)\n",
|
||||
"embeddings = OpenAIEmbeddings()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"attachments": {},
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"id": "43e68215",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Storing and querying with LanceDB\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Let's connect to LanceDB so we can store our documents. We'll create a Table to store them in:"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 48,
|
||||
"id": "74780a58",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"db = lancedb.connect('/tmp/lancedb')\n",
|
||||
"table = db.create_table(\"pandas_docs\", data=[\n",
|
||||
" {\"vector\": embeddings.embed_query(\"Hello World\"), \"text\": \"Hello World\", \"id\": \"1\"}\n",
|
||||
"], mode=\"overwrite\")\n",
|
||||
"docsearch = LanceDB.from_documents(documents, embeddings, connection=table)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"attachments": {},
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"id": "3cb1dc5d",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"Now let's create our RetrievalQA chain using the LanceDB vector store:"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 49,
|
||||
"id": "6a5891ad",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"qa = RetrievalQA.from_chain_type(llm=OpenAI(), chain_type=\"stuff\", retriever=docsearch.as_retriever())"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"attachments": {},
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"id": "28d93b85",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"And that's it! We're all set up. The next step is to run some queries, let's try a few:"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 50,
|
||||
"id": "70d88316",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"data": {
|
||||
"text/plain": [
|
||||
"' The major differences in pandas 2.0 include installing optional dependencies with pip extras, the ability to use any numpy numeric dtype in an Index, and enhancements, notable bug fixes, backwards incompatible API changes, deprecations, and performance improvements.'"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
"execution_count": 50,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"output_type": "execute_result"
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"query = \"What are the major differences in pandas 2.0?\"\n",
|
||||
"qa.run(query)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 51,
|
||||
"id": "85a0397c",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"data": {
|
||||
"text/plain": [
|
||||
"' 2.0.0rc0'"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
"execution_count": 51,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"output_type": "execute_result"
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"query = \"What's the current version of pandas?\"\n",
|
||||
"qa.run(query)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 52,
|
||||
"id": "923f86c6",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"data": {
|
||||
"text/plain": [
|
||||
"' Optional dependencies can be installed with pip install \"pandas[all]\" or \"pandas[performance]\". This will install all recommended performance dependencies such as numexpr, bottleneck and numba.'"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
"execution_count": 52,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"output_type": "execute_result"
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"query = \"How do I make use of installing optional dependencies?\"\n",
|
||||
"qa.run(query)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 53,
|
||||
"id": "02082f83",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"data": {
|
||||
"text/plain": [
|
||||
"\" \\n\\nPandas 2.0 includes a number of API breaking changes, such as increased minimum versions for dependencies, the use of os.linesep for DataFrame.to_csv's line_terminator, and reorganization of the library. See the release notes for a full list of changes.\""
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
"execution_count": 53,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"output_type": "execute_result"
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"query = \"What are the backwards incompatible API changes in Pandas 2.0?\"\n",
|
||||
"qa.run(query)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"id": "75cea547",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": []
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"kernelspec": {
|
||||
"display_name": "Python 3 (ipykernel)",
|
||||
"language": "python",
|
||||
"name": "python3"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"language_info": {
|
||||
"codemirror_mode": {
|
||||
"name": "ipython",
|
||||
"version": 3
|
||||
},
|
||||
"file_extension": ".py",
|
||||
"mimetype": "text/x-python",
|
||||
"name": "python",
|
||||
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
|
||||
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
|
||||
"version": "3.10.11"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"nbformat": 4,
|
||||
"nbformat_minor": 5
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -1,297 +0,0 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cells": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" <a href=\"https://colab.research.google.com/github/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/examples/multimodal_clip/main.ipynb\"><img src=\"https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg\" alt=\"Open In Colab\"></a>| [](./examples/multimodal_clip/main.py) |"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 2,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stdout",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\u001B[1m[\u001B[0m\u001B[34;49mnotice\u001B[0m\u001B[1;39;49m]\u001B[0m\u001B[39;49m A new release of pip available: \u001B[0m\u001B[31;49m22.3.1\u001B[0m\u001B[39;49m -> \u001B[0m\u001B[32;49m23.1.2\u001B[0m\n",
|
||||
"\u001B[1m[\u001B[0m\u001B[34;49mnotice\u001B[0m\u001B[1;39;49m]\u001B[0m\u001B[39;49m To update, run: \u001B[0m\u001B[32;49mpip install --upgrade pip\u001B[0m\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\u001B[1m[\u001B[0m\u001B[34;49mnotice\u001B[0m\u001B[1;39;49m]\u001B[0m\u001B[39;49m A new release of pip available: \u001B[0m\u001B[31;49m22.3.1\u001B[0m\u001B[39;49m -> \u001B[0m\u001B[32;49m23.1.2\u001B[0m\n",
|
||||
"\u001B[1m[\u001B[0m\u001B[34;49mnotice\u001B[0m\u001B[1;39;49m]\u001B[0m\u001B[39;49m To update, run: \u001B[0m\u001B[32;49mpip install --upgrade pip\u001B[0m\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"!pip install --quiet -U lancedb\n",
|
||||
"!pip install --quiet gradio transformers torch torchvision"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 1,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"import io\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"import PIL\n",
|
||||
"import duckdb\n",
|
||||
"import lancedb"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## First run setup: Download data and pre-process"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Get dataset\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"!wget https://eto-public.s3.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/datasets/diffusiondb_lance.tar.gz\n",
|
||||
"!tar -xvf diffusiondb_lance.tar.gz\n",
|
||||
"!mv diffusiondb_test rawdata.lance\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 30,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"data": {
|
||||
"text/plain": [
|
||||
"<lance.dataset.LanceDataset at 0x3045db590>"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
"execution_count": 30,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"output_type": "execute_result"
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# remove null prompts\n",
|
||||
"import lance\n",
|
||||
"import pyarrow.compute as pc\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# download s3://eto-public/datasets/diffusiondb/small_10k.lance to this uri\n",
|
||||
"data = lance.dataset(\"~/datasets/rawdata.lance\").to_table()\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# First data processing and full-text-search index\n",
|
||||
"db = lancedb.connect(\"~/datasets/demo\")\n",
|
||||
"tbl = db.create_table(\"diffusiondb\", data.filter(~pc.field(\"prompt\").is_null()))\n",
|
||||
"tbl = tbl.create_fts_index([\"prompt\"])"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Create / Open LanceDB Table"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 2,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"db = lancedb.connect(\"~/datasets/demo\")\n",
|
||||
"tbl = db.open_table(\"diffusiondb\")"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Create CLIP embedding function for the text"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 3,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from transformers import CLIPModel, CLIPProcessor, CLIPTokenizerFast\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"MODEL_ID = \"openai/clip-vit-base-patch32\"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"tokenizer = CLIPTokenizerFast.from_pretrained(MODEL_ID)\n",
|
||||
"model = CLIPModel.from_pretrained(MODEL_ID)\n",
|
||||
"processor = CLIPProcessor.from_pretrained(MODEL_ID)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"def embed_func(query):\n",
|
||||
" inputs = tokenizer([query], padding=True, return_tensors=\"pt\")\n",
|
||||
" text_features = model.get_text_features(**inputs)\n",
|
||||
" return text_features.detach().numpy()[0]"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Search functions for Gradio"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 4,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"def find_image_vectors(query):\n",
|
||||
" emb = embed_func(query)\n",
|
||||
" code = (\n",
|
||||
" \"import lancedb\\n\"\n",
|
||||
" \"db = lancedb.connect('~/datasets/demo')\\n\"\n",
|
||||
" \"tbl = db.open_table('diffusiondb')\\n\\n\"\n",
|
||||
" f\"embedding = embed_func('{query}')\\n\"\n",
|
||||
" \"tbl.search(embedding).limit(9).to_pandas()\"\n",
|
||||
" )\n",
|
||||
" return (_extract(tbl.search(emb).limit(9).to_pandas()), code)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"def find_image_keywords(query):\n",
|
||||
" code = (\n",
|
||||
" \"import lancedb\\n\"\n",
|
||||
" \"db = lancedb.connect('~/datasets/demo')\\n\"\n",
|
||||
" \"tbl = db.open_table('diffusiondb')\\n\\n\"\n",
|
||||
" f\"tbl.search('{query}').limit(9).to_pandas()\"\n",
|
||||
" )\n",
|
||||
" return (_extract(tbl.search(query).limit(9).to_pandas()), code)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"def find_image_sql(query):\n",
|
||||
" code = (\n",
|
||||
" \"import lancedb\\n\"\n",
|
||||
" \"import duckdb\\n\"\n",
|
||||
" \"db = lancedb.connect('~/datasets/demo')\\n\"\n",
|
||||
" \"tbl = db.open_table('diffusiondb')\\n\\n\"\n",
|
||||
" \"diffusiondb = tbl.to_lance()\\n\"\n",
|
||||
" f\"duckdb.sql('{query}').to_df()\"\n",
|
||||
" ) \n",
|
||||
" diffusiondb = tbl.to_lance()\n",
|
||||
" return (_extract(duckdb.sql(query).to_df()), code)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"def _extract(df):\n",
|
||||
" image_col = \"image\"\n",
|
||||
" return [(PIL.Image.open(io.BytesIO(row[image_col])), row[\"prompt\"]) for _, row in df.iterrows()]"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Setup Gradio interface"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 28,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stdout",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"Running on local URL: http://127.0.0.1:7881\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"To create a public link, set `share=True` in `launch()`.\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"data": {
|
||||
"text/html": [
|
||||
"<div><iframe src=\"http://127.0.0.1:7881/\" width=\"100%\" height=\"500\" allow=\"autoplay; camera; microphone; clipboard-read; clipboard-write;\" frameborder=\"0\" allowfullscreen></iframe></div>"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"text/plain": [
|
||||
"<IPython.core.display.HTML object>"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"output_type": "display_data"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"data": {
|
||||
"text/plain": []
|
||||
},
|
||||
"execution_count": 28,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"output_type": "execute_result"
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"import gradio as gr\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"with gr.Blocks() as demo:\n",
|
||||
" with gr.Row():\n",
|
||||
" with gr.Tab(\"Embeddings\"):\n",
|
||||
" vector_query = gr.Textbox(value=\"portraits of a person\", show_label=False)\n",
|
||||
" b1 = gr.Button(\"Submit\")\n",
|
||||
" with gr.Tab(\"Keywords\"):\n",
|
||||
" keyword_query = gr.Textbox(value=\"ninja turtle\", show_label=False)\n",
|
||||
" b2 = gr.Button(\"Submit\")\n",
|
||||
" with gr.Tab(\"SQL\"):\n",
|
||||
" sql_query = gr.Textbox(value=\"SELECT * from diffusiondb WHERE image_nsfw >= 2 LIMIT 9\", show_label=False)\n",
|
||||
" b3 = gr.Button(\"Submit\")\n",
|
||||
" with gr.Row():\n",
|
||||
" code = gr.Code(label=\"Code\", language=\"python\")\n",
|
||||
" with gr.Row():\n",
|
||||
" gallery = gr.Gallery(\n",
|
||||
" label=\"Found images\", show_label=False, elem_id=\"gallery\"\n",
|
||||
" ).style(columns=[3], rows=[3], object_fit=\"contain\", height=\"auto\") \n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
" b1.click(find_image_vectors, inputs=vector_query, outputs=[gallery, code])\n",
|
||||
" b2.click(find_image_keywords, inputs=keyword_query, outputs=[gallery, code])\n",
|
||||
" b3.click(find_image_sql, inputs=sql_query, outputs=[gallery, code])\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
"demo.launch()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": []
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"kernelspec": {
|
||||
"display_name": "Python 3.11.4 64-bit",
|
||||
"language": "python",
|
||||
"name": "python3"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"language_info": {
|
||||
"codemirror_mode": {
|
||||
"name": "ipython",
|
||||
"version": 3
|
||||
},
|
||||
"file_extension": ".py",
|
||||
"mimetype": "text/x-python",
|
||||
"name": "python",
|
||||
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
|
||||
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
|
||||
"version": "3.11.4"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"vscode": {
|
||||
"interpreter": {
|
||||
"hash": "b0fa6594d8f4cbf19f97940f81e996739fb7646882a419484c72d19e05852a7e"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"nbformat": 4,
|
||||
"nbformat_minor": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
File diff suppressed because one or more lines are too long
51
docs/src/rag/adaptive_rag.md
Normal file
51
docs/src/rag/adaptive_rag.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,51 @@
|
||||
**Adaptive RAG 🤹♂️**
|
||||
====================================================================
|
||||
Adaptive RAG introduces a RAG technique that combines query analysis with self-corrective RAG.
|
||||
|
||||
For Query Analysis, it uses a small classifier(LLM), to decide the query’s complexity. Query Analysis helps routing smoothly to adjust between different retrieval strategies No retrieval, Single-shot RAG or Iterative RAG.
|
||||
|
||||
**[Official Paper](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2403.14403)**
|
||||
|
||||
<figure markdown="span">
|
||||

|
||||
<figcaption>Adaptive-RAG: <a href="https://github.com/starsuzi/Adaptive-RAG">Source</a>
|
||||
</figcaption>
|
||||
</figure>
|
||||
|
||||
**[Offical Implementation](https://github.com/starsuzi/Adaptive-RAG)**
|
||||
|
||||
Here’s a code snippet for query analysis
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
|
||||
from langchain_core.pydantic_v1 import BaseModel, Field
|
||||
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
|
||||
|
||||
class RouteQuery(BaseModel):
|
||||
"""Route a user query to the most relevant datasource."""
|
||||
|
||||
datasource: Literal["vectorstore", "web_search"] = Field(
|
||||
...,
|
||||
description="Given a user question choose to route it to web search or a vectorstore.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# LLM with function call
|
||||
llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-3.5-turbo-0125", temperature=0)
|
||||
structured_llm_router = llm.with_structured_output(RouteQuery)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For defining and querying retriever
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# add documents in LanceDB
|
||||
vectorstore = LanceDB.from_documents(
|
||||
documents=doc_splits,
|
||||
embedding=OpenAIEmbeddings(),
|
||||
)
|
||||
retriever = vectorstore.as_retriever()
|
||||
|
||||
# query using defined retriever
|
||||
question = "How adaptive RAG works"
|
||||
docs = retriever.get_relevant_documents(question)
|
||||
```
|
||||
38
docs/src/rag/advanced_techniques/flare.md
Normal file
38
docs/src/rag/advanced_techniques/flare.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
|
||||
**FLARE 💥**
|
||||
====================================================================
|
||||
FLARE, stands for Forward-Looking Active REtrieval augmented generation is a generic retrieval-augmented generation method that actively decides when and what to retrieve using a prediction of the upcoming sentence to anticipate future content and utilize it as the query to retrieve relevant documents if it contains low-confidence tokens.
|
||||
|
||||
**[Official Paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2305.06983)**
|
||||
|
||||
<figure markdown="span">
|
||||

|
||||
<figcaption>FLARE: <a href="https://github.com/jzbjyb/FLARE">Source</a></figcaption>
|
||||
</figure>
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/examples/better-rag-FLAIR/main.ipynb)
|
||||
|
||||
Here’s a code snippet for using FLARE with Langchain
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from langchain.vectorstores import LanceDB
|
||||
from langchain.document_loaders import ArxivLoader
|
||||
from langchain.chains import FlareChain
|
||||
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
|
||||
from langchain.chains import LLMChain
|
||||
from langchain.llms import OpenAI
|
||||
|
||||
llm = OpenAI()
|
||||
|
||||
# load dataset
|
||||
|
||||
# LanceDB retriever
|
||||
vector_store = LanceDB.from_documents(doc_chunks, embeddings, connection=table)
|
||||
retriever = vector_store.as_retriever()
|
||||
|
||||
# define flare chain
|
||||
flare = FlareChain.from_llm(llm=llm,retriever=vector_store_retriever,max_generation_len=300,min_prob=0.45)
|
||||
|
||||
result = flare.run(input_text)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/examples/better-rag-FLAIR/main.ipynb)
|
||||
55
docs/src/rag/advanced_techniques/hyde.md
Normal file
55
docs/src/rag/advanced_techniques/hyde.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,55 @@
|
||||
**HyDE: Hypothetical Document Embeddings 🤹♂️**
|
||||
====================================================================
|
||||
HyDE, stands for Hypothetical Document Embeddings is an approach used for precise zero-shot dense retrieval without relevance labels. It focuses on augmenting and improving similarity searches, often intertwined with vector stores in information retrieval. The method generates a hypothetical document for an incoming query, which is then embedded and used to look up real documents that are similar to the hypothetical document.
|
||||
|
||||
**[Official Paper](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2212.10496)**
|
||||
|
||||
<figure markdown="span">
|
||||

|
||||
<figcaption>HyDE: <a href="https://arxiv.org/pdf/2212.10496">Source</a></figcaption>
|
||||
</figure>
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/examples/Advance-RAG-with-HyDE/main.ipynb)
|
||||
|
||||
Here’s a code snippet for using HyDE with Langchain
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from langchain.llms import OpenAI
|
||||
from langchain.embeddings import OpenAIEmbeddings
|
||||
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
|
||||
from langchain.chains import LLMChain, HypotheticalDocumentEmbedder
|
||||
from langchain.vectorstores import LanceDB
|
||||
|
||||
# set OPENAI_API_KEY as env variable before this step
|
||||
# initialize LLM and embedding function
|
||||
llm = OpenAI()
|
||||
emebeddings = OpenAIEmbeddings()
|
||||
|
||||
# HyDE embedding
|
||||
embeddings = HypotheticalDocumentEmbedder(llm_chain=llm_chain,base_embeddings=embeddings)
|
||||
|
||||
# load dataset
|
||||
|
||||
# LanceDB retriever
|
||||
retriever = LanceDB.from_documents(documents, embeddings, connection=table)
|
||||
|
||||
# prompt template
|
||||
prompt_template = """
|
||||
As a knowledgeable and helpful research assistant, your task is to provide informative answers based on the given context. Use your extensive knowledge base to offer clear, concise, and accurate responses to the user's inquiries.
|
||||
if quetion is not related to documents simply say you dont know
|
||||
Question: {question}
|
||||
|
||||
Answer:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = PromptTemplate(input_variables=["question"], template=prompt_template)
|
||||
|
||||
# LLM Chain
|
||||
llm_chain = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=prompt)
|
||||
|
||||
# vector search
|
||||
retriever.similarity_search(query)
|
||||
llm_chain.run(query)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/examples/Advance-RAG-with-HyDE/main.ipynb)
|
||||
101
docs/src/rag/agentic_rag.md
Normal file
101
docs/src/rag/agentic_rag.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,101 @@
|
||||
**Agentic RAG 🤖**
|
||||
====================================================================
|
||||
Agentic RAG is Agent-based RAG introduces an advanced framework for answering questions by using intelligent agents instead of just relying on large language models. These agents act like expert researchers, handling complex tasks such as detailed planning, multi-step reasoning, and using external tools. They navigate multiple documents, compare information, and generate accurate answers. This system is easily scalable, with each new document set managed by a sub-agent, making it a powerful tool for tackling a wide range of information needs.
|
||||
|
||||
<figure markdown="span">
|
||||
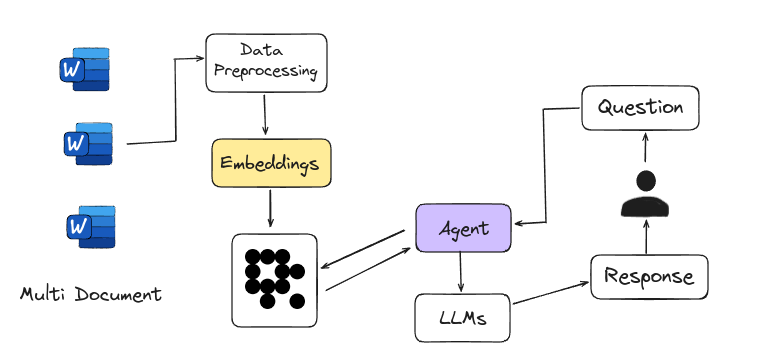
|
||||
<figcaption>Agent-based RAG</figcaption>
|
||||
</figure>
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/tutorials/Agentic_RAG/main.ipynb)
|
||||
|
||||
Here’s a code snippet for defining retriever using Langchain
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from langchain.text_splitter import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
|
||||
from langchain_community.document_loaders import WebBaseLoader
|
||||
from langchain_community.vectorstores import LanceDB
|
||||
from langchain_openai import OpenAIEmbeddings
|
||||
|
||||
urls = [
|
||||
"https://content.dgft.gov.in/Website/CIEP.pdf",
|
||||
"https://content.dgft.gov.in/Website/GAE.pdf",
|
||||
"https://content.dgft.gov.in/Website/HTE.pdf",
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
docs = [WebBaseLoader(url).load() for url in urls]
|
||||
docs_list = [item for sublist in docs for item in sublist]
|
||||
|
||||
text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter.from_tiktoken_encoder(
|
||||
chunk_size=100, chunk_overlap=50
|
||||
)
|
||||
doc_splits = text_splitter.split_documents(docs_list)
|
||||
|
||||
# add documents in LanceDB
|
||||
vectorstore = LanceDB.from_documents(
|
||||
documents=doc_splits,
|
||||
embedding=OpenAIEmbeddings(),
|
||||
)
|
||||
retriever = vectorstore.as_retriever()
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Agent that formulates an improved query for better retrieval results and then grades the retrieved documents
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
def grade_documents(state) -> Literal["generate", "rewrite"]:
|
||||
class grade(BaseModel):
|
||||
binary_score: str = Field(description="Relevance score 'yes' or 'no'")
|
||||
|
||||
model = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0, model="gpt-4-0125-preview", streaming=True)
|
||||
llm_with_tool = model.with_structured_output(grade)
|
||||
prompt = PromptTemplate(
|
||||
template="""You are a grader assessing relevance of a retrieved document to a user question. \n
|
||||
Here is the retrieved document: \n\n {context} \n\n
|
||||
Here is the user question: {question} \n
|
||||
If the document contains keyword(s) or semantic meaning related to the user question, grade it as relevant. \n
|
||||
Give a binary score 'yes' or 'no' score to indicate whether the document is relevant to the question.""",
|
||||
input_variables=["context", "question"],
|
||||
)
|
||||
chain = prompt | llm_with_tool
|
||||
|
||||
messages = state["messages"]
|
||||
last_message = messages[-1]
|
||||
question = messages[0].content
|
||||
docs = last_message.content
|
||||
|
||||
scored_result = chain.invoke({"question": question, "context": docs})
|
||||
score = scored_result.binary_score
|
||||
|
||||
return "generate" if score == "yes" else "rewrite"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def agent(state):
|
||||
messages = state["messages"]
|
||||
model = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0, streaming=True, model="gpt-4-turbo")
|
||||
model = model.bind_tools(tools)
|
||||
response = model.invoke(messages)
|
||||
return {"messages": [response]}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def rewrite(state):
|
||||
messages = state["messages"]
|
||||
question = messages[0].content
|
||||
msg = [
|
||||
HumanMessage(
|
||||
content=f""" \n
|
||||
Look at the input and try to reason about the underlying semantic intent / meaning. \n
|
||||
Here is the initial question:
|
||||
\n ------- \n
|
||||
{question}
|
||||
\n ------- \n
|
||||
Formulate an improved question: """,
|
||||
)
|
||||
]
|
||||
model = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0, model="gpt-4-0125-preview", streaming=True)
|
||||
response = model.invoke(msg)
|
||||
return {"messages": [response]}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/tutorials/Agentic_RAG/main.ipynb)
|
||||
120
docs/src/rag/corrective_rag.md
Normal file
120
docs/src/rag/corrective_rag.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,120 @@
|
||||
**Corrective RAG ✅**
|
||||
====================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
Corrective-RAG (CRAG) is a strategy for Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) that includes self-reflection and self-grading of retrieved documents. Here’s a simplified breakdown of the steps involved:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Relevance Check**: If at least one document meets the relevance threshold, the process moves forward to the generation phase.
|
||||
2. **Knowledge Refinement**: Before generating an answer, the process refines the knowledge by dividing the document into smaller segments called "knowledge strips."
|
||||
3. **Grading and Filtering**: Each "knowledge strip" is graded, and irrelevant ones are filtered out.
|
||||
4. **Additional Data Source**: If all documents are below the relevance threshold, or if the system is unsure about their relevance, it will seek additional information by performing a web search to supplement the retrieved data.
|
||||
|
||||
Above steps are mentioned in
|
||||
**[Official Paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2401.15884)**
|
||||
|
||||
<figure markdown="span">
|
||||

|
||||
<figcaption>Corrective RAG: <a href="https://github.com/HuskyInSalt/CRAG">Source</a>
|
||||
</figcaption>
|
||||
</figure>
|
||||
|
||||
Corrective Retrieval-Augmented Generation (CRAG) is a method that works like a **built-in fact-checker**.
|
||||
|
||||
**[Offical Implementation](https://github.com/HuskyInSalt/CRAG)**
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/tutorials/Corrective-RAG-with_Langgraph/CRAG_with_Langgraph.ipynb)
|
||||
|
||||
Here’s a code snippet for defining a table with the [Embedding API](https://lancedb.github.io/lancedb/embeddings/embedding_functions/), and retrieves the relevant documents.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import pandas as pd
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
from lancedb.pydantic import LanceModel, Vector
|
||||
from lancedb.embeddings import get_registry
|
||||
|
||||
db = lancedb.connect("/tmp/db")
|
||||
model = get_registry().get("sentence-transformers").create(name="BAAI/bge-small-en-v1.5", device="cpu")
|
||||
|
||||
class Docs(LanceModel):
|
||||
text: str = model.SourceField()
|
||||
vector: Vector(model.ndims()) = model.VectorField()
|
||||
|
||||
table = db.create_table("docs", schema=Docs)
|
||||
|
||||
# considering chunks are in list format
|
||||
df = pd.DataFrame({'text':chunks})
|
||||
table.add(data=df)
|
||||
|
||||
# as per document feeded
|
||||
query = "How Transformers work?"
|
||||
actual = table.search(query).limit(1).to_list()[0]
|
||||
print(actual.text)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Code snippet for grading retrieved documents, filtering out irrelevant ones, and performing a web search if necessary:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
def grade_documents(state):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Determines whether the retrieved documents are relevant to the question
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
state (dict): The current graph state
|
||||
|
||||
Returns:
|
||||
state (dict): Updates documents key with relevant documents
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
state_dict = state["keys"]
|
||||
question = state_dict["question"]
|
||||
documents = state_dict["documents"]
|
||||
|
||||
class grade(BaseModel):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Binary score for relevance check
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
binary_score: str = Field(description="Relevance score 'yes' or 'no'")
|
||||
|
||||
model = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0, model="gpt-4-0125-preview", streaming=True)
|
||||
# grading using openai
|
||||
grade_tool_oai = convert_to_openai_tool(grade)
|
||||
llm_with_tool = model.bind(
|
||||
tools=[convert_to_openai_tool(grade_tool_oai)],
|
||||
tool_choice={"type": "function", "function": {"name": "grade"}},
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
parser_tool = PydanticToolsParser(tools=[grade])
|
||||
prompt = PromptTemplate(
|
||||
template="""You are a grader assessing relevance of a retrieved document to a user question. \n
|
||||
Here is the retrieved document: \n\n {context} \n\n
|
||||
Here is the user question: {question} \n
|
||||
If the document contains keyword(s) or semantic meaning related to the user question, grade it as relevant. \n
|
||||
Give a binary score 'yes' or 'no' score to indicate whether the document is relevant to the question.""",
|
||||
input_variables=["context", "question"],
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
chain = prompt | llm_with_tool | parser_tool
|
||||
|
||||
filtered_docs = []
|
||||
search = "No"
|
||||
for d in documents:
|
||||
score = chain.invoke({"question": question, "context": d.page_content})
|
||||
grade = score[0].binary_score
|
||||
if grade == "yes":
|
||||
filtered_docs.append(d)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
search = "Yes"
|
||||
continue
|
||||
|
||||
return {
|
||||
"keys": {
|
||||
"documents": filtered_docs,
|
||||
"question": question,
|
||||
"run_web_search": search,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Check Colab for the Implementation of CRAG with Langgraph
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/tutorials/Corrective-RAG-with_Langgraph/CRAG_with_Langgraph.ipynb)
|
||||
54
docs/src/rag/graph_rag.md
Normal file
54
docs/src/rag/graph_rag.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,54 @@
|
||||
**Graph RAG 📊**
|
||||
====================================================================
|
||||
Graph RAG uses knowledge graphs together with large language models (LLMs) to improve how information is retrieved and generated. It overcomes the limits of traditional search methods by using knowledge graphs, which organize data as connected entities and relationships.
|
||||
|
||||
One of the main benefits of Graph RAG is its ability to capture and represent complex relationships between entities, something that traditional text-based retrieval systems struggle with. By using this structured knowledge, LLMs can better grasp the context and details of a query, resulting in more accurate and insightful answers.
|
||||
|
||||
**[Official Paper](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2404.16130)**
|
||||
|
||||
**[Offical Implementation](https://github.com/microsoft/graphrag)**
|
||||
|
||||
[Microsoft Research Blog](https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/blog/graphrag-unlocking-llm-discovery-on-narrative-private-data/)
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note "Default VectorDB"
|
||||
|
||||
Graph RAG uses LanceDB as the default vector database for performing vector search to retrieve relevant entities.
|
||||
|
||||
Working with Graph RAG is quite straightforward
|
||||
|
||||
- **Installation and API KEY as env variable**
|
||||
|
||||
Set `OPENAI_API_KEY` as `GRAPHRAG_API_KEY`
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install graphrag
|
||||
export GRAPHRAG_API_KEY="sk-..."
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- **Initial structure for indexing dataset**
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python3 -m graphrag.index --init --root dataset-dir
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- **Index Dataset**
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python3 -m graphrag.index --root dataset-dir
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- **Execute Query**
|
||||
|
||||
Global Query Execution gives a broad overview of dataset
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python3 -m graphrag.query --root dataset-dir --method global "query-question"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Local Query Execution gives a detailed and specific answers based on the context of the entities
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python3 -m graphrag.query --root dataset-dir --method local "query-question"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/examples/Graphrag/main.ipynb)
|
||||
49
docs/src/rag/multi_head_rag.md
Normal file
49
docs/src/rag/multi_head_rag.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,49 @@
|
||||
**Multi-Head RAG 📃**
|
||||
====================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
Multi-head RAG (MRAG) is designed to handle queries that need multiple documents with diverse content. These queries are tough because the documents’ embeddings can be far apart, making retrieval difficult. MRAG simplifies this by using the activations from a Transformer's multi-head attention layer, rather than the decoder layer, to fetch these varied documents. Different attention heads capture different aspects of the data, so using these activations helps create embeddings that better represent various data facets and improves retrieval accuracy for complex queries.
|
||||
|
||||
**[Official Paper](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2406.05085)**
|
||||
|
||||
<figure markdown="span">
|
||||

|
||||
<figcaption>Multi-Head RAG: <a href="https://github.com/spcl/MRAG">Source</a>
|
||||
</figcaption>
|
||||
</figure>
|
||||
|
||||
MRAG is cost-effective and energy-efficient because it avoids extra LLM queries, multiple model instances, increased storage, and additional inference passes.
|
||||
|
||||
**[Official Implementation](https://github.com/spcl/MRAG)**
|
||||
|
||||
Here’s a code snippet for defining different embedding spaces with the [Embedding API](https://lancedb.github.io/lancedb/embeddings/embedding_functions/)
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
from lancedb.pydantic import LanceModel, Vector
|
||||
from lancedb.embeddings import get_registry
|
||||
|
||||
# model definition using LanceDB Embedding API
|
||||
model1 = get_registry().get("openai").create()
|
||||
model2 = get_registry().get("ollama").create(name="llama3")
|
||||
model3 = get_registry().get("ollama").create(name="mistral")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# define schema for creating embedding spaces with Embedding API
|
||||
class Space1(LanceModel):
|
||||
text: str = model1.SourceField()
|
||||
vector: Vector(model1.ndims()) = model1.VectorField()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Space2(LanceModel):
|
||||
text: str = model2.SourceField()
|
||||
vector: Vector(model2.ndims()) = model2.VectorField()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Space3(LanceModel):
|
||||
text: str = model3.SourceField()
|
||||
vector: Vector(model3.ndims()) = model3.VectorField()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Create different tables using defined embedding spaces, then make queries to each embedding space. Use the resulted closest documents from each embedding space to generate answers.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
96
docs/src/rag/self_rag.md
Normal file
96
docs/src/rag/self_rag.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,96 @@
|
||||
**Self RAG 🤳**
|
||||
====================================================================
|
||||
Self-RAG is a strategy for Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) to get better retrieved information, generated text, and checking their own work, all without losing their flexibility. Unlike the traditional Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) method, Self-RAG retrieves information as needed, can skip retrieval if not needed, and evaluates its own output while generating text. It also uses a process to pick the best output based on different preferences.
|
||||
|
||||
**[Official Paper](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2310.11511)**
|
||||
|
||||
<figure markdown="span">
|
||||

|
||||
<figcaption>Self RAG: <a href="https://github.com/AkariAsai/self-rag">Source</a>
|
||||
</figcaption>
|
||||
</figure>
|
||||
|
||||
**[Offical Implementation](https://github.com/AkariAsai/self-rag)**
|
||||
|
||||
Self-RAG starts by generating a response without retrieving extra info if it's not needed. For questions that need more details, it retrieves to get the necessary information.
|
||||
|
||||
Here’s a code snippet for defining retriever using Langchain
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from langchain.text_splitter import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
|
||||
from langchain_community.document_loaders import WebBaseLoader
|
||||
from langchain_community.vectorstores import LanceDB
|
||||
from langchain_openai import OpenAIEmbeddings
|
||||
|
||||
urls = [
|
||||
"https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent/",
|
||||
"https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-03-15-prompt-engineering/",
|
||||
"https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-10-25-adv-attack-llm/",
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
docs = [WebBaseLoader(url).load() for url in urls]
|
||||
docs_list = [item for sublist in docs for item in sublist]
|
||||
|
||||
text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter.from_tiktoken_encoder(
|
||||
chunk_size=100, chunk_overlap=50
|
||||
)
|
||||
doc_splits = text_splitter.split_documents(docs_list)
|
||||
|
||||
# add documents in LanceDB
|
||||
vectorstore = LanceDB.from_documents(
|
||||
documents=doc_splits,
|
||||
embedding=OpenAIEmbeddings(),
|
||||
)
|
||||
retriever = vectorstore.as_retriever()
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Functions that grades the retrieved documents and if required formulates an improved query for better retrieval results
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
def grade_documents(state) -> Literal["generate", "rewrite"]:
|
||||
class grade(BaseModel):
|
||||
binary_score: str = Field(description="Relevance score 'yes' or 'no'")
|
||||
|
||||
model = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0, model="gpt-4-0125-preview", streaming=True)
|
||||
llm_with_tool = model.with_structured_output(grade)
|
||||
prompt = PromptTemplate(
|
||||
template="""You are a grader assessing relevance of a retrieved document to a user question. \n
|
||||
Here is the retrieved document: \n\n {context} \n\n
|
||||
Here is the user question: {question} \n
|
||||
If the document contains keyword(s) or semantic meaning related to the user question, grade it as relevant. \n
|
||||
Give a binary score 'yes' or 'no' score to indicate whether the document is relevant to the question.""",
|
||||
input_variables=["context", "question"],
|
||||
)
|
||||
chain = prompt | llm_with_tool
|
||||
|
||||
messages = state["messages"]
|
||||
last_message = messages[-1]
|
||||
question = messages[0].content
|
||||
docs = last_message.content
|
||||
|
||||
scored_result = chain.invoke({"question": question, "context": docs})
|
||||
score = scored_result.binary_score
|
||||
|
||||
return "generate" if score == "yes" else "rewrite"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def rewrite(state):
|
||||
messages = state["messages"]
|
||||
question = messages[0].content
|
||||
msg = [
|
||||
HumanMessage(
|
||||
content=f""" \n
|
||||
Look at the input and try to reason about the underlying semantic intent / meaning. \n
|
||||
Here is the initial question:
|
||||
\n ------- \n
|
||||
{question}
|
||||
\n ------- \n
|
||||
Formulate an improved question: """,
|
||||
)
|
||||
]
|
||||
model = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0, model="gpt-4-0125-preview", streaming=True)
|
||||
response = model.invoke(msg)
|
||||
return {"messages": [response]}
|
||||
```
|
||||
54
docs/src/rag/vanilla_rag.md
Normal file
54
docs/src/rag/vanilla_rag.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,54 @@
|
||||
**Vanilla RAG 🌱**
|
||||
====================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
RAG(Retrieval-Augmented Generation) works by finding documents related to the user's question, combining them with a prompt for a large language model (LLM), and then using the LLM to create more accurate and relevant answers.
|
||||
|
||||
Here’s a simple guide to building a RAG pipeline from scratch:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Data Loading**: Gather and load the documents you want to use for answering questions.
|
||||
|
||||
2. **Chunking and Embedding**: Split the documents into smaller chunks and convert them into numerical vectors (embeddings) that capture their meaning.
|
||||
|
||||
3. **Vector Store**: Create a LanceDB table to store and manage these vectors for quick access during retrieval.
|
||||
|
||||
4. **Retrieval & Prompt Preparation**: When a question is asked, find the most relevant document chunks from the table and prepare a prompt combining these chunks with the question.
|
||||
|
||||
5. **Answer Generation**: Send the prepared prompt to a LLM to generate a detailed and accurate answer.
|
||||
|
||||
<figure markdown="span">
|
||||

|
||||
<figcaption>Vanilla RAG
|
||||
</figcaption>
|
||||
</figure>
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/tutorials/RAG-from-Scratch/RAG_from_Scratch.ipynb)
|
||||
|
||||
Here’s a code snippet for defining a table with the [Embedding API](https://lancedb.github.io/lancedb/embeddings/embedding_functions/), which simplifies the process by handling embedding extraction and querying in one step.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import pandas as pd
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
from lancedb.pydantic import LanceModel, Vector
|
||||
from lancedb.embeddings import get_registry
|
||||
|
||||
db = lancedb.connect("/tmp/db")
|
||||
model = get_registry().get("sentence-transformers").create(name="BAAI/bge-small-en-v1.5", device="cpu")
|
||||
|
||||
class Docs(LanceModel):
|
||||
text: str = model.SourceField()
|
||||
vector: Vector(model.ndims()) = model.VectorField()
|
||||
|
||||
table = db.create_table("docs", schema=Docs)
|
||||
|
||||
# considering chunks are in list format
|
||||
df = pd.DataFrame({'text':chunks})
|
||||
table.add(data=df)
|
||||
|
||||
query = "What is issue date of lease?"
|
||||
actual = table.search(query).limit(1).to_list()[0]
|
||||
print(actual.text)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Check Colab for the complete code
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/lancedb/vectordb-recipes/blob/main/tutorials/RAG-from-Scratch/RAG_from_Scratch.ipynb)
|
||||
74
docs/src/reranking/answerdotai.md
Normal file
74
docs/src/reranking/answerdotai.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,74 @@
|
||||
# AnswersDotAI Rerankers
|
||||
|
||||
This integration allows using answersdotai's rerankers to rerank the search results. [Rerankers](https://github.com/AnswerDotAI/rerankers)
|
||||
A lightweight, low-dependency, unified API to use all common reranking and cross-encoder models.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note
|
||||
Supported Query Types: Hybrid, Vector, FTS
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import numpy
|
||||
import lancedb
|
||||
from lancedb.embeddings import get_registry
|
||||
from lancedb.pydantic import LanceModel, Vector
|
||||
from lancedb.rerankers import AnswerdotaiRerankers
|
||||
|
||||
embedder = get_registry().get("sentence-transformers").create()
|
||||
db = lancedb.connect("~/.lancedb")
|
||||
|
||||
class Schema(LanceModel):
|
||||
text: str = embedder.SourceField()
|
||||
vector: Vector(embedder.ndims()) = embedder.VectorField()
|
||||
|
||||
data = [
|
||||
{"text": "hello world"},
|
||||
{"text": "goodbye world"}
|
||||
]
|
||||
tbl = db.create_table("test", schema=Schema, mode="overwrite")
|
||||
tbl.add(data)
|
||||
reranker = AnswerdotaiRerankers()
|
||||
|
||||
# Run vector search with a reranker
|
||||
result = tbl.search("hello").rerank(reranker=reranker).to_list()
|
||||
|
||||
# Run FTS search with a reranker
|
||||
result = tbl.search("hello", query_type="fts").rerank(reranker=reranker).to_list()
|
||||
|
||||
# Run hybrid search with a reranker
|
||||
tbl.create_fts_index("text", replace=True)
|
||||
result = tbl.search("hello", query_type="hybrid").rerank(reranker=reranker).to_list()
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Accepted Arguments
|
||||
----------------
|
||||
| Argument | Type | Default | Description |
|
||||
| --- | --- | --- | --- |
|
||||
| `model_type` | `str` | `"colbert"` | The type of model to use. Supported model types can be found here - https://github.com/AnswerDotAI/rerankers |
|
||||
| `model_name` | `str` | `"answerdotai/answerai-colbert-small-v1"` | The name of the reranker model to use. |
|
||||
| `column` | `str` | `"text"` | The name of the column to use as input to the cross encoder model. |
|
||||
| `return_score` | str | `"relevance"` | Options are "relevance" or "all". The type of score to return. If "relevance", will return only the `_relevance_score. If "all" is supported, will return relevance score along with the vector and/or fts scores depending on query type |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Supported Scores for each query type
|
||||
You can specify the type of scores you want the reranker to return. The following are the supported scores for each query type:
|
||||
|
||||
### Hybrid Search
|
||||
|`return_score`| Status | Description |
|
||||
| --- | --- | --- |
|
||||
| `relevance` | ✅ Supported | Returns only have the `_relevance_score` column |
|
||||
| `all` | ❌ Not Supported | Returns have vector(`_distance`) and FTS(`score`) along with Hybrid Search score(`_relevance_score`) |
|
||||
|
||||
### Vector Search
|
||||
|`return_score`| Status | Description |
|
||||
| --- | --- | --- |
|
||||
| `relevance` | ✅ Supported | Returns only have the `_relevance_score` column |
|
||||
| `all` | ✅ Supported | Returns have vector(`_distance`) along with Hybrid Search score(`_relevance_score`) |
|
||||
|
||||
### FTS Search
|
||||
|`return_score`| Status | Description |
|
||||
| --- | --- | --- |
|
||||
| `relevance` | ✅ Supported | Returns only have the `_relevance_score` column |
|
||||
| `all` | ✅ Supported | Returns have FTS(`score`) along with Hybrid Search score(`_relevance_score`) |
|
||||
@@ -45,6 +45,23 @@ tbl.create_fts_index("text")
|
||||
result = tbl.query("hello", query_type="hybrid").rerank(reranker).to_list()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Multi-vector reranking
|
||||
Most rerankers support reranking based on multiple vectors. To rerank based on multiple vectors, you can pass a list of vectors to the `rerank` method. Here's an example of how to rerank based on multiple vector columns using the `CrossEncoderReranker`:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from lancedb.rerankers import CrossEncoderReranker
|
||||
|
||||
reranker = CrossEncoderReranker()
|
||||
|
||||
query = "hello"
|
||||
|
||||
res1 = table.search(query, vector_column_name="vector").limit(3)
|
||||
res2 = table.search(query, vector_column_name="text_vector").limit(3)
|
||||
res3 = table.search(query, vector_column_name="meta_vector").limit(3)
|
||||
|
||||
reranked = reranker.rerank_multivector([res1, res2, res3], deduplicate=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Available Rerankers
|
||||
LanceDB comes with some built-in rerankers. Here are some of the rerankers that are available in LanceDB:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -54,6 +71,8 @@ LanceDB comes with some built-in rerankers. Here are some of the rerankers that
|
||||
- [OpenAI Reranker](./openai.md)
|
||||
- [Linear Combination Reranker](./linear_combination.md)
|
||||
- [Jina Reranker](./jina.md)
|
||||
- [AnswerDotAI Rerankers](./answerdotai.md)
|
||||
- [Reciprocal Rank Fusion Reranker](./rrf.md)
|
||||
|
||||
## Creating Custom Rerankers
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
4
docs/src/studies/overview.md
Normal file
4
docs/src/studies/overview.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,4 @@
|
||||
This is a list of benchmarks and reports we've worked on at LanceDB. Some of these are continuously updated, while others are one-off reports.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Improve retrievers with hybrid search and reranking](https://blog.lancedb.com/hybrid-search-and-reranking-report/)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -19,6 +19,12 @@ excluded_globs = [
|
||||
"../src/hybrid_search/hybrid_search.md",
|
||||
"../src/reranking/*.md",
|
||||
"../src/guides/tuning_retrievers/*.md",
|
||||
"../src/embeddings/available_embedding_models/text_embedding_functions/*.md",
|
||||
"../src/embeddings/available_embedding_models/multimodal_embedding_functions/*.md",
|
||||
"../src/rag/*.md",
|
||||
"../src/rag/advanced_techniques/*.md"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
python_prefix = "py"
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -2,7 +2,7 @@
|
||||
name = "lancedb-jni"
|
||||
description = "JNI bindings for LanceDB"
|
||||
# TODO modify lancedb/Cargo.toml for version and dependencies
|
||||
version = "0.4.18"
|
||||
version = "0.10.0"
|
||||
edition.workspace = true
|
||||
repository.workspace = true
|
||||
readme.workspace = true
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -8,7 +8,7 @@
|
||||
<parent>
|
||||
<groupId>com.lancedb</groupId>
|
||||
<artifactId>lancedb-parent</artifactId>
|
||||
<version>0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
|
||||
<version>0.10.0</version>
|
||||
<relativePath>../pom.xml</relativePath>
|
||||
</parent>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -44,7 +44,7 @@
|
||||
<dependency>
|
||||
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
|
||||
<artifactId>junit-jupiter</artifactId>
|
||||
<scope>test</scope>
|
||||
<scope>test</scope>
|
||||
</dependency>
|
||||
</dependencies>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -68,7 +68,7 @@
|
||||
</goals>
|
||||
<configuration>
|
||||
<path>lancedb-jni</path>
|
||||
<!--<release>true</release>-->
|
||||
<release>true</release>
|
||||
<!-- Copy native libraries to target/classes for runtime access -->
|
||||
<copyTo>${project.build.directory}/classes/nativelib</copyTo>
|
||||
<copyWithPlatformDir>true</copyWithPlatformDir>
|
||||
|
||||
148
java/pom.xml
148
java/pom.xml
@@ -6,15 +6,28 @@
|
||||
|
||||
<groupId>com.lancedb</groupId>
|
||||
<artifactId>lancedb-parent</artifactId>
|
||||
<version>0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
|
||||
<version>0.10.0</version>
|
||||
<packaging>pom</packaging>
|
||||
|
||||
<name>Lance Parent</name>
|
||||
<name>LanceDB Parent</name>
|
||||
<description>LanceDB vector database Java API</description>
|
||||
<url>http://lancedb.com/</url>
|
||||
|
||||
<developers>
|
||||
<developer>
|
||||
<name>Lance DB Dev Group</name>
|
||||
<email>dev@lancedb.com</email>
|
||||
</developer>
|
||||
</developers>
|
||||
<licenses>
|
||||
<license>
|
||||
<name>The Apache Software License, Version 2.0</name>
|
||||
<url>http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0.txt</url>
|
||||
</license>
|
||||
</licenses>
|
||||
|
||||
<properties>
|
||||
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
|
||||
<maven.compiler.source>11</maven.compiler.source>
|
||||
<maven.compiler.target>11</maven.compiler.target>
|
||||
<arrow.version>15.0.0</arrow.version>
|
||||
</properties>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -22,6 +35,12 @@
|
||||
<module>core</module>
|
||||
</modules>
|
||||
|
||||
<scm>
|
||||
<connection>scm:git:https://github.com/lancedb/lancedb.git</connection>
|
||||
<developerConnection>scm:git:ssh://git@github.com/lancedb/lancedb.git</developerConnection>
|
||||
<url>https://github.com/lancedb/lancedb</url>
|
||||
</scm>
|
||||
|
||||
<dependencyManagement>
|
||||
<dependencies>
|
||||
<dependency>
|
||||
@@ -62,8 +81,45 @@
|
||||
</dependencies>
|
||||
</dependencyManagement>
|
||||
|
||||
<build>
|
||||
<distributionManagement>
|
||||
<snapshotRepository>
|
||||
<id>ossrh</id>
|
||||
<url>https://s01.oss.sonatype.org/content/repositories/snapshots</url>
|
||||
</snapshotRepository>
|
||||
<repository>
|
||||
<id>ossrh</id>
|
||||
<url>https://s01.oss.sonatype.org/service/local/staging/deploy/maven2/</url>
|
||||
</repository>
|
||||
</distributionManagement>
|
||||
|
||||
<build>
|
||||
<plugins>
|
||||
<plugin>
|
||||
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
|
||||
<artifactId>maven-source-plugin</artifactId>
|
||||
<version>2.2.1</version>
|
||||
<executions>
|
||||
<execution>
|
||||
<id>attach-sources</id>
|
||||
<goals>
|
||||
<goal>jar-no-fork</goal>
|
||||
</goals>
|
||||
</execution>
|
||||
</executions>
|
||||
</plugin>
|
||||
<plugin>
|
||||
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
|
||||
<artifactId>maven-javadoc-plugin</artifactId>
|
||||
<version>2.9.1</version>
|
||||
<executions>
|
||||
<execution>
|
||||
<id>attach-javadocs</id>
|
||||
<goals>
|
||||
<goal>jar</goal>
|
||||
</goals>
|
||||
</execution>
|
||||
</executions>
|
||||
</plugin>
|
||||
<plugin>
|
||||
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
|
||||
<artifactId>maven-checkstyle-plugin</artifactId>
|
||||
@@ -111,7 +167,8 @@
|
||||
<version>3.2.5</version>
|
||||
<configuration>
|
||||
<argLine>--add-opens=java.base/java.nio=ALL-UNNAMED</argLine>
|
||||
<forkNode implementation="org.apache.maven.plugin.surefire.extensions.SurefireForkNodeFactory"/>
|
||||
<forkNode
|
||||
implementation="org.apache.maven.plugin.surefire.extensions.SurefireForkNodeFactory" />
|
||||
<useSystemClassLoader>false</useSystemClassLoader>
|
||||
</configuration>
|
||||
</plugin>
|
||||
@@ -126,4 +183,83 @@
|
||||
</plugins>
|
||||
</pluginManagement>
|
||||
</build>
|
||||
|
||||
<profiles>
|
||||
<profile>
|
||||
<id>jdk8</id>
|
||||
<activation>
|
||||
<jdk>[1.8,1.8.999]</jdk>
|
||||
</activation>
|
||||
<properties>
|
||||
<maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source>
|
||||
<maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target>
|
||||
</properties>
|
||||
</profile>
|
||||
<profile>
|
||||
<id>jdk11+</id>
|
||||
<activation>
|
||||
<jdk>[11,)</jdk>
|
||||
</activation>
|
||||
<properties>
|
||||
<maven.compiler.source>11</maven.compiler.source>
|
||||
<maven.compiler.target>11</maven.compiler.target>
|
||||
</properties>
|
||||
<build>
|
||||
<plugins>
|
||||
<plugin>
|
||||
<artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
|
||||
<version>3.2.5</version>
|
||||
<configuration>
|
||||
<argLine>--add-opens=java.base/java.nio=ALL-UNNAMED</argLine>
|
||||
<forkNode
|
||||
implementation="org.apache.maven.plugin.surefire.extensions.SurefireForkNodeFactory" />
|
||||
<useSystemClassLoader>false</useSystemClassLoader>
|
||||
</configuration>
|
||||
</plugin>
|
||||
</plugins>
|
||||
</build>
|
||||
</profile>
|
||||
<profile>
|
||||
<id>deploy-to-ossrh</id>
|
||||
<build>
|
||||
<plugins>
|
||||
<plugin>
|
||||
<groupId>org.sonatype.central</groupId>
|
||||
<artifactId>central-publishing-maven-plugin</artifactId>
|
||||
<version>0.4.0</version>
|
||||
<extensions>true</extensions>
|
||||
<configuration>
|
||||
<publishingServerId>ossrh</publishingServerId>
|
||||
<tokenAuth>true</tokenAuth>
|
||||
</configuration>
|
||||
</plugin>
|
||||
<plugin>
|
||||
<groupId>org.sonatype.plugins</groupId>
|
||||
<artifactId>nexus-staging-maven-plugin</artifactId>
|
||||
<version>1.6.13</version>
|
||||
<extensions>true</extensions>
|
||||
<configuration>
|
||||
<serverId>ossrh</serverId>
|
||||
<nexusUrl>https://s01.oss.sonatype.org/</nexusUrl>
|
||||
<autoReleaseAfterClose>true</autoReleaseAfterClose>
|
||||
</configuration>
|
||||
</plugin>
|
||||
<plugin>
|
||||
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
|
||||
<artifactId>maven-gpg-plugin</artifactId>
|
||||
<version>1.5</version>
|
||||
<executions>
|
||||
<execution>
|
||||
<id>sign-artifacts</id>
|
||||
<phase>verify</phase>
|
||||
<goals>
|
||||
<goal>sign</goal>
|
||||
</goals>
|
||||
</execution>
|
||||
</executions>
|
||||
</plugin>
|
||||
</plugins>
|
||||
</build>
|
||||
</profile>
|
||||
</profiles>
|
||||
</project>
|
||||
|
||||
4
node/package-lock.json
generated
4
node/package-lock.json
generated
@@ -1,12 +1,12 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "vectordb",
|
||||
"version": "0.10.0-beta.0",
|
||||
"version": "0.10.0",
|
||||
"lockfileVersion": 3,
|
||||
"requires": true,
|
||||
"packages": {
|
||||
"": {
|
||||
"name": "vectordb",
|
||||
"version": "0.10.0-beta.0",
|
||||
"version": "0.10.0",
|
||||
"cpu": [
|
||||
"x64",
|
||||
"arm64"
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "vectordb",
|
||||
"version": "0.10.0-beta.0",
|
||||
"version": "0.10.0",
|
||||
"description": " Serverless, low-latency vector database for AI applications",
|
||||
"main": "dist/index.js",
|
||||
"types": "dist/index.d.ts",
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -60,7 +60,7 @@ export {
|
||||
type MakeArrowTableOptions
|
||||
} from "./arrow";
|
||||
|
||||
const defaultAwsRegion = "us-west-2";
|
||||
const defaultAwsRegion = "us-east-1";
|
||||
|
||||
const defaultRequestTimeout = 10_000
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -111,7 +111,7 @@ export interface ConnectionOptions {
|
||||
*/
|
||||
apiKey?: string
|
||||
|
||||
/** Region to connect */
|
||||
/** Region to connect. Default is 'us-east-1' */
|
||||
region?: string
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
@@ -197,28 +197,31 @@ export async function connect(
|
||||
export async function connect(
|
||||
arg: string | Partial<ConnectionOptions>
|
||||
): Promise<Connection> {
|
||||
let opts: ConnectionOptions;
|
||||
let partOpts: Partial<ConnectionOptions>;
|
||||
if (typeof arg === "string") {
|
||||
opts = { uri: arg };
|
||||
partOpts = { uri: arg };
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
const keys = Object.keys(arg);
|
||||
if (keys.length === 1 && keys[0] === "uri" && typeof arg.uri === "string") {
|
||||
opts = { uri: arg.uri };
|
||||
partOpts = { uri: arg.uri };
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
opts = Object.assign(
|
||||
{
|
||||
uri: "",
|
||||
awsCredentials: undefined,
|
||||
awsRegion: defaultAwsRegion,
|
||||
apiKey: undefined,
|
||||
region: defaultAwsRegion,
|
||||
timeout: defaultRequestTimeout
|
||||
},
|
||||
arg
|
||||
);
|
||||
partOpts = arg;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
let defaultRegion = process.env.AWS_REGION ?? process.env.AWS_DEFAULT_REGION;
|
||||
defaultRegion = (defaultRegion ?? "").trim() !== "" ? defaultRegion : defaultAwsRegion;
|
||||
|
||||
const opts: ConnectionOptions = {
|
||||
uri: partOpts.uri ?? "",
|
||||
awsCredentials: partOpts.awsCredentials ?? undefined,
|
||||
awsRegion: partOpts.awsRegion ?? defaultRegion,
|
||||
apiKey: partOpts.apiKey ?? undefined,
|
||||
region: partOpts.region ?? defaultRegion,
|
||||
timeout: partOpts.timeout ?? defaultRequestTimeout,
|
||||
readConsistencyInterval: partOpts.readConsistencyInterval ?? undefined,
|
||||
storageOptions: partOpts.storageOptions ?? undefined
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (opts.uri.startsWith("db://")) {
|
||||
// Remote connection
|
||||
return new RemoteConnection(opts);
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -82,7 +82,7 @@ async function callWithMiddlewares (
|
||||
|
||||
interface MiddlewareInvocationOptions {
|
||||
responseType?: ResponseType
|
||||
timeout?: number,
|
||||
timeout?: number
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
@@ -130,8 +130,8 @@ export class HttpLancedbClient {
|
||||
url: string,
|
||||
apiKey: string,
|
||||
timeout?: number,
|
||||
private readonly _dbName?: string,
|
||||
|
||||
private readonly _dbName?: string
|
||||
|
||||
) {
|
||||
this._url = url
|
||||
this._apiKey = () => apiKey
|
||||
@@ -237,7 +237,7 @@ export class HttpLancedbClient {
|
||||
try {
|
||||
response = await callWithMiddlewares(req, this._middlewares, {
|
||||
responseType,
|
||||
timeout: this._timeout,
|
||||
timeout: this._timeout
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
// return response
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -93,6 +93,30 @@ describe("LanceDB client", function () {
|
||||
const con = await lancedb.connect(uri);
|
||||
assert.deepEqual(await con.tableNames(), ["vectors"]);
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
it("read consistency level", async function () {
|
||||
const uri = await createTestDB();
|
||||
const db1 = await lancedb.connect({ uri });
|
||||
const table1 = await db1.openTable("vectors");
|
||||
|
||||
const db2 = await lancedb.connect({
|
||||
uri,
|
||||
readConsistencyInterval: 0
|
||||
})
|
||||
const table2 = await db2.openTable("vectors");
|
||||
|
||||
assert.equal(await table2.countRows(), 2);
|
||||
await table1.add([
|
||||
{
|
||||
id: 3,
|
||||
name: 'name_2',
|
||||
price: 10,
|
||||
is_active: true,
|
||||
vector: [0, 0.1]
|
||||
}
|
||||
]);
|
||||
assert.equal(await table2.countRows(), 3);
|
||||
});
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
describe("when querying an existing dataset", function () {
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -12,9 +12,11 @@
|
||||
// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
// limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
import { readdirSync } from "fs";
|
||||
import { Field, Float64, Schema } from "apache-arrow";
|
||||
import * as tmp from "tmp";
|
||||
import { Connection, Table, connect } from "../lancedb";
|
||||
import { LocalTable } from "../lancedb/table";
|
||||
|
||||
describe("when connecting", () => {
|
||||
let tmpDir: tmp.DirResult;
|
||||
@@ -105,7 +107,7 @@ describe("given a connection", () => {
|
||||
const data = [...Array(10000).keys()].map((i) => ({ id: i }));
|
||||
|
||||
// Create in v1 mode
|
||||
let table = await db.createTable("test", data);
|
||||
let table = await db.createTable("test", data, { useLegacyFormat: true });
|
||||
|
||||
const isV2 = async (table: Table) => {
|
||||
const data = await table.query().toArrow({ maxBatchLength: 100000 });
|
||||
@@ -116,7 +118,7 @@ describe("given a connection", () => {
|
||||
await expect(isV2(table)).resolves.toBe(false);
|
||||
|
||||
// Create in v2 mode
|
||||
table = await db.createTable("test_v2", data, { useLegacyFormat: false });
|
||||
table = await db.createTable("test_v2", data);
|
||||
|
||||
await expect(isV2(table)).resolves.toBe(true);
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -134,4 +136,57 @@ describe("given a connection", () => {
|
||||
await table.add(data);
|
||||
await expect(isV2(table)).resolves.toBe(true);
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
it("should be able to create tables with V2 manifest paths", async () => {
|
||||
const db = await connect(tmpDir.name);
|
||||
let table = (await db.createEmptyTable(
|
||||
"test_manifest_paths_v2_empty",
|
||||
new Schema([new Field("id", new Float64(), true)]),
|
||||
{
|
||||
enableV2ManifestPaths: true,
|
||||
},
|
||||
)) as LocalTable;
|
||||
expect(await table.usesV2ManifestPaths()).toBe(true);
|
||||
|
||||
let manifestDir =
|
||||
tmpDir.name + "/test_manifest_paths_v2_empty.lance/_versions";
|
||||
readdirSync(manifestDir).forEach((file) => {
|
||||
expect(file).toMatch(/^\d{20}\.manifest$/);
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
table = (await db.createTable("test_manifest_paths_v2", [{ id: 1 }], {
|
||||
enableV2ManifestPaths: true,
|
||||
})) as LocalTable;
|
||||
expect(await table.usesV2ManifestPaths()).toBe(true);
|
||||
manifestDir = tmpDir.name + "/test_manifest_paths_v2.lance/_versions";
|
||||
readdirSync(manifestDir).forEach((file) => {
|
||||
expect(file).toMatch(/^\d{20}\.manifest$/);
|
||||
});
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
it("should be able to migrate tables to the V2 manifest paths", async () => {
|
||||
const db = await connect(tmpDir.name);
|
||||
const table = (await db.createEmptyTable(
|
||||
"test_manifest_path_migration",
|
||||
new Schema([new Field("id", new Float64(), true)]),
|
||||
{
|
||||
enableV2ManifestPaths: false,
|
||||
},
|
||||
)) as LocalTable;
|
||||
|
||||
expect(await table.usesV2ManifestPaths()).toBe(false);
|
||||
|
||||
const manifestDir =
|
||||
tmpDir.name + "/test_manifest_path_migration.lance/_versions";
|
||||
readdirSync(manifestDir).forEach((file) => {
|
||||
expect(file).toMatch(/^\d\.manifest$/);
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
await table.migrateManifestPathsV2();
|
||||
expect(await table.usesV2ManifestPaths()).toBe(true);
|
||||
|
||||
readdirSync(manifestDir).forEach((file) => {
|
||||
expect(file).toMatch(/^\d{20}\.manifest$/);
|
||||
});
|
||||
});
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -396,6 +396,10 @@ describe("When creating an index", () => {
|
||||
.toArrow();
|
||||
expect(rst2.numRows).toBe(2);
|
||||
expect(rst.toString()).toEqual(rst2.toString());
|
||||
|
||||
// test offset
|
||||
rst = await tbl.query().limit(2).offset(1).nearestTo(queryVec).toArrow();
|
||||
expect(rst.numRows).toBe(1);
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
it("should allow parameters to be specified", async () => {
|
||||
@@ -440,6 +444,26 @@ describe("When creating an index", () => {
|
||||
expect(fs.readdirSync(indexDir)).toHaveLength(1);
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
test("create a hnswPq index", async () => {
|
||||
await tbl.createIndex("vec", {
|
||||
config: Index.hnswPq({
|
||||
numPartitions: 10,
|
||||
}),
|
||||
});
|
||||
const indexDir = path.join(tmpDir.name, "test.lance", "_indices");
|
||||
expect(fs.readdirSync(indexDir)).toHaveLength(1);
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
test("create a HnswSq index", async () => {
|
||||
await tbl.createIndex("vec", {
|
||||
config: Index.hnswSq({
|
||||
numPartitions: 10,
|
||||
}),
|
||||
});
|
||||
const indexDir = path.join(tmpDir.name, "test.lance", "_indices");
|
||||
expect(fs.readdirSync(indexDir)).toHaveLength(1);
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
test("create a label list index", async () => {
|
||||
await tbl.createIndex("tags", {
|
||||
config: Index.labelList(),
|
||||
@@ -840,6 +864,38 @@ describe.each([arrow13, arrow14, arrow15, arrow16, arrow17])(
|
||||
expect(results[0].text).toBe(data[0].text);
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
test("full text search without positions", async () => {
|
||||
const db = await connect(tmpDir.name);
|
||||
const data = [
|
||||
{ text: "hello world", vector: [0.1, 0.2, 0.3] },
|
||||
{ text: "goodbye world", vector: [0.4, 0.5, 0.6] },
|
||||
];
|
||||
const table = await db.createTable("test", data);
|
||||
await table.createIndex("text", {
|
||||
config: Index.fts({ withPosition: false }),
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
const results = await table.search("hello").toArray();
|
||||
expect(results[0].text).toBe(data[0].text);
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
test("full text search phrase query", async () => {
|
||||
const db = await connect(tmpDir.name);
|
||||
const data = [
|
||||
{ text: "hello world", vector: [0.1, 0.2, 0.3] },
|
||||
{ text: "goodbye world", vector: [0.4, 0.5, 0.6] },
|
||||
];
|
||||
const table = await db.createTable("test", data);
|
||||
await table.createIndex("text", {
|
||||
config: Index.fts(),
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
const results = await table.search("world").toArray();
|
||||
expect(results.length).toBe(2);
|
||||
const phraseResults = await table.search('"hello world"').toArray();
|
||||
expect(phraseResults.length).toBe(1);
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
test.each([
|
||||
[0.4, 0.5, 0.599], // number[]
|
||||
Float32Array.of(0.4, 0.5, 0.599), // Float32Array
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -44,20 +44,30 @@ export interface CreateTableOptions {
|
||||
* The available options are described at https://lancedb.github.io/lancedb/guides/storage/
|
||||
*/
|
||||
storageOptions?: Record<string, string>;
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* The version of the data storage format to use.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* The default is `legacy`, which is Lance format v1.
|
||||
* `stable` is the new format, which is Lance format v2.
|
||||
* The default is `stable`.
|
||||
* Set to "legacy" to use the old format.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
dataStorageVersion?: string;
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Use the new V2 manifest paths. These paths provide more efficient
|
||||
* opening of datasets with many versions on object stores. WARNING:
|
||||
* turning this on will make the dataset unreadable for older versions
|
||||
* of LanceDB (prior to 0.10.0). To migrate an existing dataset, instead
|
||||
* use the {@link LocalTable#migrateManifestPathsV2} method.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
enableV2ManifestPaths?: boolean;
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* If true then data files will be written with the legacy format
|
||||
*
|
||||
* The default is true while the new format is in beta
|
||||
* The default is false.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Deprecated.
|
||||
* Deprecated. Use data storage version instead.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
useLegacyFormat?: boolean;
|
||||
schema?: SchemaLike;
|
||||
@@ -257,7 +267,7 @@ export class LocalConnection extends Connection {
|
||||
throw new Error("data is required");
|
||||
}
|
||||
const { buf, mode } = await Table.parseTableData(data, options);
|
||||
let dataStorageVersion = "legacy";
|
||||
let dataStorageVersion = "stable";
|
||||
if (options?.dataStorageVersion !== undefined) {
|
||||
dataStorageVersion = options.dataStorageVersion;
|
||||
} else if (options?.useLegacyFormat !== undefined) {
|
||||
@@ -270,6 +280,7 @@ export class LocalConnection extends Connection {
|
||||
mode,
|
||||
cleanseStorageOptions(options?.storageOptions),
|
||||
dataStorageVersion,
|
||||
options?.enableV2ManifestPaths,
|
||||
);
|
||||
|
||||
return new LocalTable(innerTable);
|
||||
@@ -293,7 +304,7 @@ export class LocalConnection extends Connection {
|
||||
metadata = registry.getTableMetadata([embeddingFunction]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
let dataStorageVersion = "legacy";
|
||||
let dataStorageVersion = "stable";
|
||||
if (options?.dataStorageVersion !== undefined) {
|
||||
dataStorageVersion = options.dataStorageVersion;
|
||||
} else if (options?.useLegacyFormat !== undefined) {
|
||||
@@ -308,6 +319,7 @@ export class LocalConnection extends Connection {
|
||||
mode,
|
||||
cleanseStorageOptions(options?.storageOptions),
|
||||
dataStorageVersion,
|
||||
options?.enableV2ManifestPaths,
|
||||
);
|
||||
return new LocalTable(innerTable);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -113,6 +113,234 @@ export interface IvfPqOptions {
|
||||
sampleRate?: number;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Options to create an `HNSW_PQ` index
|
||||
*/
|
||||
export interface HnswPqOptions {
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* The distance metric used to train the index.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Default value is "l2".
|
||||
*
|
||||
* The following distance types are available:
|
||||
*
|
||||
* "l2" - Euclidean distance. This is a very common distance metric that
|
||||
* accounts for both magnitude and direction when determining the distance
|
||||
* between vectors. L2 distance has a range of [0, ∞).
|
||||
*
|
||||
* "cosine" - Cosine distance. Cosine distance is a distance metric
|
||||
* calculated from the cosine similarity between two vectors. Cosine
|
||||
* similarity is a measure of similarity between two non-zero vectors of an
|
||||
* inner product space. It is defined to equal the cosine of the angle
|
||||
* between them. Unlike L2, the cosine distance is not affected by the
|
||||
* magnitude of the vectors. Cosine distance has a range of [0, 2].
|
||||
*
|
||||
* "dot" - Dot product. Dot distance is the dot product of two vectors. Dot
|
||||
* distance has a range of (-∞, ∞). If the vectors are normalized (i.e. their
|
||||
* L2 norm is 1), then dot distance is equivalent to the cosine distance.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
distanceType?: "l2" | "cosine" | "dot";
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* The number of IVF partitions to create.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* For HNSW, we recommend a small number of partitions. Setting this to 1 works
|
||||
* well for most tables. For very large tables, training just one HNSW graph
|
||||
* will require too much memory. Each partition becomes its own HNSW graph, so
|
||||
* setting this value higher reduces the peak memory use of training.
|
||||
*
|
||||
*/
|
||||
numPartitions?: number;
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Number of sub-vectors of PQ.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* This value controls how much the vector is compressed during the quantization step.
|
||||
* The more sub vectors there are the less the vector is compressed. The default is
|
||||
* the dimension of the vector divided by 16. If the dimension is not evenly divisible
|
||||
* by 16 we use the dimension divded by 8.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* The above two cases are highly preferred. Having 8 or 16 values per subvector allows
|
||||
* us to use efficient SIMD instructions.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* If the dimension is not visible by 8 then we use 1 subvector. This is not ideal and
|
||||
* will likely result in poor performance.
|
||||
*
|
||||
*/
|
||||
numSubVectors?: number;
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Max iterations to train kmeans.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* The default value is 50.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* When training an IVF index we use kmeans to calculate the partitions. This parameter
|
||||
* controls how many iterations of kmeans to run.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Increasing this might improve the quality of the index but in most cases the parameter
|
||||
* is unused because kmeans will converge with fewer iterations. The parameter is only
|
||||
* used in cases where kmeans does not appear to converge. In those cases it is unlikely
|
||||
* that setting this larger will lead to the index converging anyways.
|
||||
*
|
||||
*/
|
||||
maxIterations?: number;
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* The rate used to calculate the number of training vectors for kmeans.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Default value is 256.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* When an IVF index is trained, we need to calculate partitions. These are groups
|
||||
* of vectors that are similar to each other. To do this we use an algorithm called kmeans.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Running kmeans on a large dataset can be slow. To speed this up we run kmeans on a
|
||||
* random sample of the data. This parameter controls the size of the sample. The total
|
||||
* number of vectors used to train the index is `sample_rate * num_partitions`.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Increasing this value might improve the quality of the index but in most cases the
|
||||
* default should be sufficient.
|
||||
*
|
||||
*/
|
||||
sampleRate?: number;
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* The number of neighbors to select for each vector in the HNSW graph.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* The default value is 20.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* This value controls the tradeoff between search speed and accuracy.
|
||||
* The higher the value the more accurate the search but the slower it will be.
|
||||
*
|
||||
*/
|
||||
m?: number;
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* The number of candidates to evaluate during the construction of the HNSW graph.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* The default value is 300.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* This value controls the tradeoff between build speed and accuracy.
|
||||
* The higher the value the more accurate the build but the slower it will be.
|
||||
* 150 to 300 is the typical range. 100 is a minimum for good quality search
|
||||
* results. In most cases, there is no benefit to setting this higher than 500.
|
||||
* This value should be set to a value that is not less than `ef` in the search phase.
|
||||
*
|
||||
*/
|
||||
efConstruction?: number;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Options to create an `HNSW_SQ` index
|
||||
*/
|
||||
export interface HnswSqOptions {
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* The distance metric used to train the index.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Default value is "l2".
|
||||
*
|
||||
* The following distance types are available:
|
||||
*
|
||||
* "l2" - Euclidean distance. This is a very common distance metric that
|
||||
* accounts for both magnitude and direction when determining the distance
|
||||
* between vectors. L2 distance has a range of [0, ∞).
|
||||
*
|
||||
* "cosine" - Cosine distance. Cosine distance is a distance metric
|
||||
* calculated from the cosine similarity between two vectors. Cosine
|
||||
* similarity is a measure of similarity between two non-zero vectors of an
|
||||
* inner product space. It is defined to equal the cosine of the angle
|
||||
* between them. Unlike L2, the cosine distance is not affected by the
|
||||
* magnitude of the vectors. Cosine distance has a range of [0, 2].
|
||||
*
|
||||
* "dot" - Dot product. Dot distance is the dot product of two vectors. Dot
|
||||
* distance has a range of (-∞, ∞). If the vectors are normalized (i.e. their
|
||||
* L2 norm is 1), then dot distance is equivalent to the cosine distance.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
distanceType?: "l2" | "cosine" | "dot";
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* The number of IVF partitions to create.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* For HNSW, we recommend a small number of partitions. Setting this to 1 works
|
||||
* well for most tables. For very large tables, training just one HNSW graph
|
||||
* will require too much memory. Each partition becomes its own HNSW graph, so
|
||||
* setting this value higher reduces the peak memory use of training.
|
||||
*
|
||||
*/
|
||||
numPartitions?: number;
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Max iterations to train kmeans.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* The default value is 50.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* When training an IVF index we use kmeans to calculate the partitions. This parameter
|
||||
* controls how many iterations of kmeans to run.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Increasing this might improve the quality of the index but in most cases the parameter
|
||||
* is unused because kmeans will converge with fewer iterations. The parameter is only
|
||||
* used in cases where kmeans does not appear to converge. In those cases it is unlikely
|
||||
* that setting this larger will lead to the index converging anyways.
|
||||
*
|
||||
*/
|
||||
maxIterations?: number;
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* The rate used to calculate the number of training vectors for kmeans.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Default value is 256.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* When an IVF index is trained, we need to calculate partitions. These are groups
|
||||
* of vectors that are similar to each other. To do this we use an algorithm called kmeans.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Running kmeans on a large dataset can be slow. To speed this up we run kmeans on a
|
||||
* random sample of the data. This parameter controls the size of the sample. The total
|
||||
* number of vectors used to train the index is `sample_rate * num_partitions`.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Increasing this value might improve the quality of the index but in most cases the
|
||||
* default should be sufficient.
|
||||
*
|
||||
*/
|
||||
sampleRate?: number;
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* The number of neighbors to select for each vector in the HNSW graph.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* The default value is 20.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* This value controls the tradeoff between search speed and accuracy.
|
||||
* The higher the value the more accurate the search but the slower it will be.
|
||||
*
|
||||
*/
|
||||
m?: number;
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* The number of candidates to evaluate during the construction of the HNSW graph.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* The default value is 300.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* This value controls the tradeoff between build speed and accuracy.
|
||||
* The higher the value the more accurate the build but the slower it will be.
|
||||
* 150 to 300 is the typical range. 100 is a minimum for good quality search
|
||||
* results. In most cases, there is no benefit to setting this higher than 500.
|
||||
* This value should be set to a value that is not less than `ef` in the search phase.
|
||||
*
|
||||
*/
|
||||
efConstruction?: number;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Options to create a full text search index
|
||||
*/
|
||||
export interface FtsOptions {
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Whether to build the index with positions.
|
||||
* True by default.
|
||||
* If set to false, the index will not store the positions of the tokens in the text,
|
||||
* which will make the index smaller and faster to build, but will not support phrase queries.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
withPosition?: boolean;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export class Index {
|
||||
private readonly inner: LanceDbIndex;
|
||||
private constructor(inner: LanceDbIndex) {
|
||||
@@ -211,8 +439,53 @@ export class Index {
|
||||
*
|
||||
* For now, the full text search index only supports English, and doesn't support phrase search.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
static fts() {
|
||||
return new Index(LanceDbIndex.fts());
|
||||
static fts(options?: Partial<FtsOptions>) {
|
||||
return new Index(LanceDbIndex.fts(options?.withPosition));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Create a hnswPq index
|
||||
*
|
||||
* HNSW-PQ stands for Hierarchical Navigable Small World - Product Quantization.
|
||||
* It is a variant of the HNSW algorithm that uses product quantization to compress
|
||||
* the vectors.
|
||||
*
|
||||
*/
|
||||
static hnswPq(options?: Partial<HnswPqOptions>) {
|
||||
return new Index(
|
||||
LanceDbIndex.hnswPq(
|
||||
options?.distanceType,
|
||||
options?.numPartitions,
|
||||
options?.numSubVectors,
|
||||
options?.maxIterations,
|
||||
options?.sampleRate,
|
||||
options?.m,
|
||||
options?.efConstruction,
|
||||
),
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Create a hnswSq index
|
||||
*
|
||||
* HNSW-SQ stands for Hierarchical Navigable Small World - Scalar Quantization.
|
||||
* It is a variant of the HNSW algorithm that uses scalar quantization to compress
|
||||
* the vectors.
|
||||
*
|
||||
*/
|
||||
static hnswSq(options?: Partial<HnswSqOptions>) {
|
||||
return new Index(
|
||||
LanceDbIndex.hnswSq(
|
||||
options?.distanceType,
|
||||
options?.numPartitions,
|
||||
options?.maxIterations,
|
||||
options?.sampleRate,
|
||||
options?.m,
|
||||
options?.efConstruction,
|
||||
),
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -234,6 +234,11 @@ export class QueryBase<NativeQueryType extends NativeQuery | NativeVectorQuery>
|
||||
return this;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
offset(offset: number): this {
|
||||
this.doCall((inner: NativeQueryType) => inner.offset(offset));
|
||||
return this;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
protected nativeExecute(
|
||||
options?: Partial<QueryExecutionOptions>,
|
||||
): Promise<NativeBatchIterator> {
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -697,4 +697,31 @@ export class LocalTable extends Table {
|
||||
on = Array.isArray(on) ? on : [on];
|
||||
return new MergeInsertBuilder(this.inner.mergeInsert(on));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Check if the table uses the new manifest path scheme.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* This function will return true if the table uses the V2 manifest
|
||||
* path scheme.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
async usesV2ManifestPaths(): Promise<boolean> {
|
||||
return await this.inner.usesV2ManifestPaths();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Migrate the table to use the new manifest path scheme.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* This function will rename all V1 manifests to V2 manifest paths.
|
||||
* These paths provide more efficient opening of datasets with many versions
|
||||
* on object stores.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* This function is idempotent, and can be run multiple times without
|
||||
* changing the state of the object store.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* However, it should not be run while other concurrent operations are happening.
|
||||
* And it should also run until completion before resuming other operations.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
async migrateManifestPathsV2(): Promise<void> {
|
||||
await this.inner.migrateManifestPathsV2();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "@lancedb/lancedb-darwin-arm64",
|
||||
"version": "0.10.0-beta.0",
|
||||
"version": "0.10.0",
|
||||
"os": ["darwin"],
|
||||
"cpu": ["arm64"],
|
||||
"main": "lancedb.darwin-arm64.node",
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "@lancedb/lancedb-darwin-x64",
|
||||
"version": "0.10.0-beta.0",
|
||||
"version": "0.10.0",
|
||||
"os": ["darwin"],
|
||||
"cpu": ["x64"],
|
||||
"main": "lancedb.darwin-x64.node",
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "@lancedb/lancedb-linux-arm64-gnu",
|
||||
"version": "0.10.0-beta.0",
|
||||
"version": "0.10.0",
|
||||
"os": ["linux"],
|
||||
"cpu": ["arm64"],
|
||||
"main": "lancedb.linux-arm64-gnu.node",
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "@lancedb/lancedb-linux-x64-gnu",
|
||||
"version": "0.10.0-beta.0",
|
||||
"version": "0.10.0",
|
||||
"os": ["linux"],
|
||||
"cpu": ["x64"],
|
||||
"main": "lancedb.linux-x64-gnu.node",
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "@lancedb/lancedb-win32-x64-msvc",
|
||||
"version": "0.10.0-beta.0",
|
||||
"version": "0.10.0",
|
||||
"os": ["win32"],
|
||||
"cpu": ["x64"],
|
||||
"main": "lancedb.win32-x64-msvc.node",
|
||||
|
||||
4
nodejs/package-lock.json
generated
4
nodejs/package-lock.json
generated
@@ -1,12 +1,12 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "@lancedb/lancedb",
|
||||
"version": "0.8.0",
|
||||
"version": "0.10.0-beta.1",
|
||||
"lockfileVersion": 3,
|
||||
"requires": true,
|
||||
"packages": {
|
||||
"": {
|
||||
"name": "@lancedb/lancedb",
|
||||
"version": "0.8.0",
|
||||
"version": "0.10.0-beta.1",
|
||||
"cpu": [
|
||||
"x64",
|
||||
"arm64"
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -10,7 +10,7 @@
|
||||
"vector database",
|
||||
"ann"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "0.10.0-beta.0",
|
||||
"version": "0.10.0",
|
||||
"main": "dist/index.js",
|
||||
"exports": {
|
||||
".": "./dist/index.js",
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -124,11 +124,13 @@ impl Connection {
|
||||
mode: String,
|
||||
storage_options: Option<HashMap<String, String>>,
|
||||
data_storage_options: Option<String>,
|
||||
enable_v2_manifest_paths: Option<bool>,
|
||||
) -> napi::Result<Table> {
|
||||
let batches = ipc_file_to_batches(buf.to_vec())
|
||||
.map_err(|e| napi::Error::from_reason(format!("Failed to read IPC file: {}", e)))?;
|
||||
let mode = Self::parse_create_mode_str(&mode)?;
|
||||
let mut builder = self.get_inner()?.create_table(&name, batches).mode(mode);
|
||||
|
||||
if let Some(storage_options) = storage_options {
|
||||
for (key, value) in storage_options {
|
||||
builder = builder.storage_option(key, value);
|
||||
@@ -140,6 +142,9 @@ impl Connection {
|
||||
.map_err(|e| napi::Error::from_reason(format!("{}", e)))?,
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
if let Some(enable_v2_manifest_paths) = enable_v2_manifest_paths {
|
||||
builder = builder.enable_v2_manifest_paths(enable_v2_manifest_paths);
|
||||
}
|
||||
let tbl = builder
|
||||
.execute()
|
||||
.await
|
||||
@@ -155,6 +160,7 @@ impl Connection {
|
||||
mode: String,
|
||||
storage_options: Option<HashMap<String, String>>,
|
||||
data_storage_options: Option<String>,
|
||||
enable_v2_manifest_paths: Option<bool>,
|
||||
) -> napi::Result<Table> {
|
||||
let schema = ipc_file_to_schema(schema_buf.to_vec()).map_err(|e| {
|
||||
napi::Error::from_reason(format!("Failed to marshal schema from JS to Rust: {}", e))
|
||||
@@ -175,6 +181,9 @@ impl Connection {
|
||||
.map_err(|e| napi::Error::from_reason(format!("{}", e)))?,
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
if let Some(enable_v2_manifest_paths) = enable_v2_manifest_paths {
|
||||
builder = builder.enable_v2_manifest_paths(enable_v2_manifest_paths);
|
||||
}
|
||||
let tbl = builder
|
||||
.execute()
|
||||
.await
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -15,7 +15,7 @@
|
||||
use std::sync::Mutex;
|
||||
|
||||
use lancedb::index::scalar::{BTreeIndexBuilder, FtsIndexBuilder};
|
||||
use lancedb::index::vector::IvfPqIndexBuilder;
|
||||
use lancedb::index::vector::{IvfHnswPqIndexBuilder, IvfHnswSqIndexBuilder, IvfPqIndexBuilder};
|
||||
use lancedb::index::Index as LanceDbIndex;
|
||||
use napi_derive::napi;
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -92,9 +92,85 @@ impl Index {
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#[napi(factory)]
|
||||
pub fn fts() -> Self {
|
||||
pub fn fts(with_position: Option<bool>) -> Self {
|
||||
let mut opts = FtsIndexBuilder::default();
|
||||
if let Some(with_position) = with_position {
|
||||
opts = opts.with_position(with_position);
|
||||
}
|
||||
Self {
|
||||
inner: Mutex::new(Some(LanceDbIndex::FTS(FtsIndexBuilder::default()))),
|
||||
inner: Mutex::new(Some(LanceDbIndex::FTS(opts))),
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#[napi(factory)]
|
||||
pub fn hnsw_pq(
|
||||
distance_type: Option<String>,
|
||||
num_partitions: Option<u32>,
|
||||
num_sub_vectors: Option<u32>,
|
||||
max_iterations: Option<u32>,
|
||||
sample_rate: Option<u32>,
|
||||
m: Option<u32>,
|
||||
ef_construction: Option<u32>,
|
||||
) -> napi::Result<Self> {
|
||||
let mut hnsw_pq_builder = IvfHnswPqIndexBuilder::default();
|
||||
if let Some(distance_type) = distance_type {
|
||||
let distance_type = parse_distance_type(distance_type)?;
|
||||
hnsw_pq_builder = hnsw_pq_builder.distance_type(distance_type);
|
||||
}
|
||||
if let Some(num_partitions) = num_partitions {
|
||||
hnsw_pq_builder = hnsw_pq_builder.num_partitions(num_partitions);
|
||||
}
|
||||
if let Some(num_sub_vectors) = num_sub_vectors {
|
||||
hnsw_pq_builder = hnsw_pq_builder.num_sub_vectors(num_sub_vectors);
|
||||
}
|
||||
if let Some(max_iterations) = max_iterations {
|
||||
hnsw_pq_builder = hnsw_pq_builder.max_iterations(max_iterations);
|
||||
}
|
||||
if let Some(sample_rate) = sample_rate {
|
||||
hnsw_pq_builder = hnsw_pq_builder.sample_rate(sample_rate);
|
||||
}
|
||||
if let Some(m) = m {
|
||||
hnsw_pq_builder = hnsw_pq_builder.num_edges(m);
|
||||
}
|
||||
if let Some(ef_construction) = ef_construction {
|
||||
hnsw_pq_builder = hnsw_pq_builder.ef_construction(ef_construction);
|
||||
}
|
||||
Ok(Self {
|
||||
inner: Mutex::new(Some(LanceDbIndex::IvfHnswPq(hnsw_pq_builder))),
|
||||
})
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#[napi(factory)]
|
||||
pub fn hnsw_sq(
|
||||
distance_type: Option<String>,
|
||||
num_partitions: Option<u32>,
|
||||
max_iterations: Option<u32>,
|
||||
sample_rate: Option<u32>,
|
||||
m: Option<u32>,
|
||||
ef_construction: Option<u32>,
|
||||
) -> napi::Result<Self> {
|
||||
let mut hnsw_sq_builder = IvfHnswSqIndexBuilder::default();
|
||||
if let Some(distance_type) = distance_type {
|
||||
let distance_type = parse_distance_type(distance_type)?;
|
||||
hnsw_sq_builder = hnsw_sq_builder.distance_type(distance_type);
|
||||
}
|
||||
if let Some(num_partitions) = num_partitions {
|
||||
hnsw_sq_builder = hnsw_sq_builder.num_partitions(num_partitions);
|
||||
}
|
||||
if let Some(max_iterations) = max_iterations {
|
||||
hnsw_sq_builder = hnsw_sq_builder.max_iterations(max_iterations);
|
||||
}
|
||||
if let Some(sample_rate) = sample_rate {
|
||||
hnsw_sq_builder = hnsw_sq_builder.sample_rate(sample_rate);
|
||||
}
|
||||
if let Some(m) = m {
|
||||
hnsw_sq_builder = hnsw_sq_builder.num_edges(m);
|
||||
}
|
||||
if let Some(ef_construction) = ef_construction {
|
||||
hnsw_sq_builder = hnsw_sq_builder.ef_construction(ef_construction);
|
||||
}
|
||||
Ok(Self {
|
||||
inner: Mutex::new(Some(LanceDbIndex::IvfHnswSq(hnsw_sq_builder))),
|
||||
})
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -64,6 +64,11 @@ impl Query {
|
||||
self.inner = self.inner.clone().limit(limit as usize);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#[napi]
|
||||
pub fn offset(&mut self, offset: u32) {
|
||||
self.inner = self.inner.clone().offset(offset as usize);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#[napi]
|
||||
pub fn nearest_to(&mut self, vector: Float32Array) -> Result<VectorQuery> {
|
||||
let inner = self
|
||||
@@ -166,6 +171,11 @@ impl VectorQuery {
|
||||
self.inner = self.inner.clone().limit(limit as usize);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#[napi]
|
||||
pub fn offset(&mut self, offset: u32) {
|
||||
self.inner = self.inner.clone().offset(offset as usize);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#[napi(catch_unwind)]
|
||||
pub async fn execute(
|
||||
&self,
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -156,7 +156,7 @@ impl Table {
|
||||
&self,
|
||||
only_if: Option<String>,
|
||||
columns: Vec<(String, String)>,
|
||||
) -> napi::Result<()> {
|
||||
) -> napi::Result<u64> {
|
||||
let mut op = self.inner_ref()?.update();
|
||||
if let Some(only_if) = only_if {
|
||||
op = op.only_if(only_if);
|
||||
@@ -347,6 +347,26 @@ impl Table {
|
||||
let on: Vec<_> = on.iter().map(String::as_str).collect();
|
||||
Ok(self.inner_ref()?.merge_insert(on.as_slice()).into())
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#[napi(catch_unwind)]
|
||||
pub async fn uses_v2_manifest_paths(&self) -> napi::Result<bool> {
|
||||
self.inner_ref()?
|
||||
.as_native()
|
||||
.ok_or_else(|| napi::Error::from_reason("This cannot be run on a remote table"))?
|
||||
.uses_v2_manifest_paths()
|
||||
.await
|
||||
.default_error()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#[napi(catch_unwind)]
|
||||
pub async fn migrate_manifest_paths_v2(&self) -> napi::Result<()> {
|
||||
self.inner_ref()?
|
||||
.as_native()
|
||||
.ok_or_else(|| napi::Error::from_reason("This cannot be run on a remote table"))?
|
||||
.migrate_manifest_paths_v2()
|
||||
.await
|
||||
.default_error()
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#[napi(object)]
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
||||
[tool.bumpversion]
|
||||
current_version = "0.13.0-beta.1"
|
||||
current_version = "0.14.0-beta.0"
|
||||
parse = """(?x)
|
||||
(?P<major>0|[1-9]\\d*)\\.
|
||||
(?P<minor>0|[1-9]\\d*)\\.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
|
||||
[package]
|
||||
name = "lancedb-python"
|
||||
version = "0.13.0-beta.1"
|
||||
version = "0.14.0-beta.0"
|
||||
edition.workspace = true
|
||||
description = "Python bindings for LanceDB"
|
||||
license.workspace = true
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -3,8 +3,7 @@ name = "lancedb"
|
||||
# version in Cargo.toml
|
||||
dependencies = [
|
||||
"deprecation",
|
||||
"pylance==0.16.1",
|
||||
"ratelimiter~=1.0",
|
||||
"pylance==0.18.0",
|
||||
"requests>=2.31.0",
|
||||
"retry>=0.9.2",
|
||||
"tqdm>=4.27.0",
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -25,6 +25,7 @@ class Connection(object):
|
||||
data: pa.RecordBatchReader,
|
||||
storage_options: Optional[Dict[str, str]] = None,
|
||||
data_storage_version: Optional[str] = None,
|
||||
enable_v2_manifest_paths: Optional[bool] = None,
|
||||
) -> Table: ...
|
||||
async def create_empty_table(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
@@ -33,6 +34,7 @@ class Connection(object):
|
||||
schema: pa.Schema,
|
||||
storage_options: Optional[Dict[str, str]] = None,
|
||||
data_storage_version: Optional[str] = None,
|
||||
enable_v2_manifest_paths: Optional[bool] = None,
|
||||
) -> Table: ...
|
||||
|
||||
class Table:
|
||||
@@ -73,6 +75,7 @@ class Query:
|
||||
def where(self, filter: str): ...
|
||||
def select(self, columns: Tuple[str, str]): ...
|
||||
def limit(self, limit: int): ...
|
||||
def offset(self, offset: int): ...
|
||||
def nearest_to(self, query_vec: pa.Array) -> VectorQuery: ...
|
||||
def nearest_to_text(self, query: dict) -> Query: ...
|
||||
async def execute(self, max_batch_legnth: Optional[int]) -> RecordBatchStream: ...
|
||||
@@ -83,6 +86,7 @@ class VectorQuery:
|
||||
def select(self, columns: List[str]): ...
|
||||
def select_with_projection(self, columns: Tuple[str, str]): ...
|
||||
def limit(self, limit: int): ...
|
||||
def offset(self, offset: int): ...
|
||||
def column(self, column: str): ...
|
||||
def distance_type(self, distance_type: str): ...
|
||||
def postfilter(self): ...
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -14,7 +14,6 @@
|
||||
from __future__ import annotations
|
||||
|
||||
import asyncio
|
||||
import inspect
|
||||
import os
|
||||
from abc import abstractmethod
|
||||
from pathlib import Path
|
||||
@@ -27,8 +26,13 @@ from pyarrow import fs
|
||||
from lancedb.common import data_to_reader, validate_schema
|
||||
|
||||
from ._lancedb import connect as lancedb_connect
|
||||
from .pydantic import LanceModel
|
||||
from .table import AsyncTable, LanceTable, Table, _sanitize_data, _table_path
|
||||
from .table import (
|
||||
AsyncTable,
|
||||
LanceTable,
|
||||
Table,
|
||||
_table_path,
|
||||
sanitize_create_table,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from .util import (
|
||||
fs_from_uri,
|
||||
get_uri_location,
|
||||
@@ -37,6 +41,7 @@ from .util import (
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if TYPE_CHECKING:
|
||||
from .pydantic import LanceModel
|
||||
from datetime import timedelta
|
||||
|
||||
from ._lancedb import Connection as LanceDbConnection
|
||||
@@ -562,6 +567,7 @@ class AsyncConnection(object):
|
||||
*,
|
||||
data_storage_version: Optional[str] = None,
|
||||
use_legacy_format: Optional[bool] = None,
|
||||
enable_v2_manifest_paths: Optional[bool] = None,
|
||||
) -> AsyncTable:
|
||||
"""Create an [AsyncTable][lancedb.table.AsyncTable] in the database.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -604,15 +610,22 @@ class AsyncConnection(object):
|
||||
connection will be inherited by the table, but can be overridden here.
|
||||
See available options at
|
||||
https://lancedb.github.io/lancedb/guides/storage/
|
||||
data_storage_version: optional, str, default "legacy"
|
||||
data_storage_version: optional, str, default "stable"
|
||||
The version of the data storage format to use. Newer versions are more
|
||||
efficient but require newer versions of lance to read. The default is
|
||||
"legacy" which will use the legacy v1 version. See the user guide
|
||||
"stable" which will use the legacy v2 version. See the user guide
|
||||
for more details.
|
||||
use_legacy_format: bool, optional, default True. (Deprecated)
|
||||
use_legacy_format: bool, optional, default False. (Deprecated)
|
||||
If True, use the legacy format for the table. If False, use the new format.
|
||||
The default is True while the new format is in beta.
|
||||
This method is deprecated, use `data_storage_version` instead.
|
||||
enable_v2_manifest_paths: bool, optional, default False
|
||||
Use the new V2 manifest paths. These paths provide more efficient
|
||||
opening of datasets with many versions on object stores. WARNING:
|
||||
turning this on will make the dataset unreadable for older versions
|
||||
of LanceDB (prior to 0.13.0). To migrate an existing dataset, instead
|
||||
use the
|
||||
[AsyncTable.migrate_manifest_paths_v2][lancedb.table.AsyncTable.migrate_manifest_paths_v2]
|
||||
method.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Returns
|
||||
@@ -722,12 +735,6 @@ class AsyncConnection(object):
|
||||
... await db.create_table("table4", make_batches(), schema=schema)
|
||||
>>> asyncio.run(iterable_example())
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if inspect.isclass(schema) and issubclass(schema, LanceModel):
|
||||
# convert LanceModel to pyarrow schema
|
||||
# note that it's possible this contains
|
||||
# embedding function metadata already
|
||||
schema = schema.to_arrow_schema()
|
||||
|
||||
metadata = None
|
||||
|
||||
# Defining defaults here and not in function prototype. In the future
|
||||
@@ -738,31 +745,9 @@ class AsyncConnection(object):
|
||||
if fill_value is None:
|
||||
fill_value = 0.0
|
||||
|
||||
if data is not None:
|
||||
data, schema = _sanitize_data(
|
||||
data,
|
||||
schema,
|
||||
metadata=metadata,
|
||||
on_bad_vectors=on_bad_vectors,
|
||||
fill_value=fill_value,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if schema is None:
|
||||
if data is None:
|
||||
raise ValueError("Either data or schema must be provided")
|
||||
elif hasattr(data, "schema"):
|
||||
schema = data.schema
|
||||
elif isinstance(data, Iterable):
|
||||
if metadata:
|
||||
raise TypeError(
|
||||
(
|
||||
"Persistent embedding functions not yet "
|
||||
"supported for generator data input"
|
||||
)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if metadata:
|
||||
schema = schema.with_metadata(metadata)
|
||||
data, schema = sanitize_create_table(
|
||||
data, schema, metadata, on_bad_vectors, fill_value
|
||||
)
|
||||
validate_schema(schema)
|
||||
|
||||
if exist_ok is None:
|
||||
@@ -773,9 +758,7 @@ class AsyncConnection(object):
|
||||
mode = "exist_ok"
|
||||
|
||||
if not data_storage_version:
|
||||
data_storage_version = (
|
||||
"legacy" if use_legacy_format is None or use_legacy_format else "stable"
|
||||
)
|
||||
data_storage_version = "legacy" if use_legacy_format else "stable"
|
||||
|
||||
if data is None:
|
||||
new_table = await self._inner.create_empty_table(
|
||||
@@ -784,6 +767,7 @@ class AsyncConnection(object):
|
||||
schema,
|
||||
storage_options=storage_options,
|
||||
data_storage_version=data_storage_version,
|
||||
enable_v2_manifest_paths=enable_v2_manifest_paths,
|
||||
)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
data = data_to_reader(data, schema)
|
||||
@@ -793,6 +777,7 @@ class AsyncConnection(object):
|
||||
data,
|
||||
storage_options=storage_options,
|
||||
data_storage_version=data_storage_version,
|
||||
enable_v2_manifest_paths=enable_v2_manifest_paths,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
return AsyncTable(new_table)
|
||||
|
||||
259
python/python/lancedb/dependencies.py
Normal file
259
python/python/lancedb/dependencies.py
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,259 @@
|
||||
# SPDX-License-Identifier: Apache-2.0
|
||||
# SPDX-FileCopyrightText: Copyright The Lance Authors
|
||||
#
|
||||
# The following code is originally from https://github.com/pola-rs/polars/blob/ea4389c31b0e87ddf20a85e4c3797b285966edb6/py-polars/polars/dependencies.py
|
||||
# and is licensed under the MIT license:
|
||||
#
|
||||
# License: MIT, Copyright (c) 2020 Ritchie Vink
|
||||
# https://github.com/pola-rs/polars/blob/main/LICENSE
|
||||
#
|
||||
# It has been modified by the LanceDB developers
|
||||
# to fit the needs of the LanceDB project.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
from __future__ import annotations
|
||||
|
||||
import re
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
from functools import lru_cache
|
||||
from importlib import import_module
|
||||
from importlib.util import find_spec
|
||||
from types import ModuleType
|
||||
from typing import TYPE_CHECKING, Any, ClassVar, Hashable, cast
|
||||
|
||||
_NUMPY_AVAILABLE = True
|
||||
_PANDAS_AVAILABLE = True
|
||||
_POLARS_AVAILABLE = True
|
||||
_TORCH_AVAILABLE = True
|
||||
_HUGGING_FACE_AVAILABLE = True
|
||||
_TENSORFLOW_AVAILABLE = True
|
||||
_RAY_AVAILABLE = True
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class _LazyModule(ModuleType):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Module that can act both as a lazy-loader and as a proxy.
|
||||
|
||||
Notes
|
||||
-----
|
||||
We do NOT register this module with `sys.modules` so as not to cause
|
||||
confusion in the global environment. This way we have a valid proxy
|
||||
module for our own use, but it lives _exclusively_ within lance.
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
__lazy__ = True
|
||||
|
||||
_mod_pfx: ClassVar[dict[str, str]] = {
|
||||
"numpy": "np.",
|
||||
"pandas": "pd.",
|
||||
"polars": "pl.",
|
||||
"torch": "torch.",
|
||||
"tensorflow": "tf.",
|
||||
"ray": "ray.",
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
module_name: str,
|
||||
*,
|
||||
module_available: bool,
|
||||
) -> None:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Initialise lazy-loading proxy module.
|
||||
|
||||
Parameters
|
||||
----------
|
||||
module_name : str
|
||||
the name of the module to lazy-load (if available).
|
||||
|
||||
module_available : bool
|
||||
indicate if the referenced module is actually available (we will proxy it
|
||||
in both cases, but raise a helpful error when invoked if it doesn't exist).
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self._module_available = module_available
|
||||
self._module_name = module_name
|
||||
self._globals = globals()
|
||||
super().__init__(module_name)
|
||||
|
||||
def _import(self) -> ModuleType:
|
||||
# import the referenced module, replacing the proxy in this module's globals
|
||||
module = import_module(self.__name__)
|
||||
self._globals[self._module_name] = module
|
||||
self.__dict__.update(module.__dict__)
|
||||
return module
|
||||
|
||||
def __getattr__(self, attr: Any) -> Any:
|
||||
# have "hasattr('__wrapped__')" return False without triggering import
|
||||
# (it's for decorators, not modules, but keeps "make doctest" happy)
|
||||
if attr == "__wrapped__":
|
||||
raise AttributeError(
|
||||
f"{self._module_name!r} object has no attribute {attr!r}"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# accessing the proxy module's attributes triggers import of the real thing
|
||||
if self._module_available:
|
||||
# import the module and return the requested attribute
|
||||
module = self._import()
|
||||
return getattr(module, attr)
|
||||
|
||||
# user has not installed the proxied/lazy module
|
||||
elif attr == "__name__":
|
||||
return self._module_name
|
||||
elif re.match(r"^__\w+__$", attr) and attr != "__version__":
|
||||
# allow some minimal introspection on private module
|
||||
# attrs to avoid unnecessary error-handling elsewhere
|
||||
return None
|
||||
else:
|
||||
# all other attribute access raises a helpful exception
|
||||
pfx = self._mod_pfx.get(self._module_name, "")
|
||||
raise ModuleNotFoundError(
|
||||
f"{pfx}{attr} requires {self._module_name!r} module to be installed"
|
||||
) from None
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _lazy_import(module_name: str) -> tuple[ModuleType, bool]:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Lazy import the given module; avoids up-front import costs.
|
||||
|
||||
Parameters
|
||||
----------
|
||||
module_name : str
|
||||
name of the module to import, eg: "polars".
|
||||
|
||||
Notes
|
||||
-----
|
||||
If the requested module is not available (eg: has not been installed), a proxy
|
||||
module is created in its place, which raises an exception on any attribute
|
||||
access. This allows for import and use as normal, without requiring explicit
|
||||
guard conditions - if the module is never used, no exception occurs; if it
|
||||
is, then a helpful exception is raised.
|
||||
|
||||
Returns
|
||||
-------
|
||||
tuple of (Module, bool)
|
||||
A lazy-loading module and a boolean indicating if the requested/underlying
|
||||
module exists (if not, the returned module is a proxy).
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
# check if module is LOADED
|
||||
if module_name in sys.modules:
|
||||
return sys.modules[module_name], True
|
||||
|
||||
# check if module is AVAILABLE
|
||||
try:
|
||||
module_spec = find_spec(module_name)
|
||||
module_available = not (module_spec is None or module_spec.loader is None)
|
||||
except ModuleNotFoundError:
|
||||
module_available = False
|
||||
|
||||
# create lazy/proxy module that imports the real one on first use
|
||||
# (or raises an explanatory ModuleNotFoundError if not available)
|
||||
return (
|
||||
_LazyModule(
|
||||
module_name=module_name,
|
||||
module_available=module_available,
|
||||
),
|
||||
module_available,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if TYPE_CHECKING:
|
||||
import datasets
|
||||
import numpy
|
||||
import pandas
|
||||
import polars
|
||||
import ray
|
||||
import tensorflow
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
else:
|
||||
# heavy/optional third party libs
|
||||
numpy, _NUMPY_AVAILABLE = _lazy_import("numpy")
|
||||
pandas, _PANDAS_AVAILABLE = _lazy_import("pandas")
|
||||
polars, _POLARS_AVAILABLE = _lazy_import("polars")
|
||||
torch, _TORCH_AVAILABLE = _lazy_import("torch")
|
||||
datasets, _HUGGING_FACE_AVAILABLE = _lazy_import("datasets")
|
||||
tensorflow, _TENSORFLOW_AVAILABLE = _lazy_import("tensorflow")
|
||||
ray, _RAY_AVAILABLE = _lazy_import("ray")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@lru_cache(maxsize=None)
|
||||
def _might_be(cls: type, type_: str) -> bool:
|
||||
# infer whether the given class "might" be associated with the given
|
||||
# module (in which case it's reasonable to do a real isinstance check)
|
||||
try:
|
||||
return any(f"{type_}." in str(o) for o in cls.mro())
|
||||
except TypeError:
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _check_for_numpy(obj: Any, *, check_type: bool = True) -> bool:
|
||||
return _NUMPY_AVAILABLE and _might_be(
|
||||
cast(Hashable, type(obj) if check_type else obj), "numpy"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _check_for_pandas(obj: Any, *, check_type: bool = True) -> bool:
|
||||
return _PANDAS_AVAILABLE and _might_be(
|
||||
cast(Hashable, type(obj) if check_type else obj), "pandas"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _check_for_polars(obj: Any, *, check_type: bool = True) -> bool:
|
||||
return _POLARS_AVAILABLE and _might_be(
|
||||
cast(Hashable, type(obj) if check_type else obj), "polars"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _check_for_torch(obj: Any, *, check_type: bool = True) -> bool:
|
||||
return _TORCH_AVAILABLE and _might_be(
|
||||
cast(Hashable, type(obj) if check_type else obj), "torch"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _check_for_hugging_face(obj: Any, *, check_type: bool = True) -> bool:
|
||||
return _HUGGING_FACE_AVAILABLE and _might_be(
|
||||
cast(Hashable, type(obj) if check_type else obj), "datasets"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _check_for_tensorflow(obj: Any, *, check_type: bool = True) -> bool:
|
||||
return _TENSORFLOW_AVAILABLE and _might_be(
|
||||
cast(Hashable, type(obj) if check_type else obj), "tensorflow"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _check_for_ray(obj: Any, *, check_type: bool = True) -> bool:
|
||||
return _RAY_AVAILABLE and _might_be(
|
||||
cast(Hashable, type(obj) if check_type else obj), "ray"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
__all__ = [
|
||||
# lazy-load third party libs
|
||||
"datasets",
|
||||
"numpy",
|
||||
"pandas",
|
||||
"polars",
|
||||
"ray",
|
||||
"tensorflow",
|
||||
"torch",
|
||||
# lazy utilities
|
||||
"_check_for_hugging_face",
|
||||
"_check_for_numpy",
|
||||
"_check_for_pandas",
|
||||
"_check_for_polars",
|
||||
"_check_for_tensorflow",
|
||||
"_check_for_torch",
|
||||
"_check_for_ray",
|
||||
"_LazyModule",
|
||||
# exported flags/guards
|
||||
"_NUMPY_AVAILABLE",
|
||||
"_PANDAS_AVAILABLE",
|
||||
"_POLARS_AVAILABLE",
|
||||
"_TORCH_AVAILABLE",
|
||||
"_HUGGING_FACE_AVAILABLE",
|
||||
"_TENSORFLOW_AVAILABLE",
|
||||
"_RAY_AVAILABLE",
|
||||
]
|
||||
@@ -26,12 +26,23 @@ class SentenceTransformerEmbeddings(TextEmbeddingFunction):
|
||||
An embedding function that uses the sentence-transformers library
|
||||
|
||||
https://huggingface.co/sentence-transformers
|
||||
|
||||
Parameters
|
||||
----------
|
||||
name: str, default "all-MiniLM-L6-v2"
|
||||
The name of the model to use.
|
||||
device: str, default "cpu"
|
||||
The device to use for the model
|
||||
normalize: bool, default True
|
||||
Whether to normalize the embeddings
|
||||
trust_remote_code: bool, default True
|
||||
Whether to trust the remote code
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
name: str = "all-MiniLM-L6-v2"
|
||||
device: str = "cpu"
|
||||
normalize: bool = True
|
||||
trust_remote_code: bool = False
|
||||
trust_remote_code: bool = True
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
|
||||
super().__init__(**kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -36,6 +36,10 @@ class TransformersEmbeddingFunction(EmbeddingFunction):
|
||||
The name of the model to use. This should be a model name that can be loaded
|
||||
by transformers.AutoModel.from_pretrained. For example, "bert-base-uncased".
|
||||
default: "colbert-ir/colbertv2.0""
|
||||
device : str
|
||||
The device to use for the model. Default is "cpu".
|
||||
show_progress_bar : bool
|
||||
Whether to show a progress bar when loading the model. Default is True.
|
||||
|
||||
to download package, run :
|
||||
`pip install transformers`
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -16,6 +16,7 @@ import math
|
||||
import random
|
||||
import socket
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
import threading
|
||||
import time
|
||||
import urllib.error
|
||||
import weakref
|
||||
@@ -38,6 +39,42 @@ IMAGES = Union[
|
||||
AUDIO = Union[str, bytes, List[str], List[bytes], pa.Array, pa.ChunkedArray, np.ndarray]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class RateLimiter:
|
||||
def __init__(self, max_calls: int = 1, period: float = 1.0):
|
||||
self.period = period
|
||||
self.max_calls = max(1, min(sys.maxsize, math.floor(max_calls)))
|
||||
|
||||
self._last_reset = time.time()
|
||||
self._num_calls = 0
|
||||
self._lock = threading.RLock()
|
||||
|
||||
def _check_sleep(self) -> float:
|
||||
current_time = time.time()
|
||||
elapsed = current_time - self._last_reset
|
||||
period_remaining = self.period - elapsed
|
||||
|
||||
# If the time window has elapsed then reset.
|
||||
if period_remaining <= 0:
|
||||
self._num_calls = 0
|
||||
self._last_reset = current_time
|
||||
|
||||
self._num_calls += 1
|
||||
|
||||
if self._num_calls > self.max_calls:
|
||||
return period_remaining
|
||||
|
||||
return 0.0
|
||||
|
||||
def __call__(self, func):
|
||||
@functools.wraps(func)
|
||||
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
|
||||
with self._lock:
|
||||
time.sleep(self._check_sleep())
|
||||
return func(*args, **kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
return wrapper
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@deprecated
|
||||
def with_embeddings(
|
||||
func: Callable,
|
||||
@@ -109,21 +146,12 @@ class FunctionWrapper:
|
||||
def embed_func(c):
|
||||
return self.func(c.tolist())
|
||||
|
||||
if len(self.rate_limiter_kwargs) > 0:
|
||||
v = int(sys.version_info.minor)
|
||||
if v >= 11:
|
||||
print(
|
||||
"WARNING: rate limit only support up to 3.10, proceeding "
|
||||
"without rate limiter"
|
||||
)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
import ratelimiter
|
||||
|
||||
max_calls = self.rate_limiter_kwargs["max_calls"]
|
||||
limiter = ratelimiter.RateLimiter(
|
||||
max_calls, period=self.rate_limiter_kwargs["period"]
|
||||
)
|
||||
embed_func = limiter(embed_func)
|
||||
if self.rate_limiter_kwargs:
|
||||
limiter = RateLimiter(
|
||||
max_calls=self.rate_limiter_kwargs["max_calls"],
|
||||
period=self.rate_limiter_kwargs["period"],
|
||||
)
|
||||
embed_func = limiter(embed_func)
|
||||
batches = self.to_batches(text)
|
||||
embeds = [emb for c in batches for emb in embed_func(c)]
|
||||
return embeds
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -78,8 +78,243 @@ class FTS:
|
||||
For example, it works with `title`, `description`, `content`, etc.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self):
|
||||
self._inner = LanceDbIndex.fts()
|
||||
def __init__(self, with_position: bool = True):
|
||||
self._inner = LanceDbIndex.fts(with_position=with_position)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class HnswPq:
|
||||
"""Describe a HNSW-PQ index configuration.
|
||||
|
||||
HNSW-PQ stands for Hierarchical Navigable Small World - Product Quantization.
|
||||
It is a variant of the HNSW algorithm that uses product quantization to compress
|
||||
the vectors. To create an HNSW-PQ index, you can specify the following parameters:
|
||||
|
||||
Parameters
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
distance_type: str, default "L2"
|
||||
|
||||
The distance metric used to train the index.
|
||||
|
||||
The following distance types are available:
|
||||
|
||||
"l2" - Euclidean distance. This is a very common distance metric that
|
||||
accounts for both magnitude and direction when determining the distance
|
||||
between vectors. L2 distance has a range of [0, ∞).
|
||||
|
||||
"cosine" - Cosine distance. Cosine distance is a distance metric
|
||||
calculated from the cosine similarity between two vectors. Cosine
|
||||
similarity is a measure of similarity between two non-zero vectors of an
|
||||
inner product space. It is defined to equal the cosine of the angle
|
||||
between them. Unlike L2, the cosine distance is not affected by the
|
||||
magnitude of the vectors. Cosine distance has a range of [0, 2].
|
||||
|
||||
"dot" - Dot product. Dot distance is the dot product of two vectors. Dot
|
||||
distance has a range of (-∞, ∞). If the vectors are normalized (i.e. their
|
||||
L2 norm is 1), then dot distance is equivalent to the cosine distance.
|
||||
|
||||
num_partitions, default sqrt(num_rows)
|
||||
|
||||
The number of IVF partitions to create.
|
||||
|
||||
For HNSW, we recommend a small number of partitions. Setting this to 1 works
|
||||
well for most tables. For very large tables, training just one HNSW graph
|
||||
will require too much memory. Each partition becomes its own HNSW graph, so
|
||||
setting this value higher reduces the peak memory use of training.
|
||||
|
||||
num_sub_vectors, default is vector dimension / 16
|
||||
|
||||
Number of sub-vectors of PQ.
|
||||
|
||||
This value controls how much the vector is compressed during the
|
||||
quantization step. The more sub vectors there are the less the vector is
|
||||
compressed. The default is the dimension of the vector divided by 16.
|
||||
If the dimension is not evenly divisible by 16 we use the dimension
|
||||
divided by 8.
|
||||
|
||||
The above two cases are highly preferred. Having 8 or 16 values per
|
||||
subvector allows us to use efficient SIMD instructions.
|
||||
|
||||
If the dimension is not visible by 8 then we use 1 subvector. This is not
|
||||
ideal and will likely result in poor performance.
|
||||
|
||||
max_iterations, default 50
|
||||
|
||||
Max iterations to train kmeans.
|
||||
|
||||
When training an IVF index we use kmeans to calculate the partitions. This
|
||||
parameter controls how many iterations of kmeans to run.
|
||||
|
||||
Increasing this might improve the quality of the index but in most cases the
|
||||
parameter is unused because kmeans will converge with fewer iterations. The
|
||||
parameter is only used in cases where kmeans does not appear to converge. In
|
||||
those cases it is unlikely that setting this larger will lead to the index
|
||||
converging anyways.
|
||||
|
||||
sample_rate, default 256
|
||||
|
||||
The rate used to calculate the number of training vectors for kmeans.
|
||||
|
||||
When an IVF index is trained, we need to calculate partitions. These are
|
||||
groups of vectors that are similar to each other. To do this we use an
|
||||
algorithm called kmeans.
|
||||
|
||||
Running kmeans on a large dataset can be slow. To speed this up we
|
||||
run kmeans on a random sample of the data. This parameter controls the
|
||||
size of the sample. The total number of vectors used to train the index
|
||||
is `sample_rate * num_partitions`.
|
||||
|
||||
Increasing this value might improve the quality of the index but in
|
||||
most cases the default should be sufficient.
|
||||
|
||||
m, default 20
|
||||
|
||||
The number of neighbors to select for each vector in the HNSW graph.
|
||||
|
||||
This value controls the tradeoff between search speed and accuracy.
|
||||
The higher the value the more accurate the search but the slower it will be.
|
||||
|
||||
ef_construction, default 300
|
||||
|
||||
The number of candidates to evaluate during the construction of the HNSW graph.
|
||||
|
||||
This value controls the tradeoff between build speed and accuracy.
|
||||
The higher the value the more accurate the build but the slower it will be.
|
||||
150 to 300 is the typical range. 100 is a minimum for good quality search
|
||||
results. In most cases, there is no benefit to setting this higher than 500.
|
||||
This value should be set to a value that is not less than `ef` in the
|
||||
search phase.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
*,
|
||||
distance_type: Optional[str] = None,
|
||||
num_partitions: Optional[int] = None,
|
||||
num_sub_vectors: Optional[int] = None,
|
||||
max_iterations: Optional[int] = None,
|
||||
sample_rate: Optional[int] = None,
|
||||
m: Optional[int] = None,
|
||||
ef_construction: Optional[int] = None,
|
||||
):
|
||||
self._inner = LanceDbIndex.hnsw_pq(
|
||||
distance_type=distance_type,
|
||||
num_partitions=num_partitions,
|
||||
num_sub_vectors=num_sub_vectors,
|
||||
max_iterations=max_iterations,
|
||||
sample_rate=sample_rate,
|
||||
m=m,
|
||||
ef_construction=ef_construction,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class HnswSq:
|
||||
"""Describe a HNSW-SQ index configuration.
|
||||
|
||||
HNSW-SQ stands for Hierarchical Navigable Small World - Scalar Quantization.
|
||||
It is a variant of the HNSW algorithm that uses scalar quantization to compress
|
||||
the vectors.
|
||||
|
||||
Parameters
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
distance_type: str, default "L2"
|
||||
|
||||
The distance metric used to train the index.
|
||||
|
||||
The following distance types are available:
|
||||
|
||||
"l2" - Euclidean distance. This is a very common distance metric that
|
||||
accounts for both magnitude and direction when determining the distance
|
||||
between vectors. L2 distance has a range of [0, ∞).
|
||||
|
||||
"cosine" - Cosine distance. Cosine distance is a distance metric
|
||||
calculated from the cosine similarity between two vectors. Cosine
|
||||
similarity is a measure of similarity between two non-zero vectors of an
|
||||
inner product space. It is defined to equal the cosine of the angle
|
||||
between them. Unlike L2, the cosine distance is not affected by the
|
||||
magnitude of the vectors. Cosine distance has a range of [0, 2].
|
||||
|
||||
"dot" - Dot product. Dot distance is the dot product of two vectors. Dot
|
||||
distance has a range of (-∞, ∞). If the vectors are normalized (i.e. their
|
||||
L2 norm is 1), then dot distance is equivalent to the cosine distance.
|
||||
|
||||
num_partitions, default sqrt(num_rows)
|
||||
|
||||
The number of IVF partitions to create.
|
||||
|
||||
For HNSW, we recommend a small number of partitions. Setting this to 1 works
|
||||
well for most tables. For very large tables, training just one HNSW graph
|
||||
will require too much memory. Each partition becomes its own HNSW graph, so
|
||||
setting this value higher reduces the peak memory use of training.
|
||||
|
||||
max_iterations, default 50
|
||||
|
||||
Max iterations to train kmeans.
|
||||
|
||||
When training an IVF index we use kmeans to calculate the partitions.
|
||||
This parameter controls how many iterations of kmeans to run.
|
||||
|
||||
Increasing this might improve the quality of the index but in most cases
|
||||
the parameter is unused because kmeans will converge with fewer iterations.
|
||||
The parameter is only used in cases where kmeans does not appear to converge.
|
||||
In those cases it is unlikely that setting this larger will lead to
|
||||
the index converging anyways.
|
||||
|
||||
sample_rate, default 256
|
||||
|
||||
The rate used to calculate the number of training vectors for kmeans.
|
||||
|
||||
When an IVF index is trained, we need to calculate partitions. These
|
||||
are groups of vectors that are similar to each other. To do this
|
||||
we use an algorithm called kmeans.
|
||||
|
||||
Running kmeans on a large dataset can be slow. To speed this up we
|
||||
run kmeans on a random sample of the data. This parameter controls the
|
||||
size of the sample. The total number of vectors used to train the index
|
||||
is `sample_rate * num_partitions`.
|
||||
|
||||
Increasing this value might improve the quality of the index but in
|
||||
most cases the default should be sufficient.
|
||||
|
||||
m, default 20
|
||||
|
||||
The number of neighbors to select for each vector in the HNSW graph.
|
||||
|
||||
This value controls the tradeoff between search speed and accuracy.
|
||||
The higher the value the more accurate the search but the slower it will be.
|
||||
|
||||
ef_construction, default 300
|
||||
|
||||
The number of candidates to evaluate during the construction of the HNSW graph.
|
||||
|
||||
This value controls the tradeoff between build speed and accuracy.
|
||||
The higher the value the more accurate the build but the slower it will be.
|
||||
150 to 300 is the typical range. 100 is a minimum for good quality search
|
||||
results. In most cases, there is no benefit to setting this higher than 500.
|
||||
This value should be set to a value that is not less than `ef` in the search
|
||||
phase.
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
*,
|
||||
distance_type: Optional[str] = None,
|
||||
num_partitions: Optional[int] = None,
|
||||
max_iterations: Optional[int] = None,
|
||||
sample_rate: Optional[int] = None,
|
||||
m: Optional[int] = None,
|
||||
ef_construction: Optional[int] = None,
|
||||
):
|
||||
self._inner = LanceDbIndex.hnsw_sq(
|
||||
distance_type=distance_type,
|
||||
num_partitions=num_partitions,
|
||||
max_iterations=max_iterations,
|
||||
sample_rate=sample_rate,
|
||||
m=m,
|
||||
ef_construction=ef_construction,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class IvfPq:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -34,9 +34,8 @@ import pydantic
|
||||
|
||||
from . import __version__
|
||||
from .arrow import AsyncRecordBatchReader
|
||||
from .common import VEC
|
||||
from .rerankers.base import Reranker
|
||||
from .rerankers.linear_combination import LinearCombinationReranker
|
||||
from .rerankers.rrf import RRFReranker
|
||||
from .util import safe_import_pandas
|
||||
|
||||
if TYPE_CHECKING:
|
||||
@@ -45,6 +44,7 @@ if TYPE_CHECKING:
|
||||
|
||||
from ._lancedb import Query as LanceQuery
|
||||
from ._lancedb import VectorQuery as LanceVectorQuery
|
||||
from .common import VEC
|
||||
from .pydantic import LanceModel
|
||||
from .table import Table
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -85,6 +85,8 @@ class Query(pydantic.BaseModel):
|
||||
|
||||
- See discussion in [Querying an ANN Index][querying-an-ann-index] for
|
||||
tuning advice.
|
||||
offset: int
|
||||
The offset to start fetching results from
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
vector_column: Optional[str] = None
|
||||
@@ -119,6 +121,8 @@ class Query(pydantic.BaseModel):
|
||||
|
||||
with_row_id: bool = False
|
||||
|
||||
offset: int = 0
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class LanceQueryBuilder(ABC):
|
||||
"""An abstract query builder. Subclasses are defined for vector search,
|
||||
@@ -132,8 +136,8 @@ class LanceQueryBuilder(ABC):
|
||||
query: Optional[Union[np.ndarray, str, "PIL.Image.Image", Tuple]],
|
||||
query_type: str,
|
||||
vector_column_name: str,
|
||||
ordering_field_name: str = None,
|
||||
fts_columns: Union[str, List[str]] = None,
|
||||
ordering_field_name: Optional[str] = None,
|
||||
fts_columns: Union[str, List[str]] = [],
|
||||
) -> LanceQueryBuilder:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Create a query builder based on the given query and query type.
|
||||
@@ -151,12 +155,15 @@ class LanceQueryBuilder(ABC):
|
||||
vector_column_name: str
|
||||
The name of the vector column to use for vector search.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if query is None:
|
||||
return LanceEmptyQueryBuilder(table)
|
||||
|
||||
# Check hybrid search first as it supports empty query pattern
|
||||
if query_type == "hybrid":
|
||||
# hybrid fts and vector query
|
||||
return LanceHybridQueryBuilder(table, query, vector_column_name)
|
||||
return LanceHybridQueryBuilder(
|
||||
table, query, vector_column_name, fts_columns=fts_columns
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if query is None:
|
||||
return LanceEmptyQueryBuilder(table)
|
||||
|
||||
# remember the string query for reranking purpose
|
||||
str_query = query if isinstance(query, str) else None
|
||||
@@ -168,7 +175,9 @@ class LanceQueryBuilder(ABC):
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if query_type == "hybrid":
|
||||
return LanceHybridQueryBuilder(table, query, vector_column_name)
|
||||
return LanceHybridQueryBuilder(
|
||||
table, query, vector_column_name, fts_columns=fts_columns
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if isinstance(query, str):
|
||||
# fts
|
||||
@@ -176,6 +185,7 @@ class LanceQueryBuilder(ABC):
|
||||
table,
|
||||
query,
|
||||
ordering_field_name=ordering_field_name,
|
||||
fts_columns=fts_columns,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if isinstance(query, list):
|
||||
@@ -201,8 +211,6 @@ class LanceQueryBuilder(ABC):
|
||||
elif query_type == "auto":
|
||||
if isinstance(query, (list, np.ndarray)):
|
||||
return query, "vector"
|
||||
if isinstance(query, tuple):
|
||||
return query, "hybrid"
|
||||
else:
|
||||
conf = table.embedding_functions.get(vector_column_name)
|
||||
if conf is not None:
|
||||
@@ -229,10 +237,13 @@ class LanceQueryBuilder(ABC):
|
||||
def __init__(self, table: "Table"):
|
||||
self._table = table
|
||||
self._limit = 10
|
||||
self._offset = 0
|
||||
self._columns = None
|
||||
self._where = None
|
||||
self._prefilter = False
|
||||
self._with_row_id = False
|
||||
self._vector = None
|
||||
self._text = None
|
||||
|
||||
@deprecation.deprecated(
|
||||
deprecated_in="0.3.1",
|
||||
@@ -357,11 +368,33 @@ class LanceQueryBuilder(ABC):
|
||||
The LanceQueryBuilder object.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if limit is None or limit <= 0:
|
||||
self._limit = None
|
||||
if isinstance(self, LanceVectorQueryBuilder):
|
||||
raise ValueError("Limit is required for ANN/KNN queries")
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self._limit = None
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self._limit = limit
|
||||
return self
|
||||
|
||||
def offset(self, offset: int) -> LanceQueryBuilder:
|
||||
"""Set the offset for the results.
|
||||
|
||||
Parameters
|
||||
----------
|
||||
offset: int
|
||||
The offset to start fetching results from.
|
||||
|
||||
Returns
|
||||
-------
|
||||
LanceQueryBuilder
|
||||
The LanceQueryBuilder object.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if offset is None or offset <= 0:
|
||||
self._offset = 0
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self._offset = offset
|
||||
return self
|
||||
|
||||
def select(self, columns: Union[list[str], dict[str, str]]) -> LanceQueryBuilder:
|
||||
"""Set the columns to return.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -457,6 +490,36 @@ class LanceQueryBuilder(ABC):
|
||||
},
|
||||
).explain_plan(verbose)
|
||||
|
||||
def vector(self, vector: Union[np.ndarray, list]) -> LanceQueryBuilder:
|
||||
"""Set the vector to search for.
|
||||
|
||||
Parameters
|
||||
----------
|
||||
vector: np.ndarray or list
|
||||
The vector to search for.
|
||||
|
||||
Returns
|
||||
-------
|
||||
LanceQueryBuilder
|
||||
The LanceQueryBuilder object.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
raise NotImplementedError
|
||||
|
||||
def text(self, text: str) -> LanceQueryBuilder:
|
||||
"""Set the text to search for.
|
||||
|
||||
Parameters
|
||||
----------
|
||||
text: str
|
||||
The text to search for.
|
||||
|
||||
Returns
|
||||
-------
|
||||
LanceQueryBuilder
|
||||
The LanceQueryBuilder object.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
raise NotImplementedError
|
||||
|
||||
@abstractmethod
|
||||
def rerank(self, reranker: Reranker) -> LanceQueryBuilder:
|
||||
"""Rerank the results using the specified reranker.
|
||||
@@ -610,6 +673,7 @@ class LanceVectorQueryBuilder(LanceQueryBuilder):
|
||||
refine_factor=self._refine_factor,
|
||||
vector_column=self._vector_column,
|
||||
with_row_id=self._with_row_id,
|
||||
offset=self._offset,
|
||||
)
|
||||
result_set = self._table._execute_query(query, batch_size)
|
||||
if self._reranker is not None:
|
||||
@@ -690,8 +754,8 @@ class LanceFtsQueryBuilder(LanceQueryBuilder):
|
||||
self,
|
||||
table: "Table",
|
||||
query: str,
|
||||
ordering_field_name: str = None,
|
||||
fts_columns: Union[str, List[str]] = None,
|
||||
ordering_field_name: Optional[str] = None,
|
||||
fts_columns: Union[str, List[str]] = [],
|
||||
):
|
||||
super().__init__(table)
|
||||
self._query = query
|
||||
@@ -741,6 +805,7 @@ class LanceFtsQueryBuilder(LanceQueryBuilder):
|
||||
"columns": self._fts_columns,
|
||||
},
|
||||
vector=[],
|
||||
offset=self._offset,
|
||||
)
|
||||
results = self._table._execute_query(query)
|
||||
results = results.read_all()
|
||||
@@ -787,7 +852,7 @@ class LanceFtsQueryBuilder(LanceQueryBuilder):
|
||||
)
|
||||
if len(row_ids) == 0:
|
||||
empty_schema = pa.schema([pa.field("_score", pa.float32())])
|
||||
return pa.Table.from_pylist([], schema=empty_schema)
|
||||
return pa.Table.from_batches([], schema=empty_schema)
|
||||
scores = pa.array(scores)
|
||||
output_tbl = self._table.to_lance().take(row_ids, columns=self._columns)
|
||||
output_tbl = output_tbl.append_column("_score", scores)
|
||||
@@ -877,42 +942,101 @@ class LanceHybridQueryBuilder(LanceQueryBuilder):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
A query builder that performs hybrid vector and full text search.
|
||||
Results are combined and reranked based on the specified reranker.
|
||||
By default, the results are reranked using the LinearCombinationReranker.
|
||||
By default, the results are reranked using the RRFReranker, which
|
||||
uses reciprocal rank fusion score for reranking.
|
||||
|
||||
To make the vector and fts results comparable, the scores are normalized.
|
||||
Instead of normalizing scores, the `normalize` parameter can be set to "rank"
|
||||
in the `rerank` method to convert the scores to ranks and then normalize them.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, table: "Table", query: str, vector_column: str):
|
||||
def __init__(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
table: "Table",
|
||||
query: str = None,
|
||||
vector_column: str = None,
|
||||
fts_columns: Union[str, List[str]] = [],
|
||||
):
|
||||
super().__init__(table)
|
||||
vector_query, fts_query = self._validate_query(query)
|
||||
self._fts_query = LanceFtsQueryBuilder(table, fts_query)
|
||||
vector_query = self._query_to_vector(table, vector_query, vector_column)
|
||||
self._vector_query = LanceVectorQueryBuilder(table, vector_query, vector_column)
|
||||
self._query = query
|
||||
self._vector_column = vector_column
|
||||
self._fts_columns = fts_columns
|
||||
self._norm = "score"
|
||||
self._reranker = LinearCombinationReranker(weight=0.7, fill=1.0)
|
||||
self._reranker = RRFReranker()
|
||||
self._nprobes = None
|
||||
self._refine_factor = None
|
||||
self._phrase_query = False
|
||||
|
||||
def _validate_query(self, query):
|
||||
# Temp hack to support vectorized queries for hybrid search
|
||||
if isinstance(query, str):
|
||||
return query, query
|
||||
elif isinstance(query, tuple):
|
||||
if len(query) != 2:
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
"The query must be a tuple of (vector_query, fts_query)."
|
||||
)
|
||||
if not isinstance(query[0], (list, np.ndarray, pa.Array, pa.ChunkedArray)):
|
||||
raise ValueError(f"The vector query must be one of {VEC}.")
|
||||
if not isinstance(query[1], str):
|
||||
raise ValueError("The fts query must be a string.")
|
||||
return query[0], query[1]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
def _validate_query(self, query, vector=None, text=None):
|
||||
if query is not None and (vector is not None or text is not None):
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
"The query must be either a string or a tuple of (vector, string)."
|
||||
"You can either provide a string query in search() method"
|
||||
"or set `vector()` and `text()` explicitly for hybrid search."
|
||||
"But not both."
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
vector_query = vector if vector is not None else query
|
||||
if not isinstance(vector_query, (str, list, np.ndarray)):
|
||||
raise ValueError("Vector query must be either a string or a vector")
|
||||
|
||||
text_query = text or query
|
||||
if text_query is None:
|
||||
raise ValueError("Text query must be provided for hybrid search.")
|
||||
if not isinstance(text_query, str):
|
||||
raise ValueError("Text query must be a string")
|
||||
|
||||
return vector_query, text_query
|
||||
|
||||
def phrase_query(self, phrase_query: bool = True) -> LanceHybridQueryBuilder:
|
||||
"""Set whether to use phrase query.
|
||||
|
||||
Parameters
|
||||
----------
|
||||
phrase_query: bool, default True
|
||||
If True, then the query will be wrapped in quotes and
|
||||
double quotes replaced by single quotes.
|
||||
|
||||
Returns
|
||||
-------
|
||||
LanceHybridQueryBuilder
|
||||
The LanceHybridQueryBuilder object.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self._phrase_query = phrase_query
|
||||
return self
|
||||
|
||||
def to_arrow(self) -> pa.Table:
|
||||
vector_query, fts_query = self._validate_query(
|
||||
self._query, self._vector, self._text
|
||||
)
|
||||
self._fts_query = LanceFtsQueryBuilder(
|
||||
self._table, fts_query, fts_columns=self._fts_columns
|
||||
)
|
||||
vector_query = self._query_to_vector(
|
||||
self._table, vector_query, self._vector_column
|
||||
)
|
||||
self._vector_query = LanceVectorQueryBuilder(
|
||||
self._table, vector_query, self._vector_column
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if self._limit:
|
||||
self._vector_query.limit(self._limit)
|
||||
self._fts_query.limit(self._limit)
|
||||
if self._columns:
|
||||
self._vector_query.select(self._columns)
|
||||
self._fts_query.select(self._columns)
|
||||
if self._where:
|
||||
self._vector_query.where(self._where, self._prefilter)
|
||||
self._fts_query.where(self._where, self._prefilter)
|
||||
if self._with_row_id:
|
||||
self._vector_query.with_row_id(True)
|
||||
self._fts_query.with_row_id(True)
|
||||
if self._phrase_query:
|
||||
self._fts_query.phrase_query(True)
|
||||
if self._nprobes:
|
||||
self._vector_query.nprobes(self._nprobes)
|
||||
if self._refine_factor:
|
||||
self._vector_query.refine_factor(self._refine_factor)
|
||||
|
||||
with ThreadPoolExecutor() as executor:
|
||||
fts_future = executor.submit(self._fts_query.with_row_id(True).to_arrow)
|
||||
vector_future = executor.submit(
|
||||
@@ -989,7 +1113,7 @@ class LanceHybridQueryBuilder(LanceQueryBuilder):
|
||||
def rerank(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
normalize="score",
|
||||
reranker: Reranker = LinearCombinationReranker(weight=0.7, fill=1.0),
|
||||
reranker: Reranker = RRFReranker(),
|
||||
) -> LanceHybridQueryBuilder:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Rerank the hybrid search results using the specified reranker. The reranker
|
||||
@@ -1001,7 +1125,7 @@ class LanceHybridQueryBuilder(LanceQueryBuilder):
|
||||
The method to normalize the scores. Can be "rank" or "score". If "rank",
|
||||
the scores are converted to ranks and then normalized. If "score", the
|
||||
scores are normalized directly.
|
||||
reranker: Reranker, default LinearCombinationReranker(weight=0.7, fill=1.0)
|
||||
reranker: Reranker, default RRFReranker()
|
||||
The reranker to use. Must be an instance of Reranker class.
|
||||
Returns
|
||||
-------
|
||||
@@ -1018,87 +1142,6 @@ class LanceHybridQueryBuilder(LanceQueryBuilder):
|
||||
|
||||
return self
|
||||
|
||||
def limit(self, limit: int) -> LanceHybridQueryBuilder:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Set the maximum number of results to return for both vector and fts search
|
||||
components.
|
||||
|
||||
Parameters
|
||||
----------
|
||||
limit: int
|
||||
The maximum number of results to return.
|
||||
|
||||
Returns
|
||||
-------
|
||||
LanceHybridQueryBuilder
|
||||
The LanceHybridQueryBuilder object.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self._vector_query.limit(limit)
|
||||
self._fts_query.limit(limit)
|
||||
self._limit = limit
|
||||
|
||||
return self
|
||||
|
||||
def select(self, columns: list) -> LanceHybridQueryBuilder:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Set the columns to return for both vector and fts search.
|
||||
|
||||
Parameters
|
||||
----------
|
||||
columns: list
|
||||
The columns to return.
|
||||
|
||||
Returns
|
||||
-------
|
||||
LanceHybridQueryBuilder
|
||||
The LanceHybridQueryBuilder object.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self._vector_query.select(columns)
|
||||
self._fts_query.select(columns)
|
||||
return self
|
||||
|
||||
def where(self, where: str, prefilter: bool = False) -> LanceHybridQueryBuilder:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Set the where clause for both vector and fts search.
|
||||
|
||||
Parameters
|
||||
----------
|
||||
where: str
|
||||
The where clause which is a valid SQL where clause. See
|
||||
`Lance filter pushdown <https://lancedb.github.io/lance/read_and_write.html#filter-push-down>`_
|
||||
for valid SQL expressions.
|
||||
|
||||
prefilter: bool, default False
|
||||
If True, apply the filter before vector search, otherwise the
|
||||
filter is applied on the result of vector search.
|
||||
|
||||
Returns
|
||||
-------
|
||||
LanceHybridQueryBuilder
|
||||
The LanceHybridQueryBuilder object.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
self._vector_query.where(where, prefilter=prefilter)
|
||||
self._fts_query.where(where)
|
||||
return self
|
||||
|
||||
def metric(self, metric: Literal["L2", "cosine"]) -> LanceHybridQueryBuilder:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Set the distance metric to use for vector search.
|
||||
|
||||
Parameters
|
||||
----------
|
||||
metric: "L2" or "cosine"
|
||||
The distance metric to use. By default "L2" is used.
|
||||
|
||||
Returns
|
||||
-------
|
||||
LanceHybridQueryBuilder
|
||||
The LanceHybridQueryBuilder object.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self._vector_query.metric(metric)
|
||||
return self
|
||||
|
||||
def nprobes(self, nprobes: int) -> LanceHybridQueryBuilder:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Set the number of probes to use for vector search.
|
||||
@@ -1116,7 +1159,7 @@ class LanceHybridQueryBuilder(LanceQueryBuilder):
|
||||
LanceHybridQueryBuilder
|
||||
The LanceHybridQueryBuilder object.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self._vector_query.nprobes(nprobes)
|
||||
self._nprobes = nprobes
|
||||
return self
|
||||
|
||||
def refine_factor(self, refine_factor: int) -> LanceHybridQueryBuilder:
|
||||
@@ -1134,7 +1177,15 @@ class LanceHybridQueryBuilder(LanceQueryBuilder):
|
||||
LanceHybridQueryBuilder
|
||||
The LanceHybridQueryBuilder object.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self._vector_query.refine_factor(refine_factor)
|
||||
self._refine_factor = refine_factor
|
||||
return self
|
||||
|
||||
def vector(self, vector: Union[np.ndarray, list]) -> LanceHybridQueryBuilder:
|
||||
self._vector = vector
|
||||
return self
|
||||
|
||||
def text(self, text: str) -> LanceHybridQueryBuilder:
|
||||
self._text = text
|
||||
return self
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1215,6 +1266,18 @@ class AsyncQueryBase(object):
|
||||
self._inner.limit(limit)
|
||||
return self
|
||||
|
||||
def offset(self, offset: int) -> AsyncQuery:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Set the offset for the results.
|
||||
|
||||
Parameters
|
||||
----------
|
||||
offset: int
|
||||
The offset to start fetching results from.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self._inner.offset(offset)
|
||||
return self
|
||||
|
||||
async def to_batches(
|
||||
self, *, max_batch_length: Optional[int] = None
|
||||
) -> AsyncRecordBatchReader:
|
||||
@@ -1383,7 +1446,7 @@ class AsyncQuery(AsyncQueryBase):
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def nearest_to_text(
|
||||
self, query: str, columns: Union[str, List[str]] = None
|
||||
self, query: str, columns: Union[str, List[str]] = []
|
||||
) -> AsyncQuery:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Find the documents that are most relevant to the given text query.
|
||||
@@ -1407,9 +1470,8 @@ class AsyncQuery(AsyncQueryBase):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if isinstance(columns, str):
|
||||
columns = [columns]
|
||||
return AsyncQuery(
|
||||
self._inner.nearest_to_text({"query": query, "columns": columns})
|
||||
)
|
||||
self._inner.nearest_to_text({"query": query, "columns": columns})
|
||||
return self
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class AsyncVectorQuery(AsyncQueryBase):
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -11,12 +11,15 @@
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
from typing import Iterable, Union
|
||||
import pyarrow as pa
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def to_ipc_binary(table: pa.Table) -> bytes:
|
||||
def to_ipc_binary(table: Union[pa.Table, Iterable[pa.RecordBatch]]) -> bytes:
|
||||
"""Serialize a PyArrow Table to IPC binary."""
|
||||
sink = pa.BufferOutputStream()
|
||||
if isinstance(table, Iterable):
|
||||
table = pa.Table.from_batches(table)
|
||||
with pa.ipc.new_stream(sink, table.schema) as writer:
|
||||
writer.write_table(table)
|
||||
return sink.getvalue().to_pybytes()
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -79,6 +79,13 @@ class RestfulLanceDBClient:
|
||||
or f"https://{self.db_name}.{self.region}.api.lancedb.com"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def __enter__(self):
|
||||
return self
|
||||
|
||||
def __exit__(self, exc_type, exc_value, traceback):
|
||||
self.close()
|
||||
return False # Do not suppress exceptions
|
||||
|
||||
def close(self):
|
||||
self.session.close()
|
||||
self.closed = True
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -11,7 +11,6 @@
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
import inspect
|
||||
import logging
|
||||
import uuid
|
||||
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor
|
||||
@@ -26,7 +25,7 @@ from ..common import DATA
|
||||
from ..db import DBConnection
|
||||
from ..embeddings import EmbeddingFunctionConfig
|
||||
from ..pydantic import LanceModel
|
||||
from ..table import Table, _sanitize_data
|
||||
from ..table import Table, sanitize_create_table
|
||||
from ..util import validate_table_name
|
||||
from .arrow import to_ipc_binary
|
||||
from .client import ARROW_STREAM_CONTENT_TYPE, RestfulLanceDBClient
|
||||
@@ -228,8 +227,6 @@ class RemoteDBConnection(DBConnection):
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
validate_table_name(name)
|
||||
if data is None and schema is None:
|
||||
raise ValueError("Either data or schema must be provided.")
|
||||
if embedding_functions is not None:
|
||||
logging.warning(
|
||||
"embedding_functions is not yet supported on LanceDB Cloud."
|
||||
@@ -239,24 +236,9 @@ class RemoteDBConnection(DBConnection):
|
||||
if mode is not None:
|
||||
logging.warning("mode is not yet supported on LanceDB Cloud.")
|
||||
|
||||
if inspect.isclass(schema) and issubclass(schema, LanceModel):
|
||||
# convert LanceModel to pyarrow schema
|
||||
# note that it's possible this contains
|
||||
# embedding function metadata already
|
||||
schema = schema.to_arrow_schema()
|
||||
|
||||
if data is not None:
|
||||
data, schema = _sanitize_data(
|
||||
data,
|
||||
schema,
|
||||
metadata=None,
|
||||
on_bad_vectors=on_bad_vectors,
|
||||
fill_value=fill_value,
|
||||
)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
if schema is None:
|
||||
raise ValueError("Either data or schema must be provided")
|
||||
data = pa.Table.from_pylist([], schema=schema)
|
||||
data, schema = sanitize_create_table(
|
||||
data, schema, on_bad_vectors=on_bad_vectors, fill_value=fill_value
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
from .table import RemoteTable
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -15,7 +15,7 @@ import logging
|
||||
import uuid
|
||||
from concurrent.futures import Future
|
||||
from functools import cached_property
|
||||
from typing import Dict, Iterable, Optional, Union, Literal
|
||||
from typing import Dict, Iterable, List, Optional, Union, Literal
|
||||
|
||||
import pyarrow as pa
|
||||
from lance import json_to_schema
|
||||
@@ -126,6 +126,7 @@ class RemoteTable(Table):
|
||||
column: str,
|
||||
*,
|
||||
replace: bool = False,
|
||||
with_position: bool = True,
|
||||
):
|
||||
data = {
|
||||
"column": column,
|
||||
@@ -268,6 +269,7 @@ class RemoteTable(Table):
|
||||
query: Union[VEC, str],
|
||||
vector_column_name: Optional[str] = None,
|
||||
query_type="auto",
|
||||
fts_columns: Optional[Union[str, List[str]]] = None,
|
||||
) -> LanceVectorQueryBuilder:
|
||||
"""Create a search query to find the nearest neighbors
|
||||
of the given query vector. We currently support [vector search][search]
|
||||
@@ -338,6 +340,7 @@ class RemoteTable(Table):
|
||||
query,
|
||||
query_type,
|
||||
vector_column_name=vector_column_name,
|
||||
fts_columns=fts_columns,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def _execute_query(
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -6,6 +6,7 @@ from .linear_combination import LinearCombinationReranker
|
||||
from .openai import OpenaiReranker
|
||||
from .jinaai import JinaReranker
|
||||
from .rrf import RRFReranker
|
||||
from .answerdotai import AnswerdotaiRerankers
|
||||
|
||||
__all__ = [
|
||||
"Reranker",
|
||||
@@ -16,4 +17,5 @@ __all__ = [
|
||||
"ColbertReranker",
|
||||
"JinaReranker",
|
||||
"RRFReranker",
|
||||
"AnswerdotaiRerankers",
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
103
python/python/lancedb/rerankers/answerdotai.py
Normal file
103
python/python/lancedb/rerankers/answerdotai.py
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,103 @@
|
||||
# Copyright (c) 2023. LanceDB Developers
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
import pyarrow as pa
|
||||
from .base import Reranker
|
||||
from ..util import attempt_import_or_raise
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class AnswerdotaiRerankers(Reranker):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Reranks the results using the Answerdotai Rerank API.
|
||||
All supported reranker model types can be found here:
|
||||
- https://github.com/AnswerDotAI/rerankers
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Parameters
|
||||
----------
|
||||
model_type : str, default "colbert"
|
||||
The type of the model to use.
|
||||
model_name : str, default "rerank-english-v2.0"
|
||||
The name of the model to use from the given model type.
|
||||
column : str, default "text"
|
||||
The name of the column to use as input to the cross encoder model.
|
||||
return_score : str, default "relevance"
|
||||
options are "relevance" or "all". Only "relevance" is supported for now.
|
||||
**kwargs
|
||||
Additional keyword arguments to pass to the model. For example, 'device'.
|
||||
See AnswerDotAI/rerankers for more information.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
model_type="colbert",
|
||||
model_name: str = "answerdotai/answerai-colbert-small-v1",
|
||||
column: str = "text",
|
||||
return_score="relevance",
|
||||
**kwargs,
|
||||
):
|
||||
super().__init__(return_score)
|
||||
self.column = column
|
||||
rerankers = attempt_import_or_raise(
|
||||
"rerankers"
|
||||
) # import here for faster ops later
|
||||
self.reranker = rerankers.Reranker(model_name, model_type, **kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
def _rerank(self, result_set: pa.Table, query: str):
|
||||
docs = result_set[self.column].to_pylist()
|
||||
doc_ids = list(range(len(docs)))
|
||||
result = self.reranker.rank(query, docs, doc_ids=doc_ids)
|
||||
|
||||
# get the scores of each document in the same order as the input
|
||||
scores = [result.get_result_by_docid(i).score for i in doc_ids]
|
||||
|
||||
# add the scores
|
||||
result_set = result_set.append_column(
|
||||
"_relevance_score", pa.array(scores, type=pa.float32())
|
||||
)
|
||||
return result_set
|
||||
|
||||
def rerank_hybrid(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
query: str,
|
||||
vector_results: pa.Table,
|
||||
fts_results: pa.Table,
|
||||
):
|
||||
combined_results = self.merge_results(vector_results, fts_results)
|
||||
combined_results = self._rerank(combined_results, query)
|
||||
if self.score == "relevance":
|
||||
combined_results = self._keep_relevance_score(combined_results)
|
||||
elif self.score == "all":
|
||||
raise NotImplementedError(
|
||||
"Answerdotai Reranker does not support score='all' yet"
|
||||
)
|
||||
combined_results = combined_results.sort_by(
|
||||
[("_relevance_score", "descending")]
|
||||
)
|
||||
return combined_results
|
||||
|
||||
def rerank_vector(self, query: str, vector_results: pa.Table):
|
||||
vector_results = self._rerank(vector_results, query)
|
||||
if self.score == "relevance":
|
||||
vector_results = vector_results.drop_columns(["_distance"])
|
||||
|
||||
vector_results = vector_results.sort_by([("_relevance_score", "descending")])
|
||||
return vector_results
|
||||
|
||||
def rerank_fts(self, query: str, fts_results: pa.Table):
|
||||
fts_results = self._rerank(fts_results, query)
|
||||
if self.score == "relevance":
|
||||
fts_results = fts_results.drop_columns(["_score"])
|
||||
|
||||
fts_results = fts_results.sort_by([("_relevance_score", "descending")])
|
||||
|
||||
return fts_results
|
||||
@@ -1,3 +1,16 @@
|
||||
# Copyright (c) 2023. LanceDB Developers
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
from abc import ABC, abstractmethod
|
||||
from packaging.version import Version
|
||||
from typing import Union, List, TYPE_CHECKING
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,3 +1,16 @@
|
||||
# Copyright (c) 2023. LanceDB Developers
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
import os
|
||||
from packaging.version import Version
|
||||
from functools import cached_property
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,10 +1,20 @@
|
||||
import pyarrow as pa
|
||||
# Copyright (c) 2023. LanceDB Developers
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
from ..util import attempt_import_or_raise
|
||||
from .base import Reranker
|
||||
from .answerdotai import AnswerdotaiRerankers
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class ColbertReranker(Reranker):
|
||||
class ColbertReranker(AnswerdotaiRerankers):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Reranks the results using the ColBERT model.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -16,80 +26,22 @@ class ColbertReranker(Reranker):
|
||||
The name of the column to use as input to the cross encoder model.
|
||||
return_score : str, default "relevance"
|
||||
options are "relevance" or "all". Only "relevance" is supported for now.
|
||||
**kwargs
|
||||
Additional keyword arguments to pass to the model, for example, 'device'.
|
||||
See AnswerDotAI/rerankers for more information.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
model_name: str = "colbert",
|
||||
model_name: str = "colbert-ir/colbertv2.0",
|
||||
column: str = "text",
|
||||
return_score="relevance",
|
||||
**kwargs,
|
||||
):
|
||||
super().__init__(return_score)
|
||||
self.model_name = model_name
|
||||
self.column = column
|
||||
rerankers = attempt_import_or_raise(
|
||||
"rerankers"
|
||||
) # import here for faster ops later
|
||||
self.colbert = rerankers.Reranker(self.model_name, model_type="colbert")
|
||||
|
||||
def _rerank(self, result_set: pa.Table, query: str):
|
||||
docs = result_set[self.column].to_pylist()
|
||||
doc_ids = list(range(len(docs)))
|
||||
result = self.colbert.rank(query, docs, doc_ids=doc_ids)
|
||||
|
||||
# get the scores of each document in the same order as the input
|
||||
scores = [result.get_result_by_docid(i).score for i in doc_ids]
|
||||
|
||||
# add the scores
|
||||
result_set = result_set.append_column(
|
||||
"_relevance_score", pa.array(scores, type=pa.float32())
|
||||
super().__init__(
|
||||
model_type="colbert",
|
||||
model_name=model_name,
|
||||
column=column,
|
||||
return_score=return_score,
|
||||
**kwargs,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
return result_set
|
||||
|
||||
def rerank_hybrid(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
query: str,
|
||||
vector_results: pa.Table,
|
||||
fts_results: pa.Table,
|
||||
):
|
||||
combined_results = self.merge_results(vector_results, fts_results)
|
||||
combined_results = self._rerank(combined_results, query)
|
||||
if self.score == "relevance":
|
||||
combined_results = self._keep_relevance_score(combined_results)
|
||||
elif self.score == "all":
|
||||
raise NotImplementedError(
|
||||
"OpenAI Reranker does not support score='all' yet"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
combined_results = combined_results.sort_by(
|
||||
[("_relevance_score", "descending")]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
return combined_results
|
||||
|
||||
def rerank_vector(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
query: str,
|
||||
vector_results: pa.Table,
|
||||
):
|
||||
result_set = self._rerank(vector_results, query)
|
||||
if self.score == "relevance":
|
||||
result_set = result_set.drop_columns(["_distance"])
|
||||
|
||||
result_set = result_set.sort_by([("_relevance_score", "descending")])
|
||||
|
||||
return result_set
|
||||
|
||||
def rerank_fts(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
query: str,
|
||||
fts_results: pa.Table,
|
||||
):
|
||||
result_set = self._rerank(fts_results, query)
|
||||
if self.score == "relevance":
|
||||
result_set = result_set.drop_columns(["_score"])
|
||||
|
||||
result_set = result_set.sort_by([("_relevance_score", "descending")])
|
||||
|
||||
return result_set
|
||||
|
||||
Some files were not shown because too many files have changed in this diff Show More
Reference in New Issue
Block a user